Getting Started With ReGraph — The Graph Visualization Toolkit for React
This step-by-step tutorial covers everything you need to know about getting started with ReGraph.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeAt Cambridge Intelligence, we recently launched an Early Access Program (EAP) for ReGraph, our brand new graph data visualization toolkit for React developers. The response from evaluators has been fantastic, and now we’re inviting more organizations to join the ReGraph EAP.
To help you get started with ReGraph, this step-by-step tutorial covers everything you need to know. Once we’ve created our visualization in a React app, we’ll load an example network of suspected terrorists and show how easy it is to apply the key analysis techniques your users need to uncover threats.
Before the tutorial, let’s learn a little more about ReGraph.
ReGraph: How it works
ReGraph contains two React components, a chart and a time bar. Both components are designed from the ground-up to fit into modern React environments. The fully data-driven approach allows for modern, responsive, and declarative visualization of your data.
Powered by WebGL, ReGraph offers fast, reliable performance even when visualizing large, complex networks. And like React, it works with all major browsers and devices.
ReGraph comes loaded with high-performance graph analysis functions and other features to help analysts discover critical insights more quickly. They can take advantage of social network analysis measures, advanced map-based analysis, automatic layouts, grouping and combining, and much more.
We’ll look at a couple of these in more detail — but first, let’s get ReGraph working in an app.
Step 1: Add ReGraph to your React project
If you don’t have a React project set up, you can bootstrap one in seconds with create-react-app:
npx create-react-app my-regraph-appNext, download ReGraph. If you haven’t already, join the EAP. You’ll get full access to the ReGraph SDK site containing the latest ReGraph package, detailed developer tutorials, interactive demos, and a fully-documented API.
Add ReGraph to your project by installing it with a package manager. We’ll use npm:
npm install ../path/to/regraph-0.5.0.tgzStep 2: Import ReGraph and create a chart
To access ReGraph from your app, simply import it alongside React:
import React from ‘react’;
import { Chart } from ‘regraph’;You can then render the Chart in JSX. To create a chart and load a dummy item, use:
<Chart items={{
node1: {
color: ‘#bbdefb’,
label: { text: 'Welcome to ReGraph!' }
}
}}/>And that’s it: ReGraph is running in your application!
Step 3: Load data
ReGraph works with any data repository — databases, web services, CSV files, etc. All you have to do is convert the data into the simple JavaScript format ReGraph expects. Here’s what our converted network of suspected terrorists looks like:
// A node with id N8
N8: {
color: '#ff867c',
label: {
text: 'Mohammed Ibrahim Makkawi',
},
data: {
country: 'Afghanistan',
}
},
// A link between N8 and N99
'N8/p/N99': {
id1: 'N8',
id2: 'N99',
width: 5,
color: '#f3e5f5'
}You’ll find descriptions of every supported prop, event, and style option on the ReGraph SDK site.
Next, we pass this object into the items prop of our chart and ReGraph automatically draws it for us. In a React app, we usually load our items from the app state or props. We’ll read from state in this example, which means we can re-render whenever the items change:
componentDidMount() {
const data = await loadData();
const items = convertData(data);
this.setState({ items });
}
render() {
const { items } = this.state;
<Chart items={items} />
}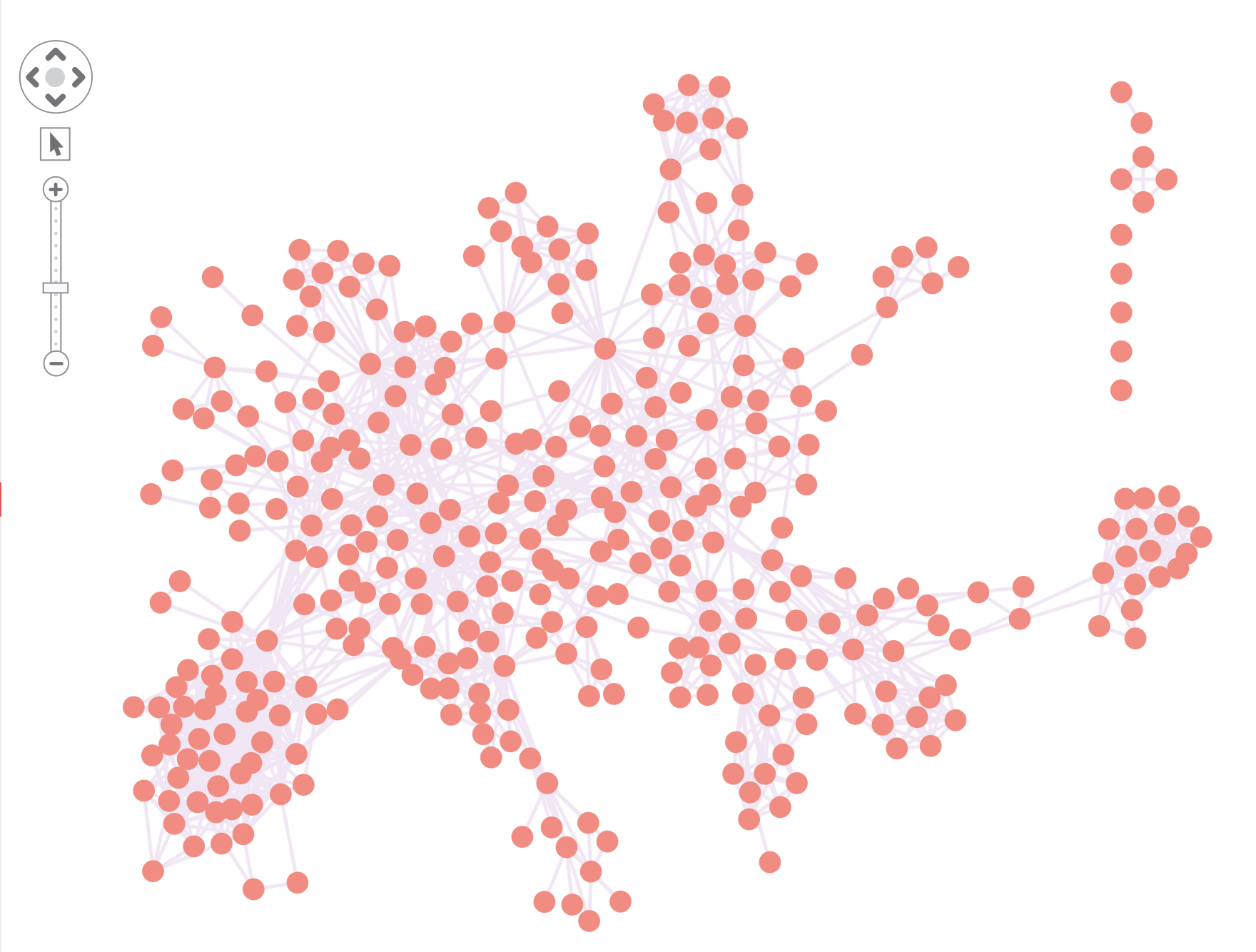
The items prop is fully reactive. When you pass a new object into it, ReGraph looks for changes since its last render and updates the chart if necessary. New items slide into view, removed items fade out, and color and position changes transition with smooth animation.
That’s it! We’ve got our chart working and our data loaded. Now let’s see how we can make sense of our chart.
Make sense of your graph visualizations
Right now, it’s hard to get useful insight from our complex network of connections, but ReGraph comes with a range of features to help you understand the data. Let’s focus on two of them: combos and SNA measures.
Reducing clutter with combos
In very busy charts with lots of nodes and links, it’s hard to differentiate between what’s important and what’s not.
The smart way to reduce the number of items is to group together nodes with similar properties. We call these combined nodes combos. For example, our dataset contains the country of origin for each terrorist suspect. Grouping suspects by country gives us a beautifully clean high-level view of the data:
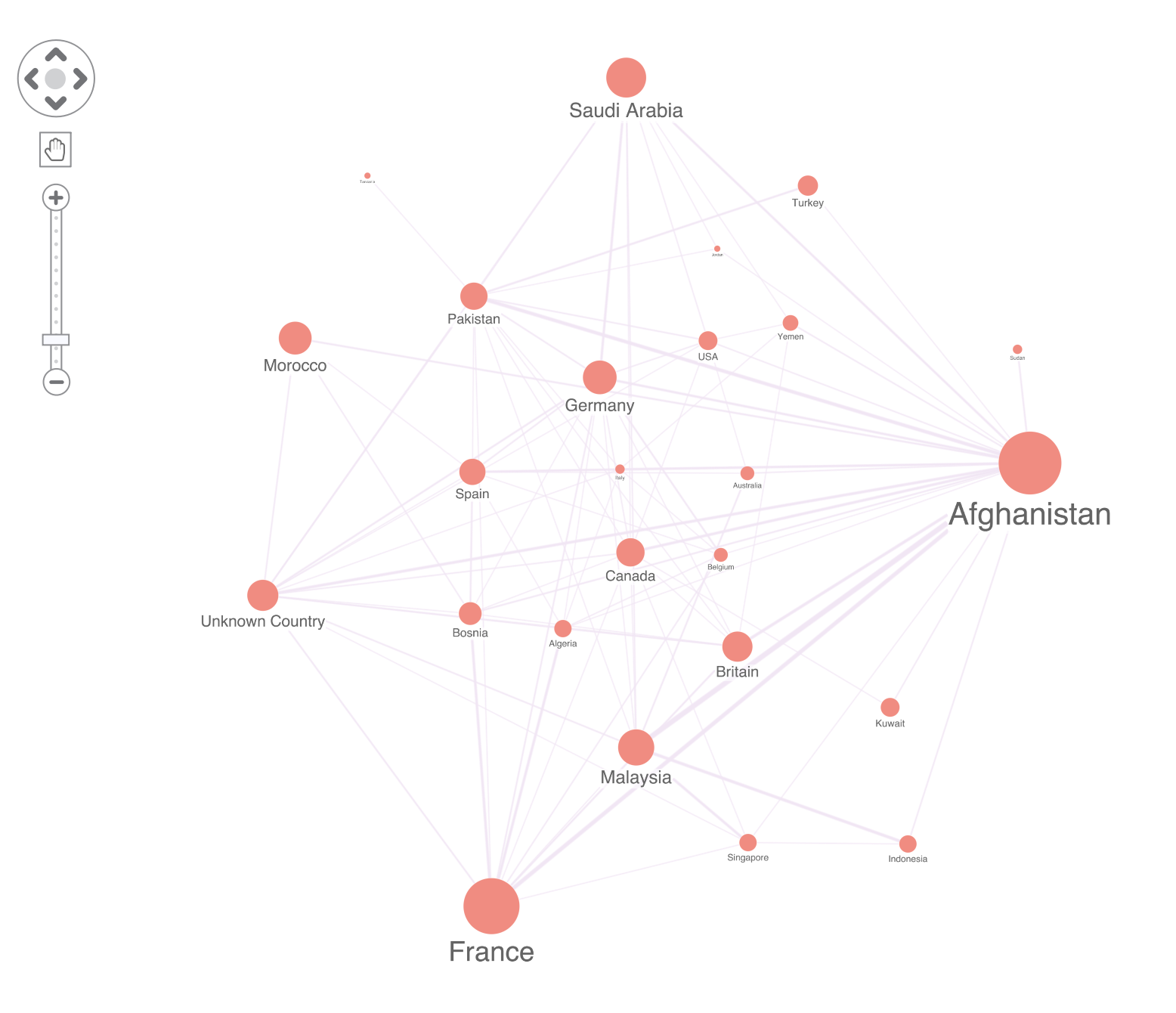
Notice how ReGraph automatically combines multiple links between nodes into a single link between combos.
Creating combos in ReGraph is really straightforward. You just set the combine prop to tell ReGraph which data properties to use for grouping. Setting the level property will enable or disable combos:
<Chart
items={items}
combine={{properties: [‘country’], level: 1}}
/>We can still drill down into the detail when we need it by “opening” each combo to show what’s inside. If there’s a specific node worth investigating further, we can easily highlight the nodes and combos it's connected to.
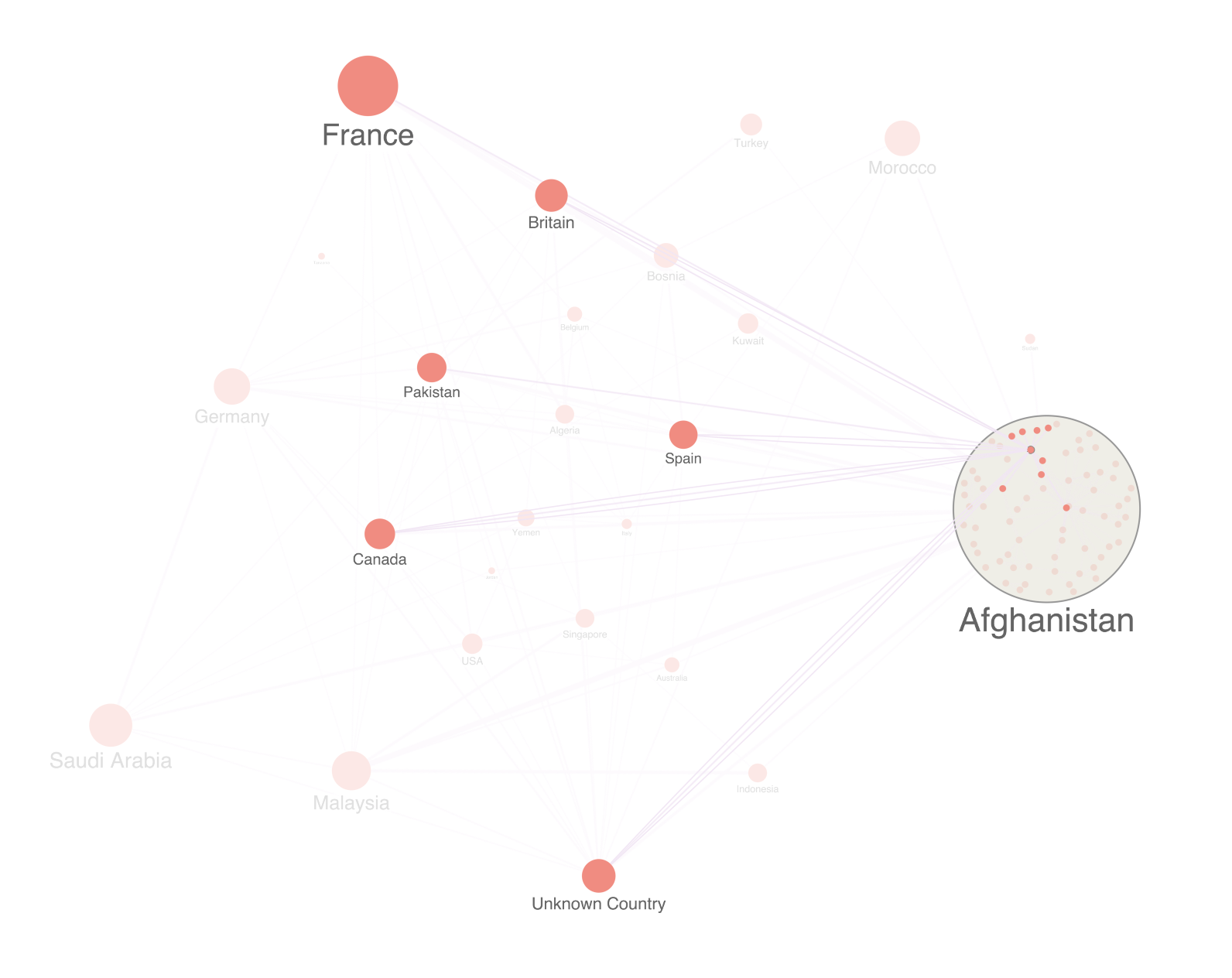
Sizing nodes by SNA centrality
Graph theory provides a number of ways to assess the importance of each node, which ReGraph exposes as a number of social network analysis (SNA) functions.
Analyzing social connections in any network can reveal important information about information flow, hidden subnetworks, dependencies, and influential nodes.
An effective way to make highly-connected nodes stand out is by making them larger. Here, we’ve counted how many connections each terrorist suspect has and sized them accordingly:
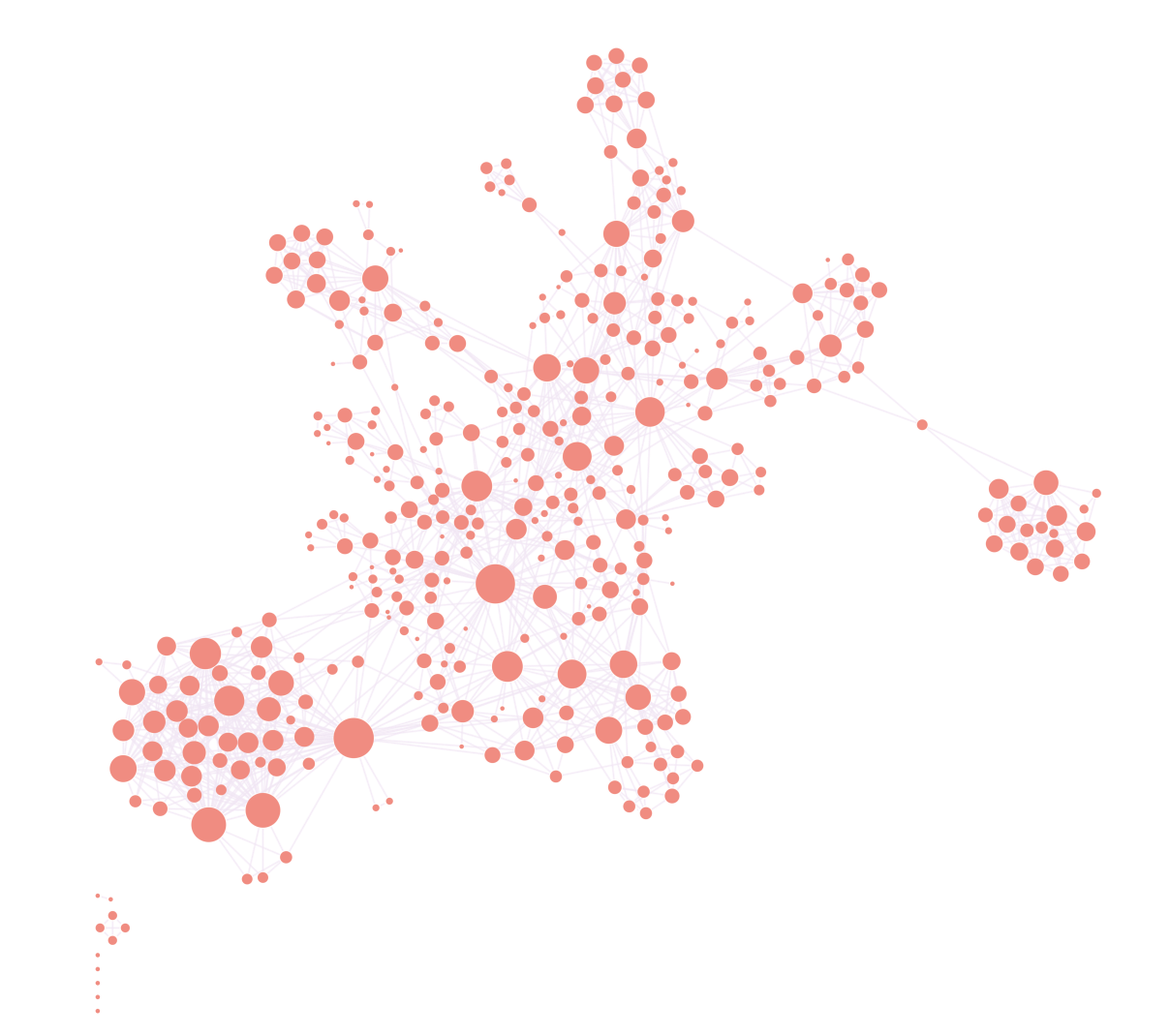

ReGraph supports other powerful SNA centrality measures too, including betweenness to find the ‘gatekeepers’ in a network, and closeness to identify how easily a node can reach the rest of the network.
All these measures are available through function calls with simple APIs — very similar to the example above — so experimenting with them is easy. The ReGraph SDK also features interactive examples of centrality measures to show how they reveal different insights from your data.
For more details on these and the other centrality measures ReGraph supports, see Social Network Analysis.
If you enjoyed this article and want to learn more about React, check out this collection of tutorials and articles on all things React.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments