Getting Started With MSK Serverless and AWS Lambda Using Go
In this post, you will learn how to deploy a Go Lambda function and trigger it in response to events sent to a topic in an MSK Serverless cluster.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn this post, you will learn how to deploy a Go Lambda function and trigger it in response to events sent to a topic in an MSK Serverless cluster.
The following topics have been covered:
- How to use the franz-go Go Kafka client to connect to MSK Serverless using IAM authentication
- Write a Go Lambda function to process data in MSK topic.
- Create the infrastructure: VPC, subnets, MSK cluster,
Cloud9etc. - Configure Lambda and
Cloud9to access MSK using IAM roles and fine-grained permissions.
MSK Serverless is a cluster type for Amazon MSK that makes it possible for you to run Apache Kafka without having to manage and scale cluster capacity. It automatically provisions and scales capacity while managing the partitions in your topic, so you can stream data without thinking about right-sizing or scaling clusters. Consider using a serverless cluster if your applications need on-demand streaming capacity that scales up and down automatically.
- MSK Serverless Developer Guide
Prerequisites
You will need an AWS account to install AWS CLI, as well as a recent version of Go (1.18 or above).
Clone this GitHub repository and change it to the right directory:
git clone https://github.com/abhirockzz/lambda-msk-serverless-trigger-golang
cd lambda-msk-serverless-trigger-golang
Infrastructure Setup
AWS CloudFormation is a service that helps you model and set up your AWS resources so that you can spend less time managing those resources and more time focusing on your applications that run in AWS. You create a template that describes all the AWS resources that you want (like Amazon EC2 instances or Amazon RDS DB instances), and CloudFormation takes care of provisioning and configuring those resources for you. You don't need to individually create and configure AWS resources and figure out what's dependent on what; CloudFormation handles that.
- AWS CloudFormation User Guide
Create VPC and Other Resources
Use a CloudFormation template for this.
aws cloudformation create-stack --stack-name msk-vpc-stack --template-body file://template.yaml
Wait for the stack creation to complete before proceeding to other steps.
Create MSK Serverless Cluster
Use AWS Console to create the cluster.
Configure the VPC and private subnets created in the previous step.
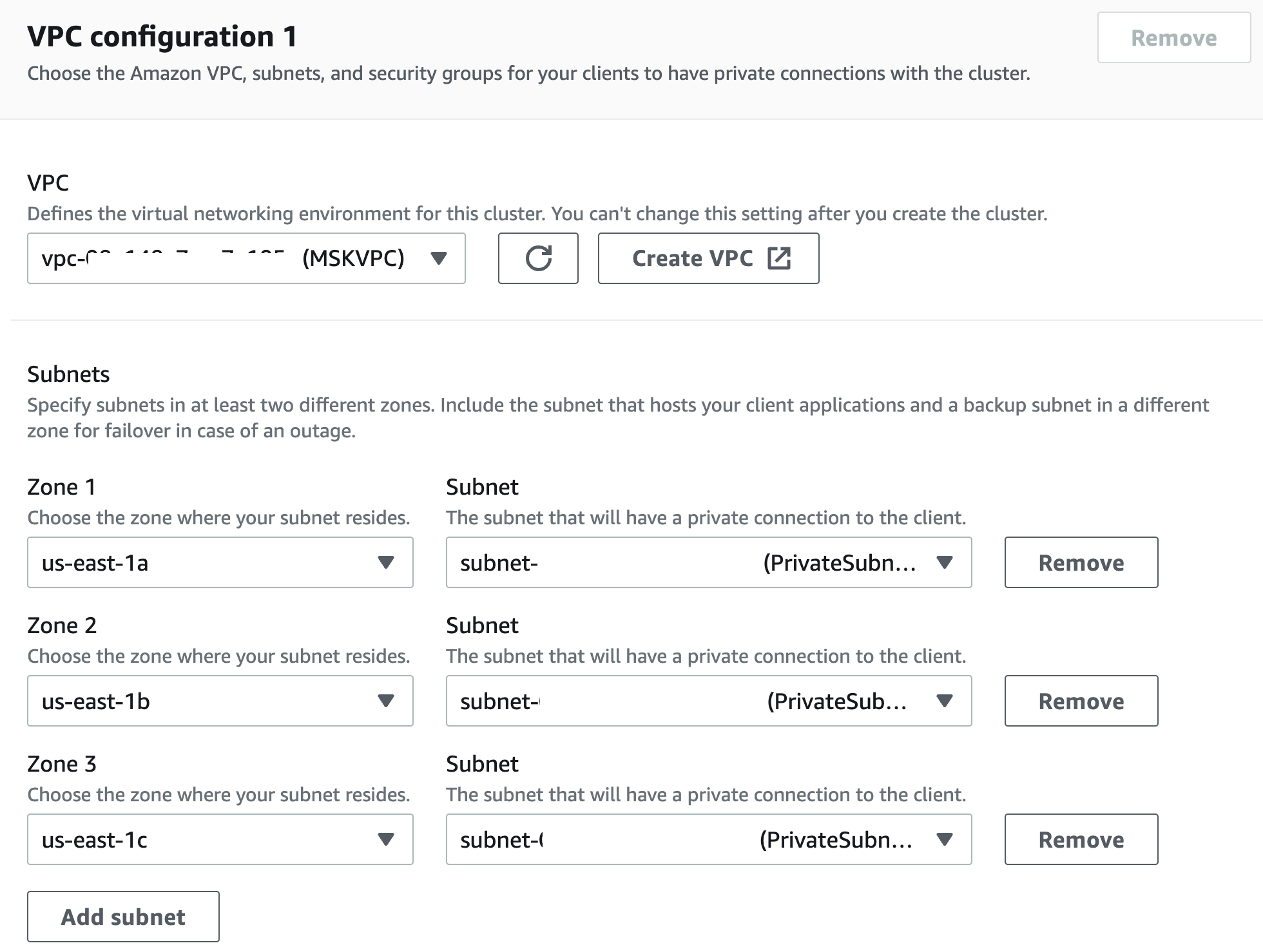
Create an AWS Cloud9 Instance
Make sure it is in the same VPC as the MSK Serverless cluster and choose the public subnet that you created earlier.
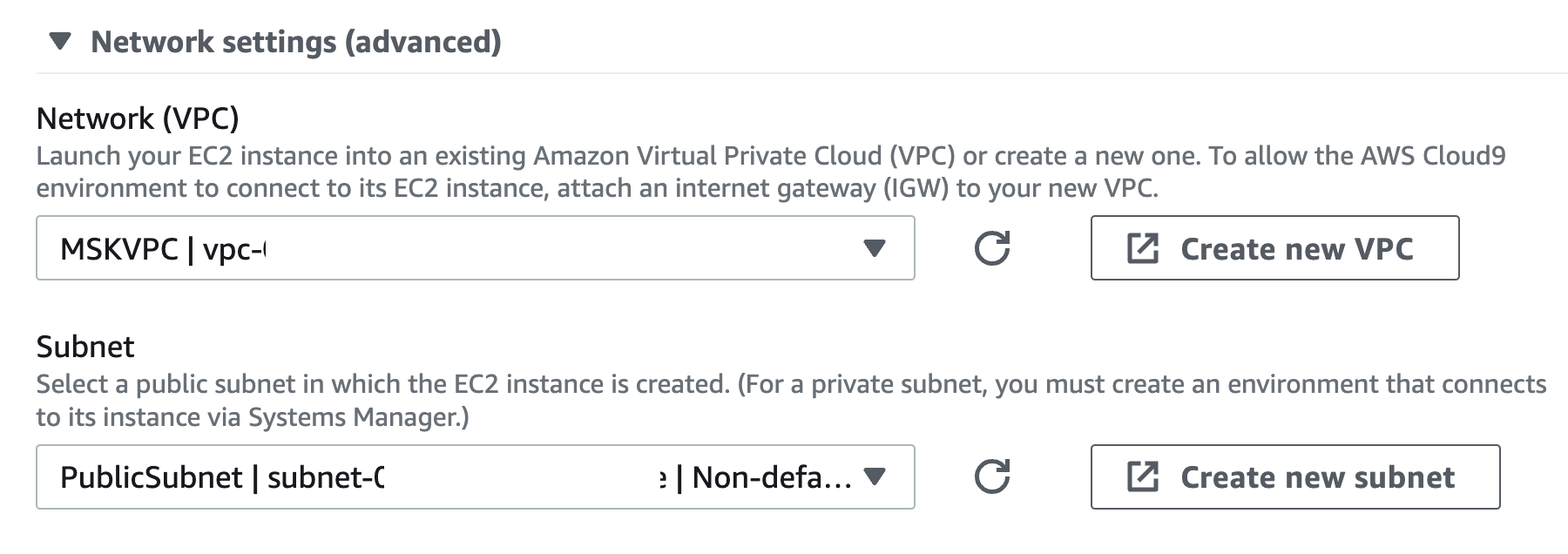
Configure MSK Cluster Security Group
After the Cloud9 instance is created, edit the MSK cluster security group to allow access from the Cloud9 instance.
Configure Cloud9 To Send Data to MSK Serverless Cluster
The code that we run from Cloud9 is going to produce data to the MSK Serverless cluster. So we need to ensure that it has the right privileges. For this, we need to create an IAM role and attach the required permissions policy.
aws iam create-role --role-name Cloud9MSKRole --assume-role-policy-document file://ec2-trust-policy.json
Before creating the policy, update the msk-producer-policy.json file to reflect the required details including MSK cluster ARN etc.
aws iam put-role-policy --role-name Cloud9MSKRole --policy-name MSKProducerPolicy --policy-document file://msk-producer-policy.json
Attach the IAM role to the Cloud9 EC2 instance:
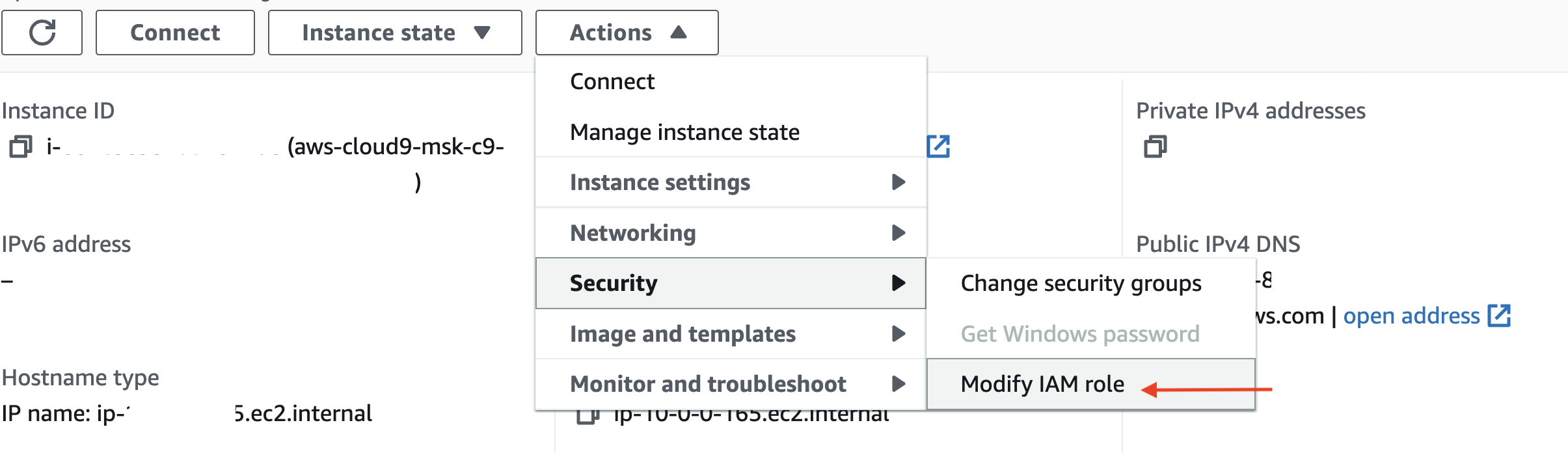
Send Data to MSK Serverless Using Producer Application
Log into the Cloud9 instance and run the producer application (it is a Docker image) from a terminal.
export MSK_BROKER=<enter the MSK Serverless endpoint>
export MSK_TOPIC=test-topic
docker run -p 8080:8080 -e MSK_BROKER=$MSK_BROKER -e MSK_TOPIC=$MSK_TOPIC public.ecr.aws/l0r2y6t0/msk-producer-app
The application exposes a REST API endpoint using which you can send data to MSK.
curl -i -X POST -d 'test event 1' http://localhost:8080
This will create the specified topic (since it was missing, to begin with) and also send the data to MSK.
Now that the cluster and producer applications are ready, we can move on to the consumer. Instead of creating a traditional consumer, we will deploy a Lambda function that will be automatically invoked in response to data being sent to the topic in MSK.
Configure and Deploy the Lambda Function
Create Lambda Execution IAM Role and Attach the Policy
A Lambda function's execution role is an AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) role that grants the function permission to access AWS services and resources. When you invoke your function, Lambda automatically provides your function with temporary credentials by assuming this role. You don't have to call sts:AssumeRole in your function code.
aws iam create-role --role-name LambdaMSKRole --assume-role-policy-document file://lambda-trust-policy.json
aws iam attach-role-policy --policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AWSLambdaMSKExecutionRole --role-name LambdaMSKRole
Before creating the policy, update the msk-consumer-policy.json file to reflect the required details including MSK cluster ARN etc.
aws iam put-role-policy --role-name LambdaMSKRole --policy-name MSKConsumerPolicy --policy-document file://msk-consumer-policy.json
Build and Deploy the Go Function and Create a Zip File
Build and zip the function code:
GOOS=linux go build -o app
zip func.zip app
Deploy to Lambda:
export LAMBDA_ROLE_ARN=<enter the ARN of the LambdaMSKRole created above e.g. arn:aws:iam::<your AWS account ID>:role/LambdaMSKRole>
aws lambda create-function \
--function-name msk-consumer-function \
--runtime go1.x \
--zip-file fileb://func.zip \
--handler app \
--role $LAMBDA_ROLE_ARN
Lambda VPC Configuration
Make sure you choose the same VPC and private subnets as the MSK cluster. Also, select the same security group ID as MSK (for convenience). If you select a different one, make sure to update the MSK security group to add an inbound rule (for port 9098), just like you did for the Cloud9 instance in an earlier step.
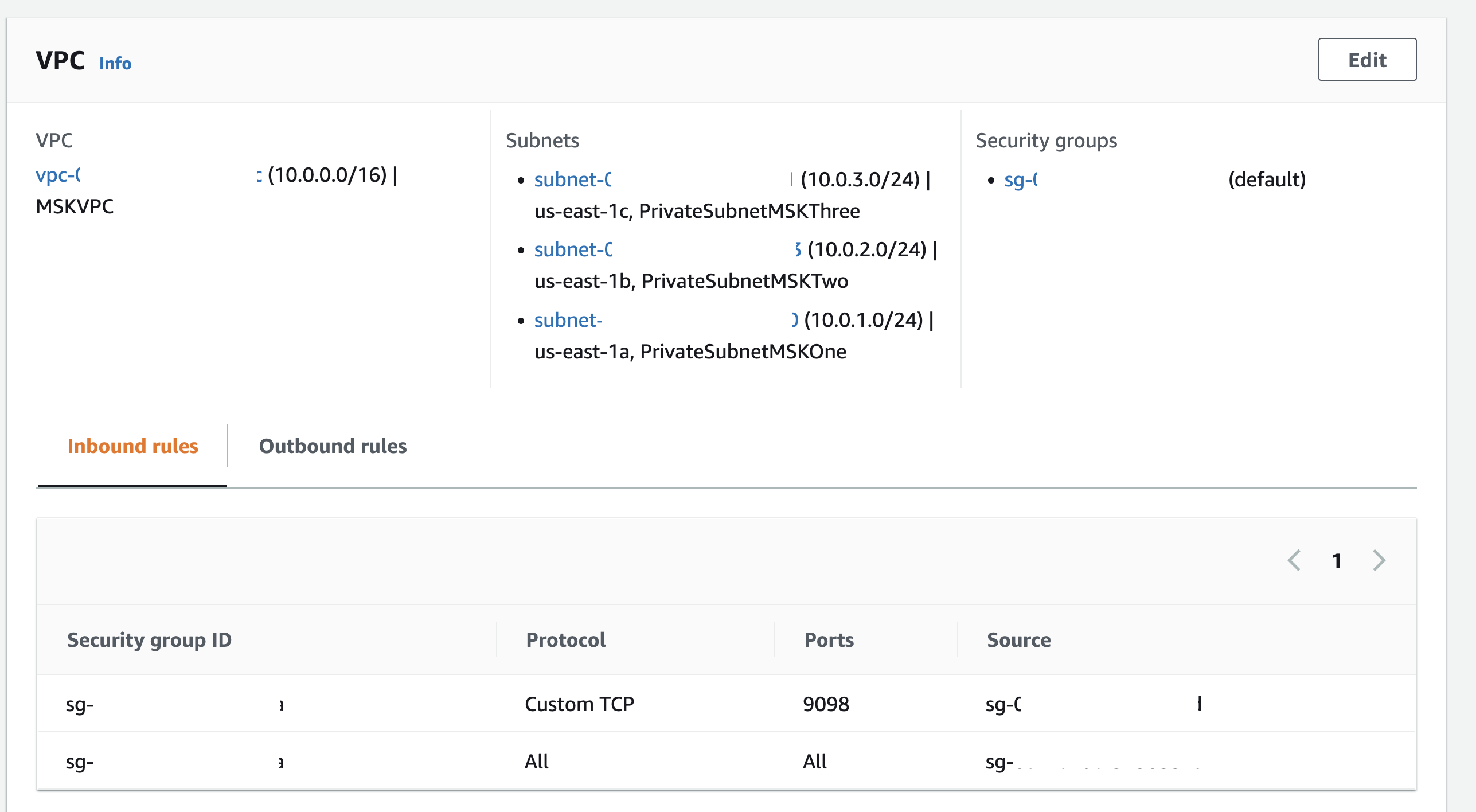
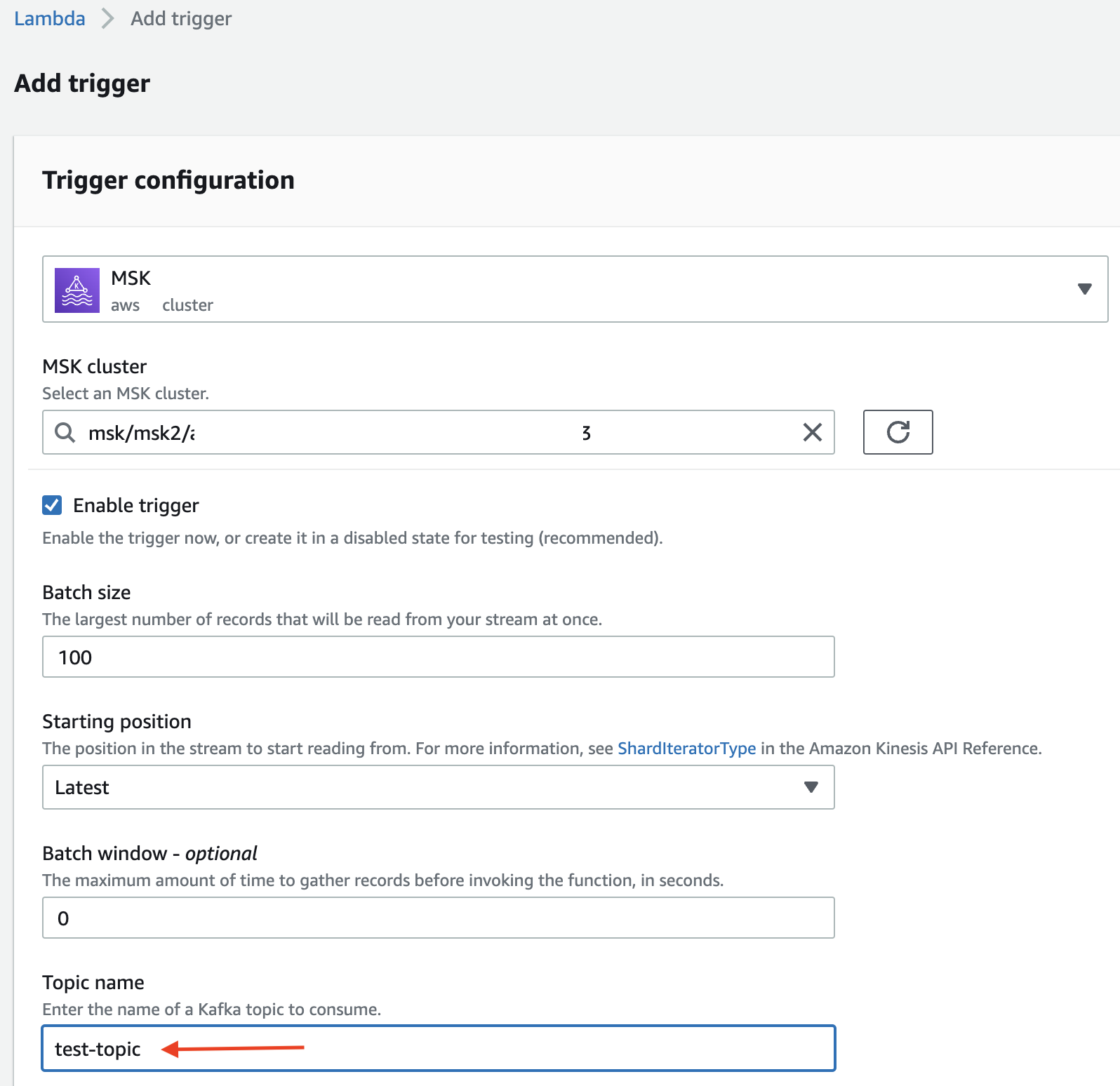
Configure the MSK Trigger for the Function
When Amazon MSK is used as an event source, Lambda internally polls for new messages from the event source and then synchronously invokes the target Lambda function. Lambda reads the messages in batches and provides these to your function as an event payload. The maximum batch size is configurable (the default is 100 messages).
Lambda reads the messages sequentially for each partition. After Lambda processes each batch, it commits the offsets of the messages in that batch. If your function returns an error for any of the messages in a batch, Lambda retries the whole batch of messages until processing succeeds or the messages expire.
Lambda sends the batch of messages in the event parameter when it invokes your function. The event payload contains an array of messages. Each array item contains details of the Amazon MSK topic and partition identifier, together with a timestamp and a base64-encoded message.
Make sure to choose the right MSK Serverless cluster and enter the correct topic name.
Verify the Integration
Go back to the Cloud9 terminal and send more data using the producer application. I used a handy JSON utility called jo (sudo yum install jo).
APP_URL=http://localhost:8080
for i in {1..5};
do jo email=user${i}@foo.com name=user${i} | curl -i -X POST -d @- $APP_URL;
done
In the Lambda function logs, you should see the messages that you sent.
Conclusion
You were able to set up, configure and deploy a Go Lambda function and trigger it in response to events sent to a topic in an MSK Serverless cluster!
Published at DZone with permission of Abhishek Gupta, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.


Comments