Framework to Load Data From Oracle To Azure
Step-by-step process to create a Python framework to extract and load data from Oracle and load into Azure blob storage and Azure Dedicated pool with a code snippet.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeOracle is a popular relational database management system (RDBMS) used by many organizations for storing and managing their data. However, with the advent of cloud computing, many organizations are moving towards cloud-based solutions for their data storage and processing needs. Azure Blob Storage and Synapse Dedicated SQL Pool are two popular cloud-based solutions offered by Microsoft for storing and processing data. In this article, we will explore how to create a framework to load data from Oracle to Azure Blob Storage as Parquet file and then load it to Synapse Dedicated SQL Pool.
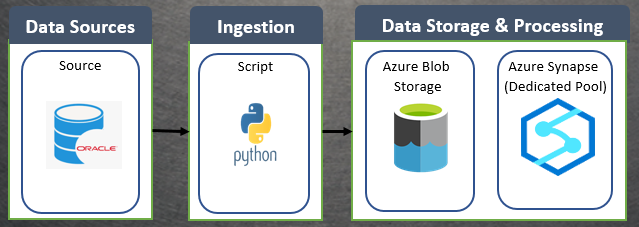
Step 1: Set Up Azure Blob Storage
The first step in this process is to set up Azure Blob Storage. You can do this by creating an Azure account and then creating a storage account. Once you have created a storage account, you can create a container in the storage account where you will store the Parquet file. Make sure to note down the connection string for the storage account and the name of the container, as you will need these later.
Step 2: Install Required Libraries
Next, you need to install the required libraries to interact with Oracle and Azure Blob Storage. You can use the following commands to install the libraries:
pip install cx_Oracle
pip install azure-storage-blobStep 3: Connect to Oracle
After installing the required libraries, you need to connect to Oracle. You can use the following code to create a connection:
import cx_Oracle
conn = cx_Oracle.connect('username/password@hostname:port/servicename')Replace the username, password, hostname, port, and service name with the appropriate values for your Oracle database.
Step 4: Query Data from Oracle
Once you have established a connection to Oracle, you can query the data that you want to transfer to Azure Blob Storage. You can use the following code to query the data:
import pandas as pd
query = 'SELECT * FROM my_table'
df = pd.read_sql(query, conn)
Replace my_table with the name of the table that you want to query.Step 5: Write Data to Parquet File
After querying the data, you need to write it to a Parquet file. You can use the following code to write the data to a Parquet file:
import pyarrow as pa
import pyarrow.parquet as pq
table = pa.Table.from_pandas(df)
pq.write_table(table, 'my_file.parquet')
Replace my_file.parquet with the name that you want to give to the Parquet file.Step 6: Upload Parquet File to Azure Blob Storage
Once you have created the Parquet file, you need to upload it to Azure Blob Storage. You can use the following code to upload the file:
from azure.storage.blob import BlobServiceClient
connection_string = 'DefaultEndpointsProtocol=https;AccountName=myaccount;AccountKey=mykey;EndpointSuffix=core.windows.net'
container_name = 'my_container'
blob_name = 'my_file.parquet'
blob_service_client = BlobServiceClient.from_connection_string(connection_string)
blob_client = blob_service_client.get_blob_client(container_name, blob_name)
with open('my_file.parquet', 'rb') as data:
blob_client.upload_blob(data)Replace myaccount, mykey, and my_container with the appropriate values for your storage account and container. Also, replace my_file.parquet with the name of the Parquet file that you created in Step 5.
Step 7: Load Parquet File to Synapse Dedicated SQL Pool
The final step is to load the Parquet file from Azure Blob Storage to Synapse Dedicated SQL Pool. You can use the following code to create an external data source in Synapse Dedicated SQL Pool:
CREATE MASTER KEY ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD = 'password';
CREATE DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL cred_name
WITH IDENTITY = 'username',
SECRET = 'password';
CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE data_source_name
WITH (
TYPE = HADOOP,
LOCATION = 'wasbs://container_name@account_name.blob.core.windows.net',
CREDENTIAL = cred_name
);Replace password, username, account_name, and container_name with the appropriate values for your Azure Blob Storage account and container.
Next, you can use the following code to create an external table in Synapse Dedicated SQL Pool:
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE external_table_name
(
column1 datatype1,
column2 datatype2,
...
)
WITH (
LOCATION = '/path/to/parquet/file',
DATA_SOURCE = data_source_name,
FILE_FORMAT = 'parquet'
);Replace external_table_name, column1, datatype1, and so on with the appropriate values for your external table.
Finally, you can use the following code to insert data from the external table to a regular table in Synapse Dedicated SQL Pool:
INSERT INTO regular_table_name
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM external_table_name;Replace regular_table_name, column1, column2, and so on with the appropriate values for your regular table.
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed how to create a framework to load data from Oracle to Azure Blob Storage as Parquet file and then load it to Synapse Dedicated SQL Pool. By following these steps, you can easily transfer your data from Oracle to Synapse Dedicated SQL Pool and take advantage of the benefits of cloud-based solutions for your data storage and processing needs.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments