Externalizing Configurations in Kubernetes Using ConfigMap and Secret
Configurations are needed to run an application. Learn how to Kubernetize your configurations using ConfigMap and Secrets.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeConfigurations are attributes needed by an application when it runs. These configurations are values that are used frequently across the application. They may be used to provide dynamic behavior of an application based on customer, geographical region, language, and locale. Frequently used configurations are database URL, username, password, etc. These values are not hardcoded along with the application code as they may change depending on different factors.
There is a 12 Factor recommendation that advises separate configuration out of code. Now the question arises if configurations are to be separated from code, how the application will access them during runtime. The answer is PLATFORM. Platform means the system on which the application runs. The configurations would be added on the platform as environment variables.
To execute the examples given in the article, you must be using a Linux system having connected to a Kubernetes cluster via the kubectl tool. This is the prerequisite.
Configurations in Kubernetes
Application workloads run on Kubernetes Pods. If a developer is transforming his application to run on Kubernetes, he must use Kubernetes ConfigMaps and Secrets to store configurations which then could be injected into Pods to be consumed by applications running inside the Pod.
ConfigMap
ConfigMap is a Kubernetes API object which stores data in form of a set of names and value pairs. It stores non-confidential data to be used by application workloads. It stores data up to 1 MB.
ConfigMaps could be used inside a Pod in 3 ways:
- As a container command argument
- As an environment variable in the container
- As a volume inside the container
The below examples show the above three use cases.
Usage of ConfigMaps
Before we use ConfigMaps in a Pod we have to first create it. ConfigMaps could be created using a command line (kubectl commands) or using manifest files.
Create ConfigMap
ConfigMap could be created in varieties of ways. We can create it using a manifest file with a ConfigMap spec. We can create it using kubectl create configmap command with literal, files option.
kubectl create configmap weekdays --from-literal=FIRST_DAY=SUNDAY --from-literal=SECOND_DAY=MONDAY --from-literal=THIRD_DAY=TUESDAY --from-literal=FOURTH_DAY=WEDNESDAY --from-literal=FIFTH_DAY=THURSDAY --from-literal=SIXTH_DAY=FRIDAY --from-literal=SEVENTH_DAY=SATURDAYIn the example above a ConfigMaps called weekdays can be created using kubectl create configmap command. The same ConfigMaps could be created using a manifest file as well.
Create a manifest file called weekdays.yaml with the below content and use the command “kubectl create -f weekdays.yaml” to create the ConfigMap called weekdays.
apiVersion: v1
data:
FIFTH_DAY: THURSDAY
FIRST_DAY: SUNDAY
FOURTH_DAY: WEDNESDAY
SECOND_DAY: MONDAY
SEVENTH_DAY: SATURDAY
SIXTH_DAY: FRIDAY
THIRD_DAY: TUESDAY
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: weekdays
The ConfigMaps creation could be verified using “kubectl get cm”, “kubectl get cm weekdays -o yaml” and “kubectl describe cm weekdays”.
ConfigMaps could also be created from existing properties files. For example, let’s say there is a file called days.properties with below content.
FIFTH_DAY: THURSDAYFIRST_DAY: SUNDAYFOURTH_DAY: WEDNESDAYSECOND_DAY: MONDAYSEVENTH_DAY: SATURDAYSIXTH_DAY: FRIDAYTHIRD_DAY: TUESDAY
A ConfigMap can be created from it using the command “kubectl create configmap weekdays –from-file=days.properties”. It will create the ConfigMap weekdays. The ConfigMap could be verified by using commands “kubectl get configmap weekdays -o yaml” or “kubectl describe configmap weekdays”.
ConfigMap as Container Command Argument and Environment Variable
Assuming that a ConfigMap called weekdays is created using the above examples, we will consume it by injecting it into a Pod. Create a file called pod.yaml with the below content and later use the command “kubectl apply -f pod.yaml”to create a pod called days-pod.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
run: days-pod
name: days-pod
spec:
containers:
- image: alpine
name: days-pod
args:
- sh
- -c
- while true;do echo "First Day of the week is ${FIRST_DAY}";sleep 5;done
envFrom:
- configMapRef:
name: weekdays
You can verify the Pod and its environment variables using commands “kubectl get pod days-pod -o yaml” and “kubectl exec -it days-pod — env”. The last command will print all the environment variables of the Pod. You can use the command “kubectl logs days-pod -f” to tail the logs from the Pod which will keep on printing “First Day of the week is SUNDAY” in every 5 seconds. If you closely watch the Pod spec in the pod.yaml file, the envFrom attribute is reading the ConfigMap weekdays and injecting it into the Pod with all names of the ConfigMap becoming environment variables of the Pod. In the echo command, we are referring to one of the environment variables FIRST_DAY.
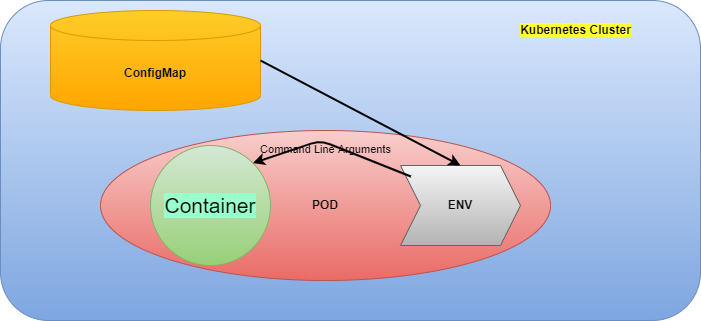
ConfigMap as Volume Mount
We can mount a ConfigMap as a volume inside a Pod. For all the keys of the ConfigMap, there will be a file inside the Pod and the value of the key will be the content of the file. One advantage in this use case is if there will be a change in the ConfigMap, the corresponding values will also be updated inside the Pod which uses it.
Assuming that there is a ConfigMap called weekdays exists, create a manifest file called pod-volume.yaml with below content and use “kubectl apply -f pod-volume.yaml” to create a pod called days-pod-volume.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
run: days-pod-volume
name: days-pod-volume
spec:
volumes:
- name: config-volume
configMap:
name: weekdays
containers:
- image: alpine
name: days-pod-volume
args:
- sh
- -c
- while true;do echo "First Day of the week is ";cat /etc/data/FIRST_DAY;sleep 5;done
volumeMounts:
- name: config-volume
mountPath: /etc/data
You can verify the creation using “kubectl get pod days-pod-volume -o yaml” and “kubectl exec -it days-pod-volume – ls -l /etc/data”. For the last command, there will be an output like this:
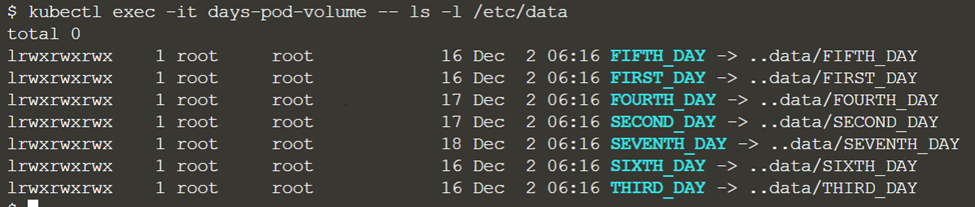
This pod has a volume mounted at /etc/data and all the 7 keys of the ConfigMap have become files inside the directory. The echo command in the container is printing the content of FIRST_DAY.
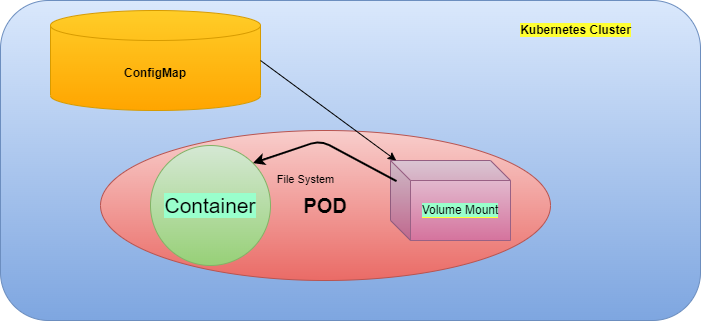
Update the ConfigMap and Observe Pod Change
Now we will update the ConfigMap and verify if the data changes in the Pod. Use the command “kubectl edit cm weekdays” and this will open the ConfigMap in the vi editor for edit. Change the value of FIRST_DAY from SUNDAY to FEBRUARY. Once done, wait 10 seconds and tail logs of the Pod days-pod-volume using “kubectl logs days-pod-volume”. You will observe that log printing FEBRUARY instead of SUNDAY.
Secrets
Secrets are configurations in Kubernetes which store sensitive information in the form of key and value pairs. The creation, usage, and consumption of Secrets are the same as ConfigMaps. The only difference is the values in Secrets are base64 encoded. It eliminates the chance of accidentally revealing any sensitive information to unintended users. Secrets store data up to 1MB. Secrets are of a different type to store different information like passwords, tokens, keys, dockerjson, basic-auth key, service account key, ssh key, tls key. We have to create the correct type of Secret to store appropriate information.
Usage of Secret
Secrets could be used inside a Pod in below following ways.
- Environment Variable
- Volume Mount as File
- Image Pull Secret
Before we use a Secret, we have to create it either using “kubectl create Secret command” or using a Secret manifest file. Secrets could also be created from files like ConfigMap.
Create Secret
Assume we need to create a Secret called db-password with key DB_PASSWORD and value administrator.
Using Command Line
kubectl create secret generic db-password --from-literal=DB_PASSWORD=administrator Execute the above command to create Secret db-password. Validate the secret creation using commands “kubectl get secrets”, “kubectl get secret db-password -o yaml” and “kubectl describe secret db-password”. The last two commands will display the output in yaml format. The output of “kubectl get secret db-password -o yaml” will look like below where you could see the value for DB_PASSWORD is bas64 encoded.
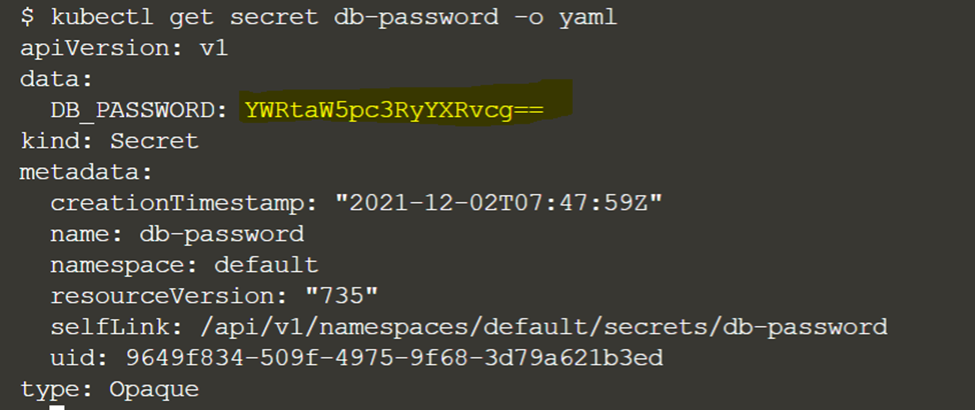
You can also create the same Secret from a password.properties file with below content.
DB_PASSWORD: administratorUse the command “kubectl create secret generic db-password –from-file=password.properties”. Validate the same by using “kubectl get secret db-password -o yaml”. The output will be like below.
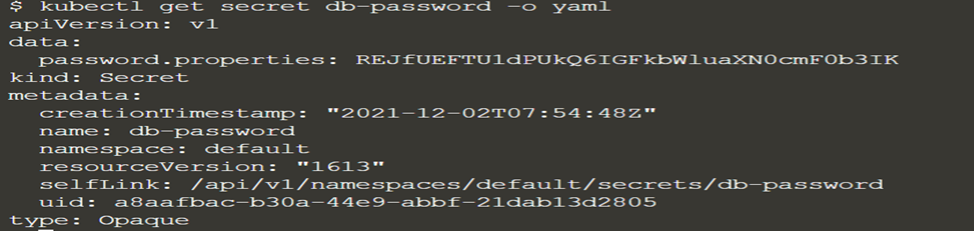
Here the key is password.properties and value is REJfUEFTU1dPUkQ6IGFkbWluaXN0cmF0b3IK. Use the command “echo REJfUEFTU1dPUkQ6IGFkbWluaXN0cmF0b3IK| base64 -d” to check the decoded value.
Using Manifest File
We will create the same Secret using the manifest file now. First, generate the base64 encoded value for string “administrator” using the command “echo administrator | base64”. The output will be “YWRtaW5pc3RyYXRvcg==” which will be used in the manifest file. Create a manifest file called secret.yaml with the below content:
apiVersion: v1data:DB_PASSWORD: YWRtaW5pc3RyYXRvcg==kind: Secretmetadata:name: db-password
Use “kubectl create -f secret.yaml” to create the secret. Validate the secret creation using commands “kubectl get secrets”, “kubectl get secret db-password -o yaml” and “kubectl describe secret db-password”.
Once the Secret is ready, we will consume it from inside a Pod.
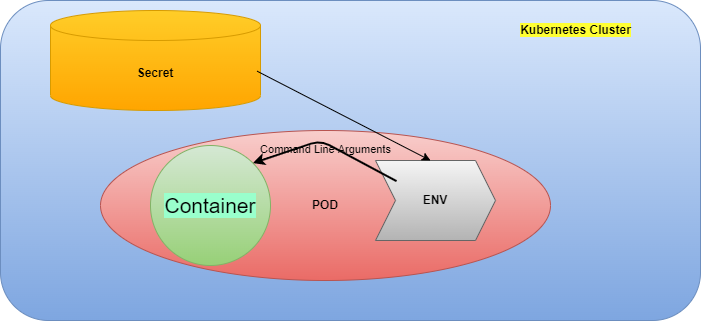
Secret as Container Argument and Environment Variable
Now we will create a Pod that will consume the Secret as an environment variable. Create a Pod manifest file called pod-secret.yaml using the below content:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
run: pod-secret
name: pod-secret
spec:
containers:
- image: alpine
name: pod-secret
args:
- sh
- -c
- while true;do echo "The Password is ${DB_PASSWORD}";sleep 5;done
envFrom:
- secretRef:
name: db-password
Use “kubectl apply -f pod-secret.yaml” to create the pod called pod-secret. You can validate the Pod creation using “kubectl get pod pod-secret -o yaml” and “kubectl describe pod pod-secret”. The logs could be tailed using “kubectl logs pod-secret -f ”where you could see the Pod printing line “The Password is administrator” every 5 seconds. The actual value of DB_PASSWORD is getting printed. The environment variable could also be checked using the command “kubectl exec -it pod-secret — env”.
Secret as Volume Mount
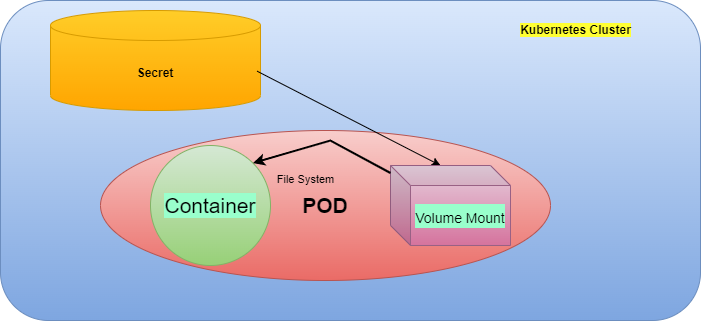
When we mount a Secret inside a Pod, for each key of the Secret a file is created in the mountPath. The value of the key becomes the content of the file. One advantage, in this case, is on changing the value of any Key, the content of the corresponding file inside the Pod also changes.
Create a Pod manifest file called pod-secret-volume.yaml using the below content:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
run: pod-secret-volume
name: pod-secret-volume
spec:
volumes:
- name: secret-volume
secret:
secretName: db-password
containers:
- image: alpine
name: pod-secret-volume
args:
- sh
- -c
- while true;do echo "The Password is "| cat /etc/data/DB_PASSWORD";sleep 5;done
volumeMounts:
- name: secret-volume
mountPath: /etc/data
Use “kubectl apply -f pod-secret-volume.yaml” to create the pod called pod-secret-volume. You can validate the Pod creation using “kubectl get pod pod-secret-volume -o yaml” and “kubectl describe pod pod-secret-volume”. The logs could be tailed using “kubectl logs pod-secret-volume -f” where you could see the Pod printing the DB_PASSWORD in every 5 seconds. The environment variable could also be checked using the command “kubectl exec -it pod-secret-volume — env”. There will be no environment variable called DB_PASSWORD as it is mounted inside the volume as a file called DB_PASSWORD. The file could be verified using the command “kubectl exec -it pod-secret-volume — cat /etc/data/DB_PASSWORD”.
Update Secret and Observe Change in Pod
We will change the value of the Secret and verify if the Pod file also changes. Execute the command “echo administrators|base64” and copy the output which we will use in Secret. Now to update the Secret by using the command “kubectl edit secret db-password” and update the value of DB_PASSWORD using the copied value generated by base64. After ten seconds execute the command “kubectl exec -it pod-secret-volume — cat /etc/data/DB_PASSWORD” and “kubectl logs pod-secret-volume -f” to observe the changed value.
Conclusion
Both Secret and ConfigMap are very powerful features of Kubernetes. Once you know how to create and consume them, you could transform your application so that they can use the Kubernetes platform for deploying applications without a hitch.
Published at DZone with permission of Aditya Bhuyan. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments