Everything You Need To Know About Storing Scraped Data on the Cloud
The “cloud” revolutionizes how we store our data and how we access them on a day-to-day basis. Scraping numerous pages makes it difficult to store data securely.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
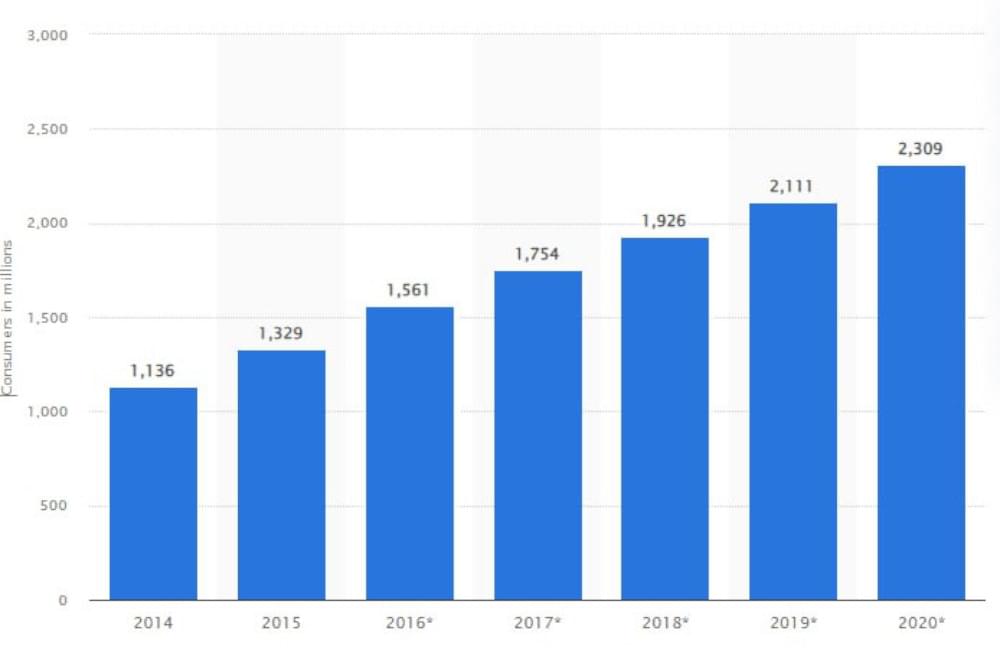
Join For FreeThe number of personal cloud storage users has been steadily increasing from 1136 in 2014 to 2309 in 2020. This represents an average annual growth rate of approximately 10.4%. By 2020, the number of personal cloud storage users had doubled.
According to Gartner, global public cloud spending will increase by 20.7% and reach $591.8 billion in 2023, compared to $490.3 billion in 2022.
Saving your important files, either personal, work, or business, on a local disk drive may look convenient at first. However, if it starts to pile up, or if you need to transfer files between machines, it may get troublesome and result in more work than necessary. Not only that, but what if something happened to your local storage? Power issues, firmware corruption, and human error are just a few things that can cause a hard disk failure. Issues like these may ultimately cost you countless unrecoverable work hours and significantly negatively impact your business.
Online storage solutions have come to replace conventional local disk storage. The “cloud” revolutionizes how we store our data and how we access them on a day-to-day basis. Cloud storage is a data storage type that includes the copied data over the internet and into a data server. These database servers are actual physical computers where companies store your files on multiple hard drives. Instead of the traditional single-storage hard disk drives, cloud storage keeps your data safe from getting lost since your backup file is technically in another location, which is often referred to as redundancy.
What Can You Store in the Cloud?
You can store just about anything on the Cloud due to its versatility. It doesn’t mean you should store something just because you can. Certain documents and applications are suitable for cloud storage, while others should be kept away from the cloud.
The cloud is an excellent platform for storing most of your data since it is secure and easy to access. The choice between storing files in a public or private cloud may be important. Cloud storage is a secure and accessible option for file storage, storing images, videos, checklists, projects, emails, blog posts, and business documents, and for hosting webpages. Storing photos is one of the main reasons why 71% of people use cloud storage services. With cloud storage, data is backed up, and it can be shared with multiple people or computers.

In general, you should move these items to cloud storage:
- Images or videos: If your scraped data includes images or videos, storing them on the cloud is a great option. Not only does it free up space on your local drive, but it also makes it easy to share these files with others.
- Checklists: Checklists are another type of data that is well-suited to cloud storage. Whether you’re managing a project or just keeping track of your personal to-do list, storing checklists on the cloud can help you stay organized and on top of things.
- Projects or group documents: If you’re working on a project with a team, storing your documents on the cloud can make collaboration much easier. You can share files with others, work on them together in real time, and access them from anywhere.
- Emails: Emails are a critical form of communication for many people, and they can also contain important data. By storing your emails on the cloud, you can access them from any device, and you can rest assured that they’re safe and secure.
- Blog posts: If you’re a blogger, storing your posts on the cloud is a great idea. It makes it easy to access your content from anywhere, and it also ensures that you have a backup in case something goes wrong with your local drive.
- Webpage hosting: If you’re running a website, hosting it on the cloud can be a cost-effective and reliable option. Cloud hosting services are designed to handle heavy traffic and can offer a high level of uptime and reliability.
- File storage: Cloud storage is an excellent option for storing any type of file, whether it’s a document, image, or video. With cloud storage, you can access your files from anywhere, and you don’t have to worry about running out of space on your local drive.
- Business documents: For businesses, storing documents on the cloud is a must. It makes it easy to share files with employees, clients, and partners, and it also ensures that your data is secure and backed up in case of a disaster.
In conclusion, cloud storage is an excellent option for storing scraped data. Whether you’re working on a project with a team or just trying to stay organized, cloud storage can help you keep your data safe, accessible, and organized.
In addition to sharing documents with multiple people or computers, it is also a convenient way to share files. You can share files, store photos, and keep to-do lists using Google Drive.
Keeping financial information on a private server is ideal, but storing payroll software on the cloud is a viable option. A private cloud is a better option for business documents since some files are safer. In addition, if a private cloud suits your needs better, you can always store your pictures and other files there.
What Data Cannot Be Stored in the Cloud?
Cloud is highly secure, but it is still possible for data breaches to occur. Cloud storage is unsuitable for some documents because they are too sensitive. Additionally, some applications won’t work well on a cloud system due to security concerns.
Documents that require FDA approval, such as health records or medical research, may not be appropriate for keeping in the cloud. Sensitive information such as date of birth, numbers, and credit card data should not be kept in the cloud. In case of a server failure, storing applications essential to your day-to-day workflow outside the Cloud is vital. Keep illegal or pirated data off the cloud, too.
Thus, you can rely on the cloud for most of your data security. Regardless of your storage method, there is always the possibility of a hack, but if you have placed the right documents in the Cloud, you can sleep more easily at night.
Why Should You Store Data in the Cloud?
Traditional on-premises storage solutions can’t compare with the advantages of storing data in the cloud. On-premises Storage is generally less scalable, less reliable, and more expensive than cloud storage. Moreover, cloud storage permits employees to access their data remotely from anywhere.
Cloud storage provides robust security measures to protect data from unauthorized access or loss. It adds an extra protective layer of security from hackers and data breaches. Cloud storage can help an organization reduce its carbon footprint by reducing the need for physical hardware and data centers.
Send Scraped Data Directly to the Cloud
Considering this, what are cloud storage’s real benefits in web crawling and scraping? How to save data on cloud storage?
Suppose you’re a beginner trying out web scraping. In that case, you’ll notice that over time, storing your scraped data may become a problem that you will need to deal with by purchasing an extra hard drive to ensure that the stored data is safely backed up to prevent the loss of your precious scraped data.
This can take your time and resources, which you could have invested in other important things like scraping or learning new ways to scrape data effectively. The same scenario can happen in small or big businesses when maintaining their database; that is why online storage solutions are an integral part of any business that deals with data nowadays.
The scalability and worry-free nature of cloud storage, which gives a major advantage in most cases, is hard to ignore.
Can Cloud Storage Be Lost?
Data stored in the Cloud can be easily lost in the same way as any other method of data storage; maybe computer crashes and backups are lost. Various factors can result in cloud data loss, including natural disasters, human error, and malicious attacks. Therefore, backups are necessary to minimize the risk of data loss, whether stored in the Cloud or on-premises. Despite backups and redundancy in place, cloud storage providers are flexible in protecting against data loss.
The cloud allows the deletion of data. A cloud storage provider may overwrite data or destroy storage media to ensure that data is completely erased. Retention policies specify how long cloud storage providers will keep data and when it will expire.
It is also possible for users to delete their data manually. It would be best to remember that simply deleting data from the Cloud is not the same as erasing it. In backups or elsewhere in the storage infrastructure, data may still exist.
How Can Data Loss Occur in the Cloud?
While cloud storage offers numerous benefits, it’s essential to understand the potential risks associated with storing your data in the cloud. Data loss can occur in the cloud due to several factors, including:
- Human error: One of the most common reasons for data loss in the cloud is human error. Users may accidentally delete or overwrite critical files or data, resulting in permanent loss.
- Security breaches: As cloud storage involves storing data on remote servers, it may become susceptible to security breaches. Malware or hacking attempts can lead to data loss or even theft. Security issues are perhaps the most significant concern when it comes to cloud storage. Data stored in the cloud is vulnerable to hacking, malware, and other cyber threats. Hackers can gain access to your data by exploiting vulnerabilities in your cloud provider’s security measures or through phishing scams.
- Technical issues: Technical glitches such as software bugs, server malfunctions, or hardware failures can lead to data loss. In some cases, these issues can cause permanent damage to the data stored on the cloud.
- Service provider errors: Sometimes, cloud service providers may make errors that can result in data loss. These could include inadequate backup procedures, data center outages, or mismanagement of data.
- Natural disasters: Natural disasters such as earthquakes, floods, or fires can lead to data loss. If the servers storing your data are in the affected areas, the data may become permanently damaged or destroyed.
- Internet connectivity issues: Since cloud storage relies on internet connectivity, any issues with the connection can cause data loss or corruption. This could happen due to problems with the internet service provider, network congestion, or hardware failure.
To prevent data loss in the cloud, it’s essential to take necessary precautions, such as regularly backing up your data, implementing robust security measures, and choosing a reliable cloud service provider. In lieu of saving costs and doing things quickly, a pattern and a standard to be followed is a must.
By understanding the potential risks and taking preventive measures, you can enjoy the numerous benefits of cloud storage while keeping your data secure.
Which Storage Cannot Be Erased?
Finance, healthcare, and government sectors require tamper-proof data storage. Data can be difficult or impossible to erase with WORM (write once, read many) cloud storage solutions. WORM, or immutable Storage, prevents future modifications or deletions by writing data once and then making it read-only. During the data’s required retention period, it remains intact and unchanged. However, some cloud storage solutions do not provide these features and may be subject to additional fees or restrictions.
Will Cloud Storage Last Forever?
Unfortunately, Cloud storage providers generally do not guarantee that the data they store on their servers will last forever. It is important to note that the longevity of cloud storage depends on several factors, such as the provider’s infrastructure, the data centers’ policies, and the quality of the storage media used.
Though cloud storage providers typically implement multiple layers of redundancy and backups, there is always the risk of data loss due to hardware failure, natural disasters, cyber-attacks, or other unexpected events. To ensure the protection of your data, it is essential to create a backup plan for critical data and evaluate and update your Storage and backup strategies regularly.
What Happens When My Cloud is Full?

After your cloud storage is full, you can store additional data once you increase your storage capacity. There are different policies for how cloud storage providers handle whole Storage, but generally, you may receive error messages or notifications indicating that you have exceeded your storage limit.
You can make space available by deleting unnecessary files, moving them to an external hard drive, or upgrading your storage plan if your provider offers. Cloud storage providers may also offer compression, deleting duplicates, or archiving old files to allow you to manage your Storage more efficiently.
What Is Crawlbase (Formerly ProxyCrawl) Cloud Storage, and How Does It Work?
Crawlbase Cloud Storage handles scaling, backing up, and managing cloud space securely so you and your team can redirect your time and effort to what matters for your business. It is an easy-to-use API where you can save your crawled or scraped data and screenshots on the cloud. You can also do a full-text search and add or delete data.
How To Save Data on Cloud Storage
The majority of corporate data, approximately 60%, is currently being stored in the cloud. To access cloud storage, Crawlbase (formerly ProxyCrawl) created an API that will securely send your data to our servers. You can use this with most of the Crawlbase (formerly ProxyCrawl) products, such as the Crawling API and Screenshot API, or even configure it with your Crawler using the Storage webhook endpoint.
Suppose you already have a Crawlbase (formerly ProxyCrawl) account and use the Crawling API to crawl and scrape web pages. In that case, you are probably familiar with making a simple call and passing parameters. For starters, you need to add the parameter &store=true to send a copy of the data to your Storage.
You Can Refer to the Sample Code Below
curl "https://api.crawlbase.com/?token=USER_TOKEN&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.amazon.com&store=true"from urllib2 import urlopen
from urllib import quote_plus
url = quote_plus('https://www.amazon.com/dp/B07H163S6J/')
handler = urlopen('https://api.crawlbase.com/?token=USER_TOKEN&store=true&url=' + url)
print handler.read()Sometimes, taking a screenshot of a webpage you are crawling will be more efficient in keeping track of the visual changes. Crawlbase (formerly ProxyCrawl) has an API dedicated just for that, and you can also send those screenshots directly to the cloud storage.
curl "https://api.crawlbase.com/screenshots?token=USER_TOKEN&url=https%3A%2F%2Fapple.com&store=true"With these few examples, you can see how simple it is to send data to the Cloud; that is why corporate clients will also be able to quickly deploy this solution since the API is scalable and can be easily integrated into any existing app or program.
Managing Cloud Storage
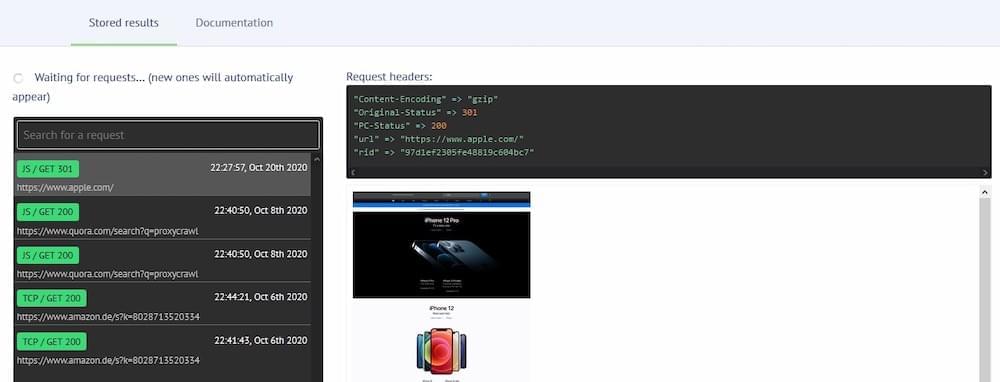
Of course, sending the data is just one part of it, and the convenience and flexibility of cloud storage continue beyond that. It is easy to manage without difficulty via the API or through the user’s web account. From the user’s account, a dedicated dashboard for stored data will let you search for any saved data and show all of the requests sent from the Crawling API, Crawler, and Screenshot API that includes the request headers with a quick view of each request.
If going to the dashboard is not your thing, or at least not possible with your workflow, Crawlbase (formerly ProxyCrawl) has prepared some parameters to let you manage your Storage via the API.
Any requests sent to the Storage API should start with the following base part:
https://api.crawlbase.com/storage
Each saved request will have two identifiers, URL and RID, which can easily manage (view or delete) your data.
To view or retrieve a crawled page (HTML or JSON), do an API call as shown below:
curl https://api.crawlbase.com/storage?token=USER_TOKEN&rid=RID
Without looking at the dashboard, you can retrieve the request headers containing the URL and RID by passing the parameter &format=, which will accept HTML or JSON as a value.
Example
https://api.crawlbase.com/storage?token=USER_TOKEN&format=json&url=ENCODED_URL
Due to the limited Storage, you may sometimes want to delete unwanted or old data from the Cloud. You can quickly delete a token and RID by sending a DELETE request.
curl -X DELETE https://api.crawlbase.com/storage?token=_USER_TOKEN_&rid=RID
If the data were deleted correctly, you would get the response below:
"success": "The Storage item has been deleted successfully."
If you want to check the total count or the actual number of data saved on your Storage, you may send this GET request that includes your private token:
https://api.crawlbase.com/storage/total_count?token=USER_TOKEN
By default, you can store a maximum of 10,000 documents in the Cloud with a retention of up to 14 days, which is currently free upon signing up. It should be plenty for starters or clients needing to test the service. However, if you need to store more data and have longer data retention, you can opt for the Developer or Business plan.
Conclusion
To summarize, there are many obvious advantages of cloud storage over local storage in terms of usability and accessibility. Your files will not just be easier to access from anywhere; it will also be the perfect backup plan for any project or business since these files’ storage is at different locations, and they can be easily retrieved at any given time.
It is a great platform that can be a manageable investment in time and money. Users can ensure additional cost savings because storage management, hardware purchase, and extra computational resources are not needed for storing data.
Crawlbase (formerly ProxyCrawl) API is compatible with most Storage API products, including the Smart Proxy, the Crawler, Screenshot API, and Crawling API. With this proxy scraper, you can scrape data anonymously with its unlimited proxies and store it in the cloud. Cloud storage service lets you store your scraped data on the cloud. You’ve seen how easy it is to save HTML, JSON, or JPEG results to the Cloud with just a few lines of code. We’ve also tackled how straightforward it is to manage the Storage using the dashboard or API.
Published at DZone with permission of Dave Wells. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments