Enabling Agile Maturity in Scrum Teams
What is Agile Maturity? Why should Agile teams or agile organizations worry about this? How can we measure agile maturity and enable it for our agile teams?
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeEnabling Agile Maturity in Scrum Teams
What is Agile Maturity? Why should agile teams or agile organizations worry about this? How can we measure the agile maturity and enable it for the agile teams?
The organizations that are in an agile-scrum transformation journey the initial focus is on streamlining the scrum process and tools but as they grow older and get experience with scrum, they look for continuous improvement across the agile-scrum value chain.
So how to enable Scrum teams to their maturity journey? There could be multiple approaches to this but Agilist should focus the road which can be measured well and easy for the travelers (read scrum teams here)

To understand the mature scrum team’s behaviors/work culture, we need to understand the team structure and processes
Scrum Team
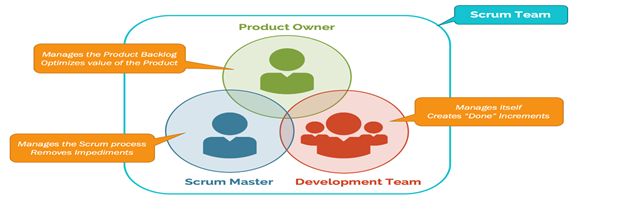
- PO: If we look at the PO role at a high level the expectation is that the PO should guide the team with a product road map and product vision. He does this activity by properly organizing the product backlog and reflecting the business stakeholders’ feedback within the product backlog
- Development Team: The development team is responsible for turning out product backlog items into real products in the hands of users.
- Scrum Master: The Scrum Master is responsible for facilitating the PO and development teams in their Scrum journey. This role can be referenced as captain of a ship whose job is guiding the sailors to the destination sometimes like a coach like a teacher.
Scrum Process
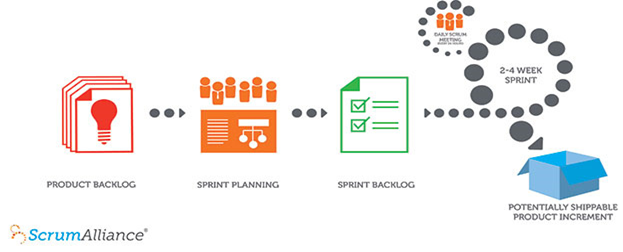
Now what if the team is new with the scrum process or they have started long back but they are still facing the issues like:
- Product Owner is absent or not regularly present in the required scrum events
- Sprints are running like mini-waterfall
- Too Many stories started early
- Consistently adding stories in a running sprint
- Consistent spill over trends
- Product quality is not being met
- Automation thinking and mindset missing
- Continuous improvement is missing in retrospective meetings
- Product features are being not accepted as a real benefit by business
- Team disconnect and working as individuals, not as one agile team
- PO assigning tasks and velocity is the most significant matrix
- Team’s delivery is not predictable
- The team is heavily dependent on Scrum master for their impediments, assignment of work
- Domain and technology learning curve is missing
The list can go long if a team is facing the above issues partially or as a whole then their Agile-scrum maturity needs to be assessed and action needs to be taken to make them mature scrum team.
Since now we have a fair idea of scrum roles, processes involved and antipatterns now let’s look at each of these components and find out what antidote they require. For simplification, let's focus on the below three categories to enable scrum maturity:
- People
- Process (Scrum)
- Technology (Engineering Practices)
People
Let’s analyze the people component of our proposed agile maturity model. The people form the base of the scrum team. The development team, PO & Scrum master are the inner core people directing affecting the scrum practice while the managers and leadership team affect the scrum practice externally. What’s the expectation from the core scrum team and leadership team in an agile maturity journey?
For keeping the measurement simple and yet effective let’s look at the below parameters and how the mature team scores for these:
- Behaviors
- Way of working
- Personal & professional goals
- Motivation level
Behavior
Each team and their members are unique but most of the people in the high performing scrum teams’ shows certain behaviors like respect for the teammates, high belongingness with the team, no personal ego, keep teams first then self, direct and open communication, empathy towards teammates and collaborative attitude towards the work and people in general
Way of working
This one might surprise you as we are talking about scrum here but then people bring their traits while working on tasks. It has been observed that collaboration, open for suggestion, always working on the top of the assigned task, participating, being vocal about the individual and team tasks as the explicit quality in individuals working with mature agile teams
Goals
The clarity of goals plays a major role in the general well-being and professional career of people. The scrum teams’ members will attain their maturity faster if they are clear about their personal and professional goals. I have seen may cross-functional teams where team members are doing agile but they are not sure what is their goal 5 years down line or what they want from their life.
It has been observed that individuals with clear goals work with an optimum level of performance
Motivation Level
One of the agile principles says that “Build projects around motivated individuals”. The question is how do you define the right motivation and what constitutes it. It has been observed that in scrum teams’ Monetary benefits are not the Only motivation factor. The factors like the freedom to choose the work, freedom to select the team, recognition of work, association with a team or group, challenging and mentally stimulating work, building solutions which affect millions of lives or building solutions which change the business work matters too.
Solutions
As Scrum Master to achieve the “behavior, way of working, Goals & Motivation level of matured scrum teams as discussed above, there is not one unique solution but an umbrella strategy.
Tuckman Model for Team Development
When it comes to scrum team development, the Tuckman model comes very handily. As a Scrum master, I have extensively used Bruce Tuckman's model of team development. Though Mr. Tuckman proposed this model in the year 1965, the model is still very relevant while enabling maturity.
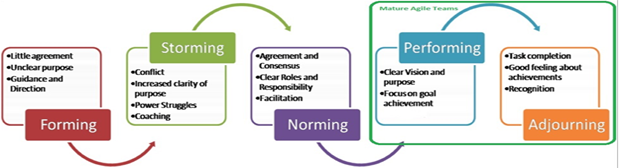
As a Scrum Master, we need to guide the team through the various stages until the scrum teams reach to performing stage. The scrum teams get immense knowledge on team dynamics and ways of working while transitioning from non-maturity stages like forming, storming, norming to the maturity stage like Performing and adjourning.
There is a variety of techniques available for this transitioning and scrum master based on the scrum team can decide which one works for the concerned team. The given below techniques are widely used
- Workshop on the Tuckman model of team development followed by activities for each stage
- One to one meeting with team members on how to achieve the transition to the performing stage
- Individual feedback on team dynamics and their contribution towards it
- Measure for the behavioral changes in the scrum team and repeat the cycle
- Devising the recognition plan- announcing rewards, positive feedbacks
Adkar Model
This model was developed by Jeff Hiatt, CEO of Prosci® Change Management (www.prosci.com), and first published in 2003. It focuses on 5 actions and outcomes necessary for successful individual change and therefore successful organizational change.
The five parts of ADKAR are:
- Awareness -of the need for change
- Desire- to participate in and support the change
- Knowledge on how to change
- Ability- to implement the required skills and behavior
- Reinforcement- to sustain the change
This model, I found very effective while guiding the team on scrum maturity because it emphasizes on changing the individual first. ADKAR emphasizes that successful organizational (read here scrum teams) change occurs only when each person can transition successfully.
Again, as a scrum master one can think of the below techniques for implementing the ADKAR in scrum teams:
- Workshop/webinar on ADKAR stressing on
- Individual Coaching- one to one meeting
- Monitoring and Tracking the change – behavioral, way of working,
- Devising the recognition plan- announcing rewards, positive feedback
Along with the above two solutions, we can also include the 3rd model which is Training teams on Scrum values.

I am going to talk about the remaining two categories for enabling scrum maturity in my next blog so stay tuned for it:
- Process (Scrum)
- Technology (Engineering Practices)
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments