Elasticsearch on Google Cloud Platform
Take a look at this simple and quick tutorial about downloading and connecting Elasticsearch to your GCP instance.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis tutorial focuses on how one can set up Elasticsearch on Google Cloud Platform (GCP). At the end of this tutorial you will be able to connect to an Elasticsearch instance and use it. In this tutorial, we will deploy Elasticsearch on a compute VM (instead of using on-click install, for the kicks of it.
Before You Start
A basic understanding of Elasticsearch is useful. If new you could browse though below first
Setup
First of all, you need to setup your Google Cloud account. Google gives away a trial version for 230 with enough credits. Once you have created an account, you need to get familarized with the GCP ecosystem. You could go through this.
Getting Started
Once your account with GCP is setup, it is time to start off with the steps.
The first thing is to create a virtual machine, click the navigation menu, where you would notice Compute Engine as one of the items (as shown in below image).
Setup Virtual Machine on Google Cloud
Below steps outline the process of creating a new VM on GCP. First, create a project and follow below steps.
- Select Virtual Machine once you hover over Compute Engine.
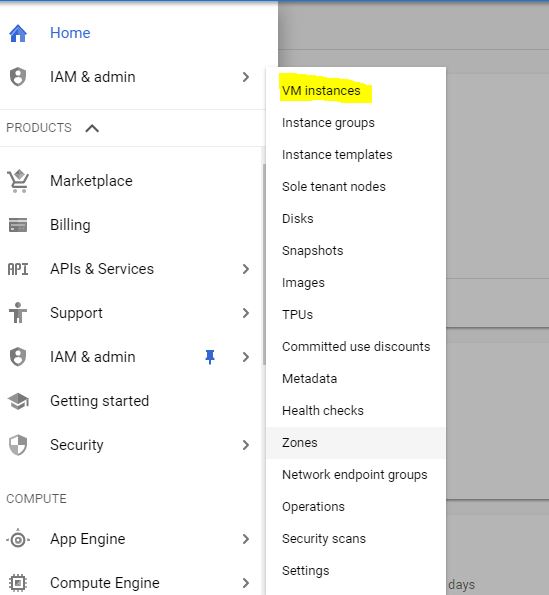
- Create a new VM instance (image below)
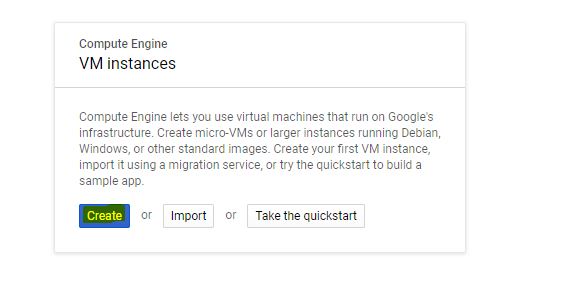
- For our demonstration purposes, we can start by creating a VM with 1vCPU (for development only). I have used Ubuntu as the OS for this tutorial (these command would not be specific to Ubuntu though).
You can choose below:
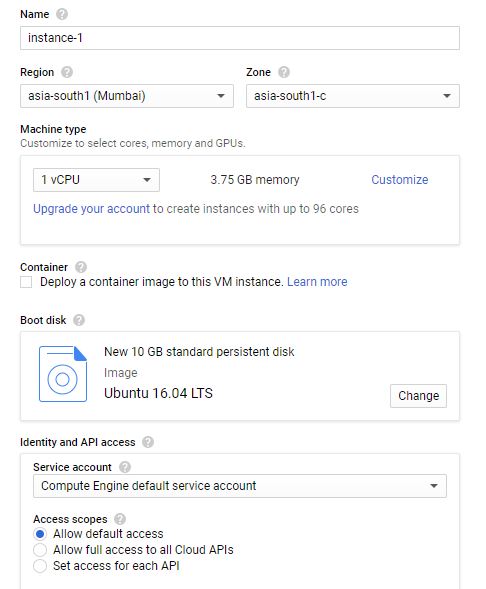 Note: Use relevant region (for India, I chose asia-south1).
Note: Use relevant region (for India, I chose asia-south1).
- Once a VM is created, you should be able to connect to it via SSH. The external IP address will be listed.

In order to connect to the VM via SSH, you need to create a pair of keys, one public and one private key. Store the public key in metadata and SSH using the private key and passphrase.
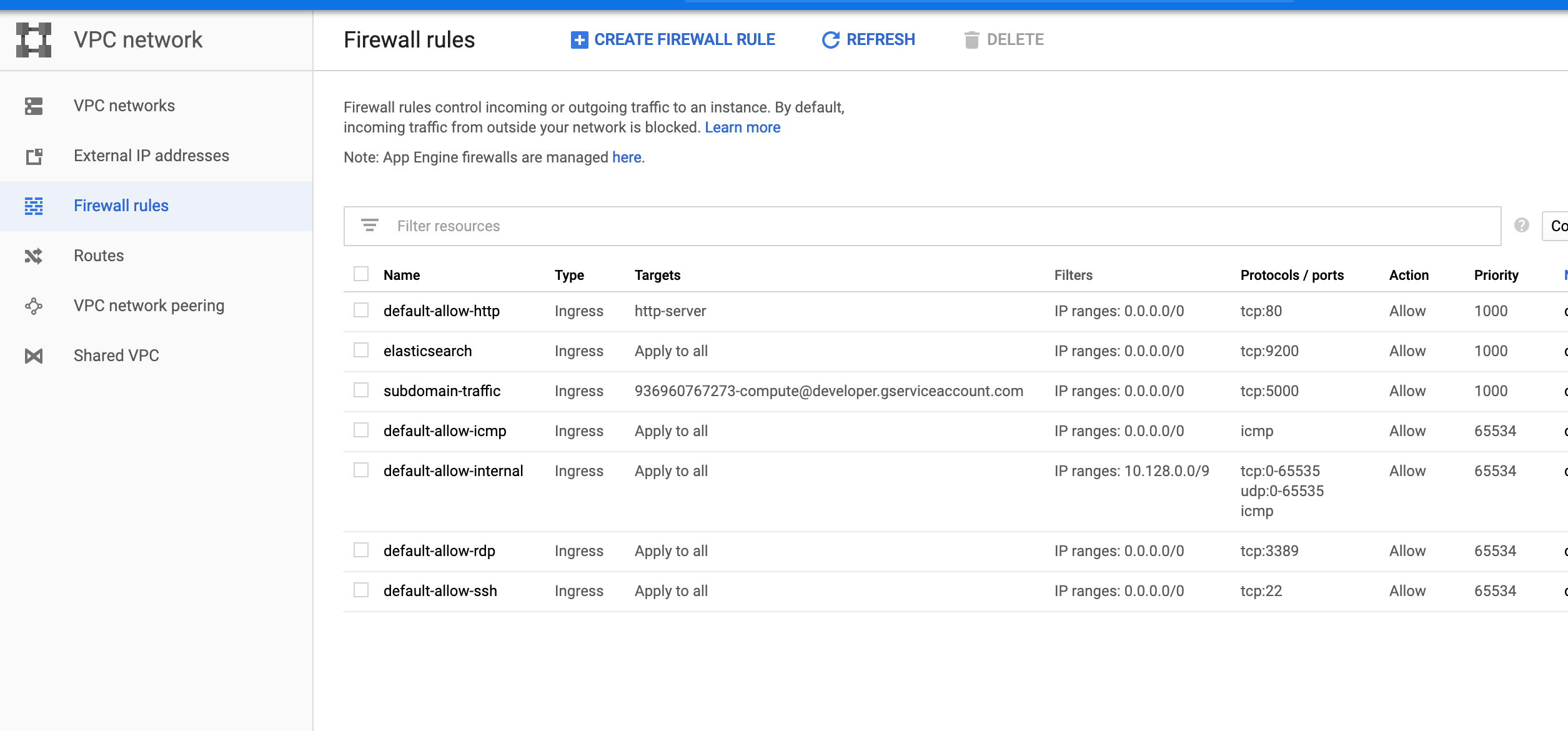
- Add a firewall rule to allow 9200 (the port used by Elasticsearch).
![Image title]()
Install Elasticsearch
Once you are able to log in to the Virtual Machine via SSH, follow these below steps to install Elasticsearch.
We will follow the process of installing without Debian/RPM packages. I have faced several problems while trying to use the Debian package and would not recommend that method.
Prerequisites
- Java: Minimum recommended version 1.8.0_131 or above
Download Elastic
- Download the zip along with the zip sha512.
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-6.6.1.zip
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-6.6.1.zip.sha512
- Use the shashum command and unzip the file.
shasum -a 512 -c elasticsearch-6.6.1.zip.sha512
unzip elasticsearch-6.6.1.zip
elasticsearch-{version}.zip: "OK" would be output of shasum command, which indicates that the package has not been tampered with.
- Change to the current working directory to the unzipped folder.
cd elasticsearch-6.6.1/We are almost there, all that we need to do now is a few configuration changes to make sure that you do not face problems while starting Elasticsearch.
Change the network.host in elastic configuration, look for the line containing network.host and uncomment it and set it to 0.0.0.0.
sudo vi /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
# ---------------------------------- Network -----------------------------------
#
# Set the bind address to a specific IP (IPv4 or IPv6):
#
network.host: 0.0.0.0
#
# Set a custom port for HTTP:
#
#http.port: 9200
#
Set the JVM configurations based on the memory allocated during the creation of the virtual machine. As we created a VM with 3.7 GB memory, let's change the max heap to 512 MB.
To change the JVM options, since we are using a zip file, locate jvm.options in the config/ folder..
# Xms represents the initial size of total heap space
# Xmx represents the maximum size of total heap space
-Xms512m
-Xmx512m
The last point is to start Elasticsearch from the command line.
./bin/elasticsearchYou journey to this point should have been smooth, but in case you see errors related to the permissions and a stack trace similar to below:
org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.StartupException: java.lang.RuntimeException: can not run elasticsearch as rootCheck to make sure you aren't using sudo to start Elastic, which won't work. Elastic has a reason behind it. To overcome it, the simplest way is to change the ownership of Elasticsearch folders.
sudo chown <nonrootuser> <unzipped-es-folder> -RYou could also start Elasticsearch as a daemon.
./bin/elasticsearch -d -p pidIf you are able to successfully accomplish all the steps you would be able to get the health of Elasticsearch.
curl -X GET "http://<VM-Public-IP>:9200/_cluster/health”
{
"name": "pfb85el",
"cluster_name": "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid": "tZNQgtSCS5CL6Kn41Z9gxg",
"version": {
"number": "6.6.1",
"build_flavor": "default",
"build_type": "zip",
"build_hash": "1fd8f69",
"build_date": "2019-02-13T17:10:04.160291Z",
"build_snapshot": false,
"lucene_version": "7.6.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version": "5.6.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version": "5.0.0"
},
"tagline": "You Know, for Search"
}Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments