Deploying Microservices: Spring Cloud vs. Kubernetes
When it comes to deploying microservices, which is better — Spring Cloud or Kubernetes? The answer is both, but they shine in different ways.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeSpring Cloud and Kubernetes both claim to be the best environment for developing and running microservices, but they are both very different in nature and address different concerns. In this article, we will look at how each platform is helping in delivering microservice-based architectures (MSA), which areas they are good at, and how to use the best of both worlds in order to succeed in the Microservices journey.
You may also enjoy Linode's Beginner's Guide to Kubernetes.
Background Story
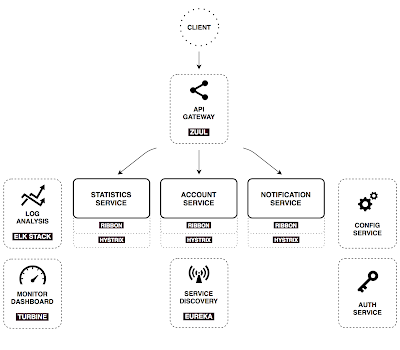
Recently, I read a great article about building Microservice Architectures With Spring Cloud and Docker by A. Lukyanchikov. If you haven't read it, you should, as it gives a comprehensive overview of what it takes to create a simple microservices-based system using Spring Cloud. In order to build a scalable and resilient microservices system that could grow to tens or hundreds of services, it must be centrally managed and governed with the help of a tool set that has extensive build time and runtime capabilities. With Spring Cloud, that involves implementing both functional services (such as statistics service, account service and notification service) and supporting infrastructure services (such as log analysis, configuration server, service discovery, auth service). A diagram describing such an MSA using Spring Cloud is below:
MSA with Spring Cloud (by A. Lukyanchikov)
This diagram covers the runtime aspects of the system, but it doesn't touch on the packaging, continuous integration, scaling, high availability, and self-healing, which are also very important in the MSA world. Assuming that the majority of Java developers are familiar with Spring Cloud, in this article, we will draw a parallel and see how Kubernetes relates to Spring Cloud by addressing these additional concerns.
Microservices Concerns
Rather than doing a feature by feature comparison, let's take a look at wider Microservices concerns and see how Spring Cloud and Kubernetes approach those. The good thing about MSA today is that it is an architectural style with well-understood benefits and trade-offs. Microservices enable strong module boundaries, with independent deployment and technology diversity. But they come at the cost of developing distributed systems and significant operational overhead. A key success factor is to focus on being surrounded by tools that will help you address as many MSA concerns as possible. Making the starting process quick and easy is important, but the journey to production is a long one, and you need to be this tall to get there.
Microservices concerns
In the diagram above, we can see a list with the most common technical concerns (we are not covering the non-technical concerns such as organization structure, culture and so on) that have to be addressed in an MSA.
Technology Mapping
The two platforms, Spring Cloud and Kubernetes, are very different and there is no direct feature parity between them. If we map each MSA concern to the technology/project used to address it in both platforms, we come up with the following table.
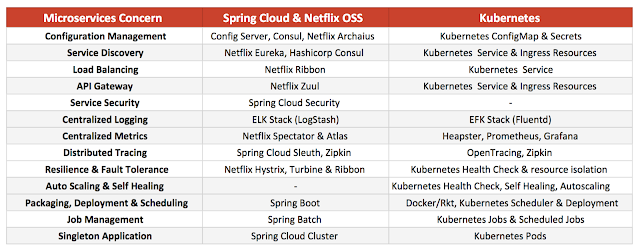 Spring Cloud and Kubernetes technologies
Spring Cloud and Kubernetes technologies
The main takeaways from the above table are:
Spring Cloud has a rich set of well-integrated Java libraries to address all runtime concerns as part of the application stack. As a result, the microservices themselves have libraries and runtime agents to do client-side service discovery, load balancing, configuration update, metrics tracking, etc. Patterns such as singleton clustered services and batch jobs are managed in the JVM too.
Kubernetes is polyglot, doesn't target only the Java platform, and addresses the distributed computing challenges in a generic way for all languages. It provides services for configuration management, service discovery, load balancing, tracing, metrics, singletons, scheduled jobs on the platform level and outside of the application stack. The application doesn't need any library or agents for client side logic and it can be written in any language.
-
In some areas, both platforms rely on similar third-party tools. For example, the ELK and EFK stacks, tracing libraries, etc. Some libraries, such as Hystrix and Spring Boot, are useful equally well on both environments. There are areas where both platforms are complementary and can be combined together to create a more powerful solution ( KubeFlix and Spring Cloud Kubernetes are such examples).
Microservices Requirements
In order to demonstrate the scope of each project, here is a table with (almost) end-to-end MSA requirements starting from the hardware on the bottom, up to the DevOps and self-service experience at the top, and how it relates to Spring Cloud and Kubernetes platforms.
Microservices requirements
In some cases, both projects address the same requirements using different approaches, and in some areas, one project may be stronger than the other. But there is also a sweet spot where both platforms are complementary to each other and can be combined for a superior microservices experience. For example, Spring Boot provides Maven plugins for building single JAR application packages. That, combined with Docker and Kubernetes' declarative Deployments and Scheduling capabilities, makes running microservice a breeze. Similarly, Spring Cloud has in-application libraries for creating resilient, fault tolerant microservices using Hystrix (with bulkhead and circuit breaker patterns) and Ribbon (for load balancing). But that alone is not enough, and when it is combined with Kubernetes' health checks, process restarts, and auto-scaling capabilities, then microservices become a true antifragile system.
Strengths and Weaknesses
Since both platforms are not directly comparable feature by feature, and rather than digging into each item, here are the (summarized) advantages and disadvantages of each platform.
Spring Cloud
Spring Cloud provides tools for developers to quickly build some of the common patterns in distributed systems such as configuration management, service discovery, circuit breakers, routing, etc. It is build on top of Netflix OSS libraries, written in Java, for Java developers.
Strengths
- The unified programing model offered by the Spring Platform itself and rapid application creation abilities of Spring Boot give developers a great microservice development experience. For example, with few annotations, you can create a Config Server, and with few more annotations, you can get the client libraries to configure your services.
- There is a rich selection of libraries covering the majority of runtime concerns. Since all libraries are written in Java, it offers multiple features, greater control, and fine tuning options.
- The different Spring Cloud libraries are well-integrated with one another. For example, a Feign client will also use Hystrix for Circuit Breaking, and Ribbon for load balancing requests. Everything is annotation driven, making it easy to develop for Java developers.
Weaknesses
- One of the major advantages of the Spring Cloud is also its drawback — it is limited to Java only. A strong motivation for the MSA is the ability to interchange technology stacks, libraries, and even languages, when required. That is not possible with Spring Cloud. If you want to consume Spring Cloud/Netflix OSS infrastructure services, such as configuration management, service discovery, or load balancing, the solution is not elegant. The Netflix Prana project implements the sidecar pattern to expose Java-based client libraries over HTTP to make it possible for applications written in non-JVM languages to exist in the NetflixOSS ecosystem, but it is not very elegant.
- There is too much responsibility for Java developers to care about and for Java applications to handle. Each microservice needs to run various clients for configuration retrieval, service discovery, and load balancing. It is easy to set those up, but that doesn't hide the buildtime and runtime dependencies to the environment. For example, developers can create a Config Server with @EnableConfigServer, but that is only the happy path. Every time developers want to run a single microservice, they need to have the Config Server up and running. For a controlled environment, developers have to think about making the Config Server highly available, and since it can be backed by Git or Svn, they need a shared file system for it. Similarly, for service discovery, developers need to start a Eureka server first. For a controlled environment, they need to cluster it with multiple instances on each AZ, etc. It feels like as a Java developers have to build and manage a non-trivial microservices platform in addition to implementing all the functional services.
- Spring Cloud alone has a shorter scope in the microservices journey, and developers will also need to consider automated deployments, scheduling, resource management, process isolation, self-healing, build pipelines, etc. for a complete microservices experience. For this point, I think it is not fair to compare Spring Cloud alone to Kubernetes, and a more fair comparison would be between Spring Cloud + Cloud Foundry (or Docker Swarm) and Kubernetes. But that also means that for a complete end-to-end microservices experience, Spring Cloud must be supplemented with an application platform like Kubernetes itself.
Kubernetes
Kubernetes is an open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. It is polyglot and provides primitives for provisioning, running, scaling and managing distributed systems.
Strengths
- Kubernetes is a polyglot and language agnostic container management platform that is capable of running both cloud-native and traditional containerized applications. The services it provides, such as configuration management, service discovery, load balancing, metrics collection, and log aggregation, are consumable by a variety of languages. This allows having one platform in the organization that can be used by multiple teams (including Java developers using Spring) and serve multiple purposes: application development, testing environments, build environments (to run source control system, build server, artifact repositories), etc.
- When compared to Spring Cloud, Kubernetes addresses a wider set of MSA concerns. In addition to providing runtime services, Kubernetes also lets you provision environments, set resource constraints, RBAC, manage application lifecycle, enable autoscaling and self-healing (behaving almost like an antifragile platform).
- Kubernetes technology is based on Google's 15 years of R&D and experience of managing containers. In addition, with close to 1000 committers, it is one of the most active Open Source communities on Github.
Weaknesses
- Kubernetes is polyglot and, as such, its services and primitives are generic and not optimized for different platforms such as Spring Cloud for JVM. For example, configurations are passed to applications as environment variables or a mounted file system. It doesn't have the fancy configuration updating capabilities offered by Spring Cloud Config.
- Kubernetes is not a developer-focused platform. It is intended to be used by DevOps-minded IT personnel. As such, Java developers need to learn some new concepts and be open to learning new ways of solving problems. Despite it being super easy to start a developer instance of Kubernetes using MiniKube, there is a significant operation overhead to install a highly available Kubernetes cluster manually.
- Kubernetes is still a relatively new platform (2 years old), and it is still actively developed and growing. Therefore there are many new features added with every release that may be difficult to keep up with. The good news is that this has been envisaged, and the API is extensible and backward compatible.
Best of Both Worlds
As you have seen, both platforms have strengths in certain areas, and things to improve upon in other areas. Spring Cloud is a quick to start with, developer-friendly platform, whereas Kubernetes is DevOps friendly, with a steeper learning curve, but covers a wider range of microservices concerns. Here is a summary of those points.
Strengths and weaknesses
Both frameworks address a different range of MSA concerns, and they do it in a fundamentally different way. The Spring Cloud approach is trying to solve every MSA challenge inside the JVM, whereas the Kubernetes approach is trying to make the problem disappear for the developers by solving it at platform level. Spring Cloud is very powerful inside the JVM, and Kubernetes is powerful in managing those JVMs. As such, it feels like a natural progression to combine them and benefit from best parts of both projects.
Spring Cloud backed by Kubernetes
With such a combination, Spring provides the application packaging, and Docker and Kubernetes provide the deployment and scheduling. Spring provides in-application bulkheading through Hystrix thread pools, and Kubernetes provides bulkheading through resource, process, and namespace isolation. Spring provides health endpoint for every microservice, and Kubernetes performs the health checks and traffic routing to healthy services. Spring externalizes and updates configurations, and Kubernetes distributes the configurations to every Microservice. And this list goes on and on.
My favorite microservices stack
What about my favorite microservices platform? I like them both. I like the developer experience offered by the Spring framework. It is all annotation driven, and there are libraries covering all kind of functional requirements. I also like Apache Camel (rather that Spring Integration) for anything to do with integration, connectors, messaging, routing, resilience and fault tolerance at the application level. Then for anything to do with clustering and managing multiple application instances, I prefer the magical Kubernetes powers. And whenever there is an overlap of functionality, such as for service discovery, load balancing, configuration management, I try to use the polyglot primitives offered by Kubernetes.
(This post was originally published on Red Hat Developers, the community to learn, code, and share faster. To read the original post, click here.)
Published at DZone with permission of Bilgin Ibryam, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.






Comments