Deploying Go Applications to AWS App Runner: A Step-By-Step Guide
In this tutorial, learn how to run a Go application to AWS App Runner using the Go platform runtime.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn this blog post, you will learn how to run a Go application to AWS App Runner using the Go platform runtime. You will start with an existing Go application on GitHub and deploy it to AWS App Runner. The application is based on the URL shortener application (with some changes) that persists data in DynamoDB.
Introduction
AWS App Runner is a robust and user-friendly service that simplifies the deployment process of web applications in the AWS Cloud. It offers developers an effortless and efficient way to deploy their source code or container image directly to a scalable and secure web application without requiring them to learn new technologies or choose the appropriate compute service.
One of the significant benefits of using AWS App Runner is that it connects directly to the code or image repository, enabling an automatic integration and delivery pipeline. This eliminates the need for developers to go through the tedious process of manually integrating their code with AWS resources.
For developers, AWS App Runner simplifies the process of deploying new versions of their code or image repository. They can easily push their code to the repository, and App Runner will automatically take care of the deployment process. On the other hand, for operations teams, App Runner allows for automatic deployments every time a new commit is pushed to the code repository or a new container image version is added to the image repository.
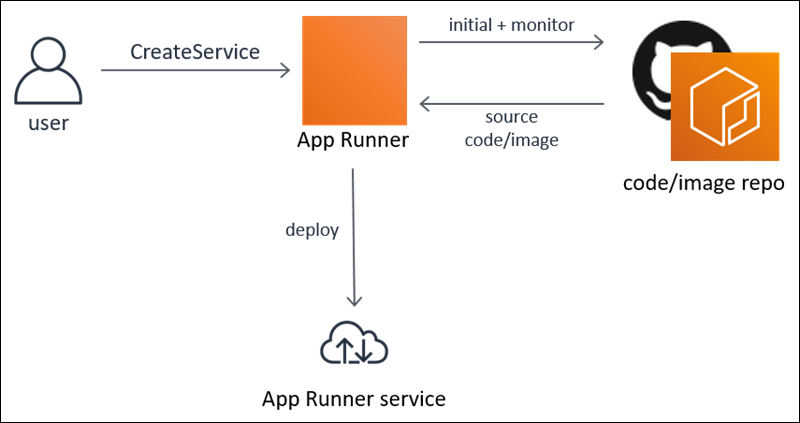
App Runner: Service Sources
With AWS App Runner, you can create and manage services based on two types of service sources:
- Source code (covered in this blog post)
- Source image
Source code is nothing but your application code that App Runner will build and deploy. All you need to do is point App Runner to a source code repository and choose a suitable runtime that corresponds to a programming platform version. App Runner provides platform-specific managed runtimes (for Python, Node.js, Java, Go, etc.).
The AWS App Runner Go platform runtime makes it easy to build and run containers with web applications based on a Go version. You don’t need to provide container configuration and build instructions such as a Dockerfile. When you use a Go runtime, App Runner starts with a managed Go runtime image which is based on the Amazon Linux Docker image and contains the runtime package for a version of Go and some tools. App Runner uses this managed runtime image as a base image and adds your application code to build a Docker image. It then deploys this image to run your web service in a container.
Let’s Get Started
Make sure you have an AWS account and install AWS CLI.
1. Create a GitHub Repo for the URL Shortener Application
Clone this GitHub repo and then upload it to a GitHub repository in your account (keep the same repo name i.e. apprunner-go-runtime-app):
git clone https://github.com/abhirockzz/apprunner-go-runtime-app
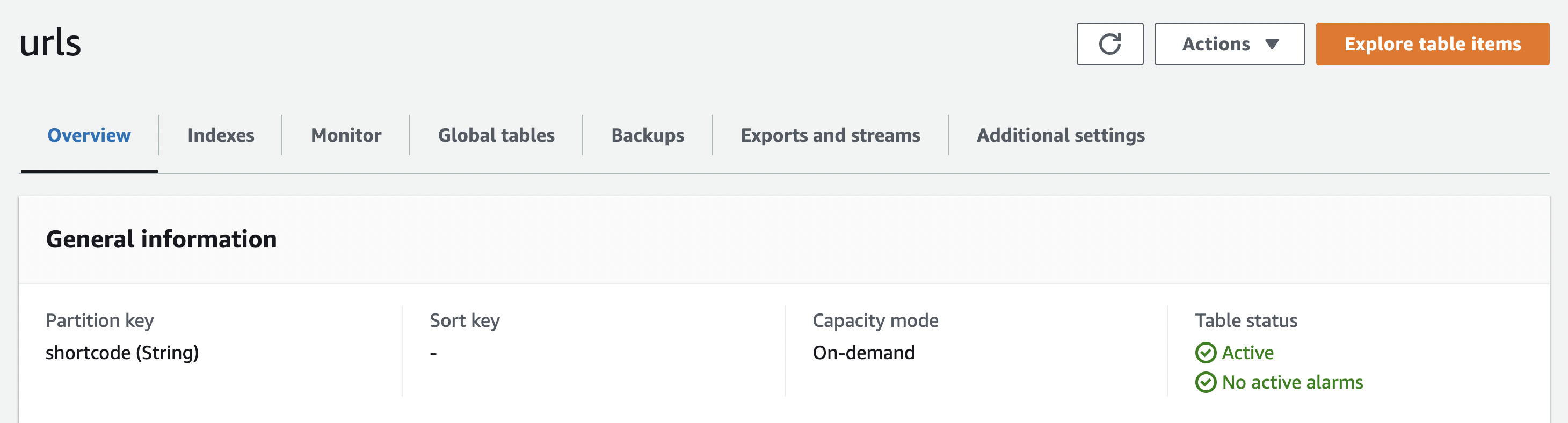
2. Create a DynamoDB Table To Store URL Information
Create a table named urls. Choose the following:
- Partition key named
shortcode(data typeString) On-Demandcapacity mode
3. Create an IAM Role With DynamoSB-Specific Permissions
export IAM_ROLE_NAME=apprunner-dynamodb-role
aws iam create-role --role-name $IAM_ROLE_NAME --assume-role-policy-document file://apprunner-trust-policy.json
Before creating the policy, update the dynamodb-access-policy.json file to reflect the DynamoDB table ARN name.
aws iam put-role-policy --role-name $IAM_ROLE_NAME --policy-name dynamodb-crud-policy --policy-document file://dynamodb-access-policy.json
Deploy the Application to AWS App Runner
If you have an existing AWS App Runner GitHub connection and want to use that, skip to the Repository selection step.
1. Create an AWS App Runner GitHub Connection
Open the App Runner console and choose Create service.

On the Source and deployment page, in the Source section, for Repository type, choose Source code repository. Under Connect to GitHub, choose Add new, and then, if prompted, provide your GitHub credentials.
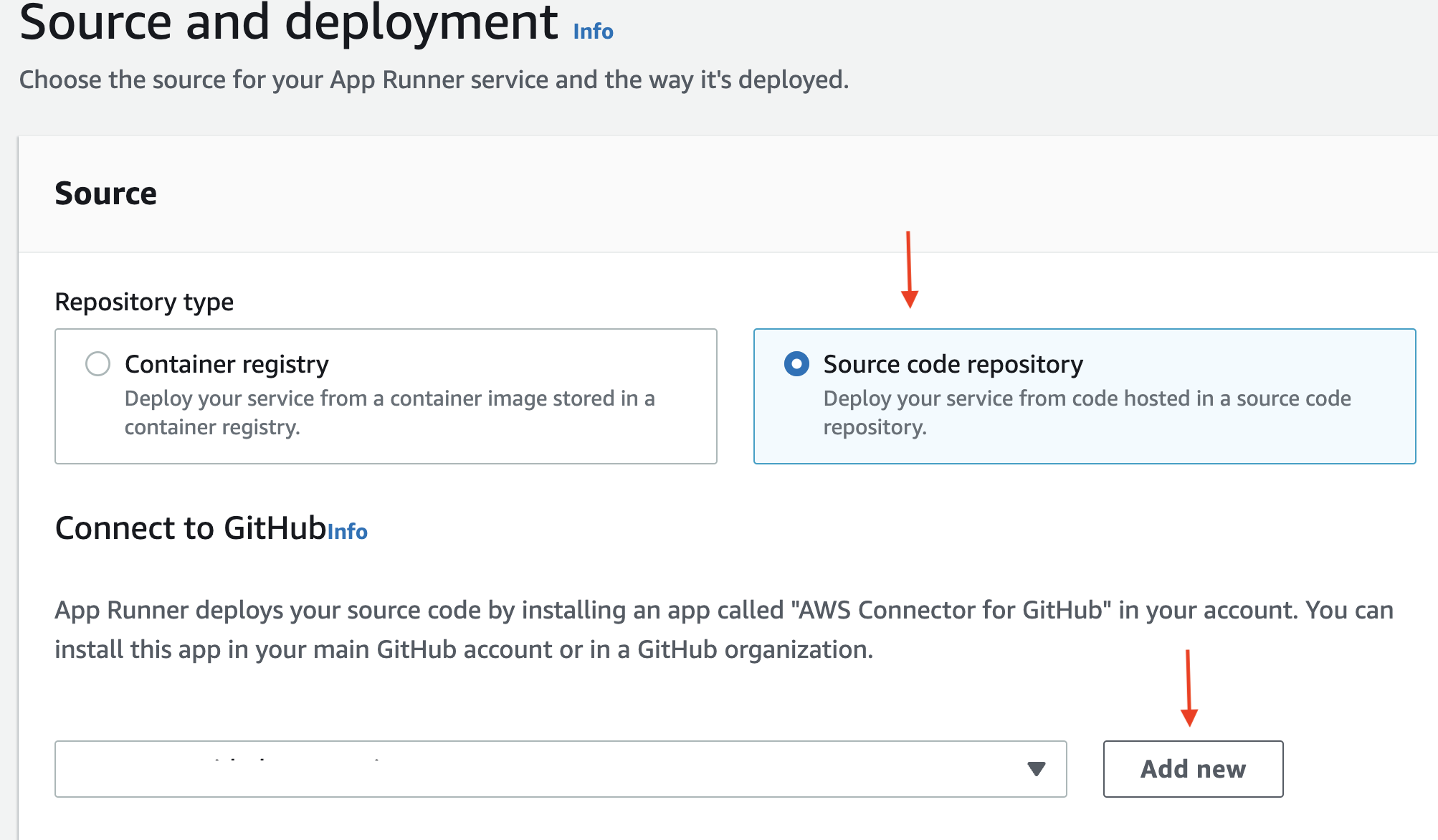
In the Install AWS Connector for GitHub dialog box, if prompted, choose your GitHub account name. If prompted to authorize the AWS Connector for GitHub, choose Authorize AWS Connections. Choose Install.
Your account name appears as the selected GitHub account/organization. You can now choose a repository in your account.
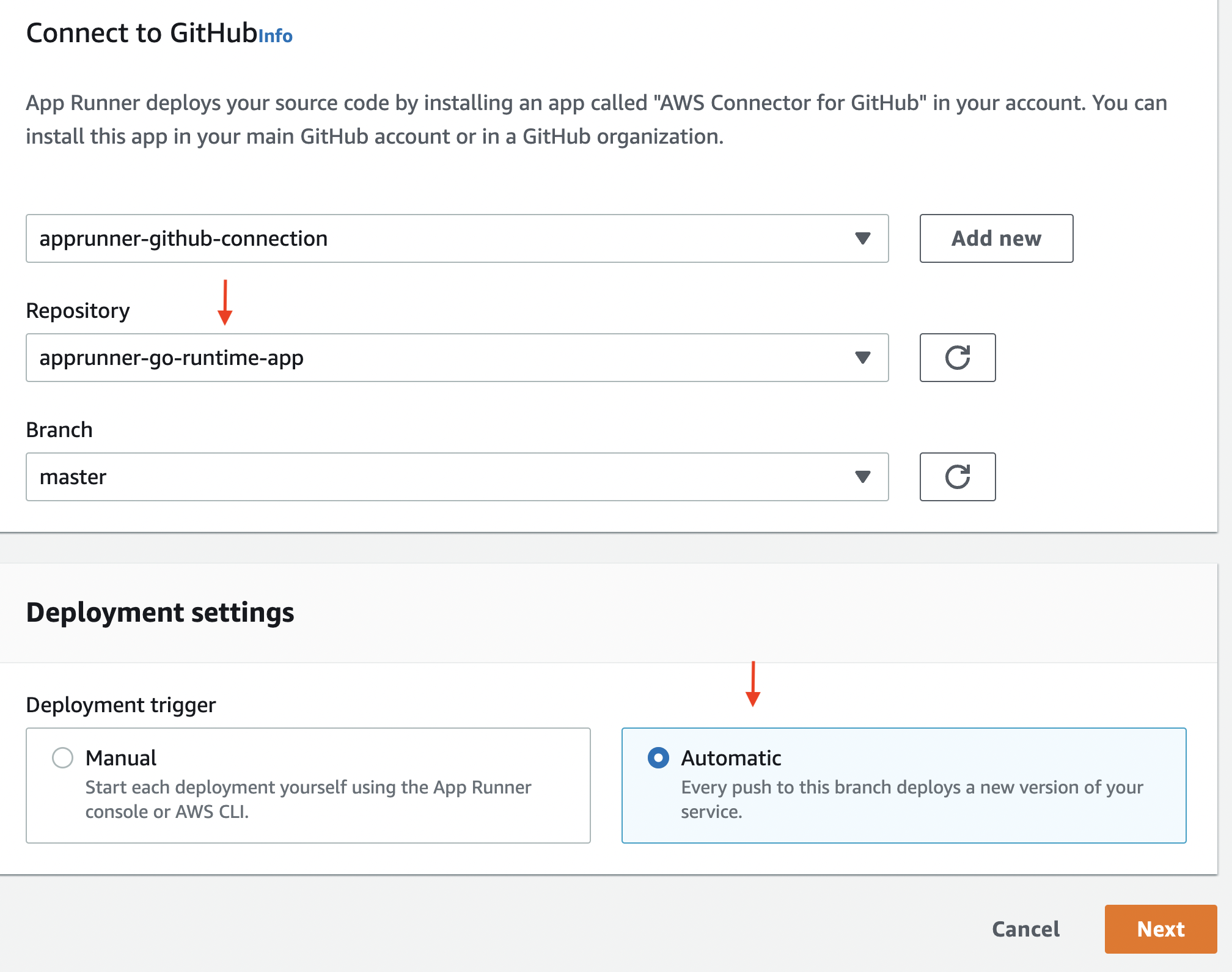
2. Repository Selection
For Repository, choose the repository you created: apprunner-go-runtime-app. For Branch, choose the default branch name of your repository (for example, main).
Configure your deployment: In the Deployment settings section, choose Automatic, and then choose Next.
3. Configure Application Build
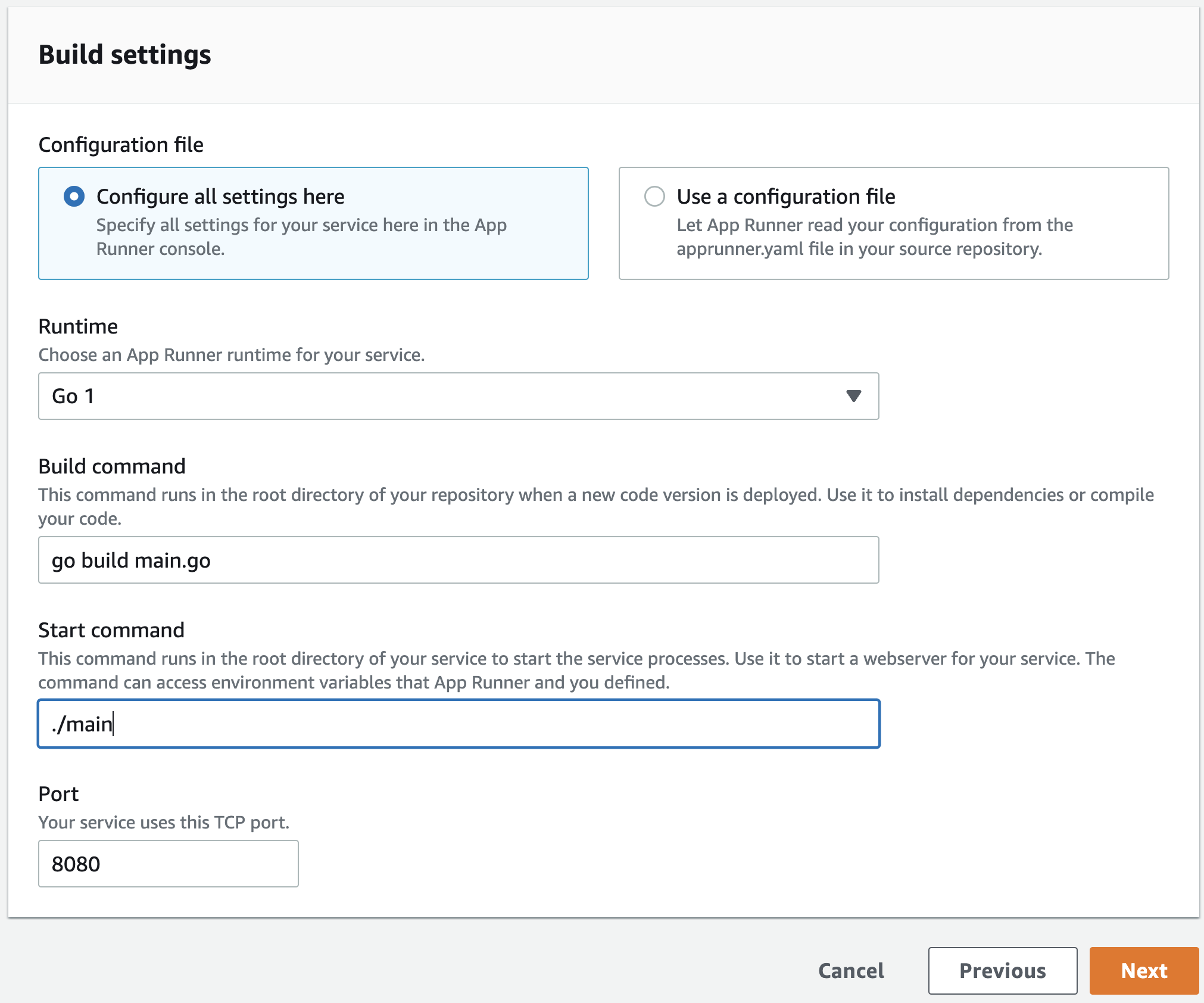
On the Configure build page, for the Configuration file, choose Configure all settings here.
Provide the following build settings:
- Runtime: Choose Go 1
- Build command: Enter go build main.go
- Start command: Enter ./main
- Port: Enter 8080
Choose Next.
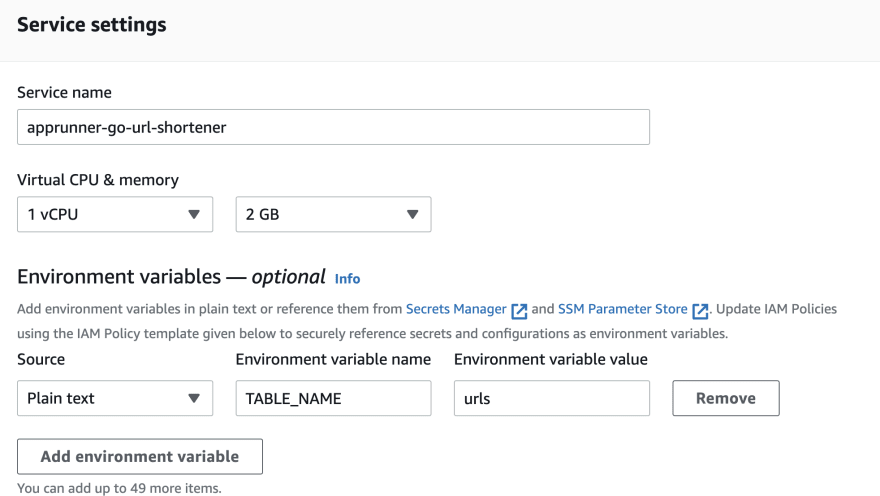
4. Configure Your Service
Under Environment variables, add an environment variable. For Key, enter TABLE_NAME, and for Value, enter the name of the DynamoDB table (urls) that you created before.
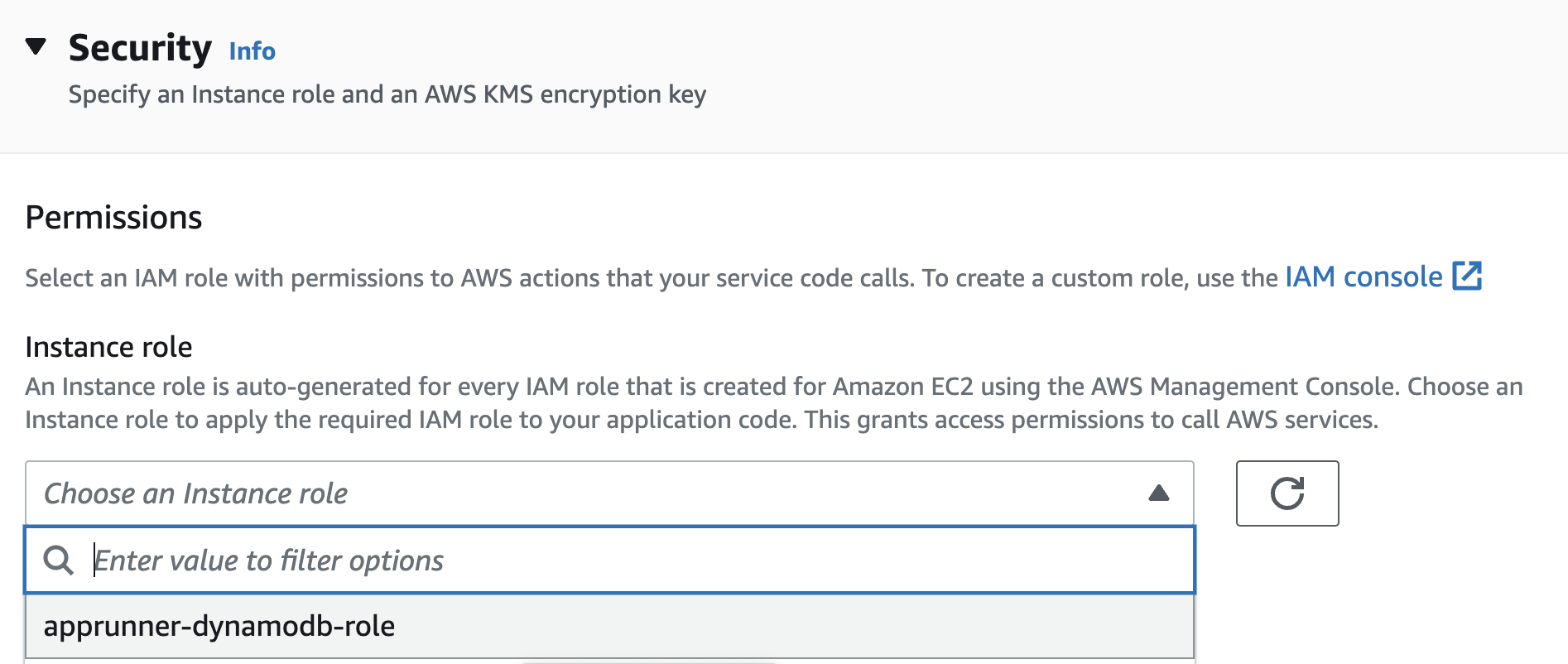
Under Security > Permissions, choose the IAM role that you had created earlier (apprunner-dynamodb-role).
Choose Next.
On the Review and create page, verify all the details you’ve entered, and then choose Create and deploy. If the service is successfully created, the console shows the service dashboard, with a Service overview of the application.
Verify URL Shortener Functionality
The application exposes two endpoints:
- To create a short link for a URL
- Access the original URL via the short link
First, export the App Runner service endpoint as an environment variable:
export APP_URL=<enter App Runner service URL>
# example
export APP_URL=https://jt6jjprtyi.us-east-1.awsapprunner.com
1. Invoke It With a URL That You Want to Access via a Short Link
curl -i -X POST -d 'https://abhirockzz.github.io/' $APP_URL
# output
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Thu, 21 Jul 2022 11:03:40 GMT
Content-Length: 25
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
{"ShortCode":"ae1e31a6"}
You should get a JSON response with a short code and see an item in the DynamoDB table as well.
You can continue to test the application with other URLs that you want to shorten!
2. Access the URL Associated With the Short Code
Enter the following in your browser http://<enter APP_URL>/<shortcode>.
For example, when you enter https://jt6jjprtyi.us-east-1.awsapprunner.com/ae1e31a6, you will be redirected to the original URL.
You can also use curl. Here is an example:
export APP_URL=https://jt6jjprtyi.us-east-1.awsapprunner.com
curl -i $APP_URL/ae1e31a6
# output
HTTP/1.1 302 Found
Location: https://abhirockzz.github.io/
Date: Thu, 21 Jul 2022 11:07:58 GMT
Content-Length: 0
Clean up
Once you complete this tutorial, don’t forget to delete the following resources:
- DynamoDB table
- App Runner service
Conclusion
In this blog post, you learned how to go from a Go application in your GitHub repository to a complete URL shortener service deployed to AWS App Runner!
Published at DZone with permission of Abhishek Gupta, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments