Data Governance: MDM and RDM (Part 3)
Master Data Management (MDM) is an essential discipline that helps organizations ensure the consistency, accuracy, and accountability of their shared data assets.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeWhat Is Data Governance?
Data governance is a framework that is developed through the collaboration of individuals with various roles and responsibilities. The purpose of this framework is to establish processes, policies, standards, and metrics that help organizations achieve their goals. These goals may include providing reliable data for business operations, developing accurate analytics to assess performance, complying with regulatory requirements, safeguarding data, ensuring data privacy, and supporting the data management life cycle.
The important areas of Data Governance are described below.
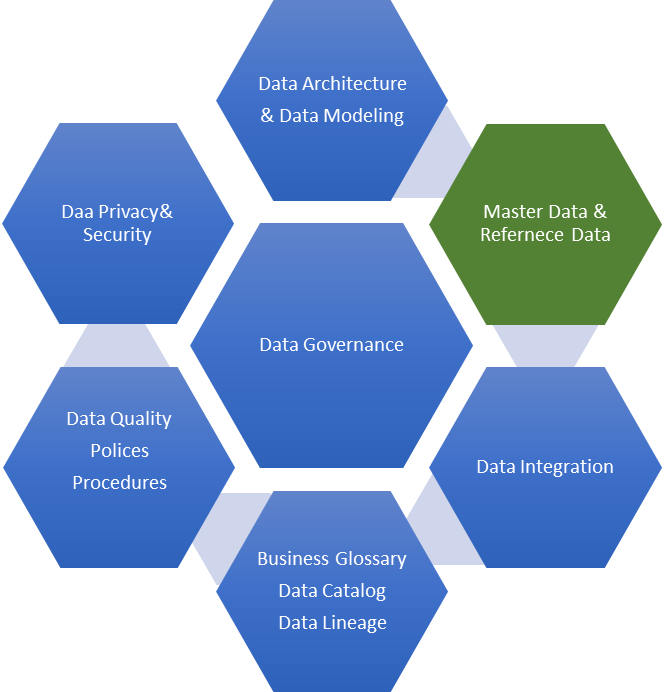
What Is Master Data Management (MDM)?
Master Data Management (MDM) is an essential discipline that helps organizations ensure the consistency, accuracy, and accountability of their shared data assets. MDM involves collaboration between the IT and business teams to maintain the semantic consistency, stewardship, and uniformity of the enterprise's official master data. The master data comprises a uniform and consistent set of attributes and identifiers that describe the critical entities of the organization, such as customers, suppliers, citizens, prospects, hierarchies, sites, products, and charts of accounts.
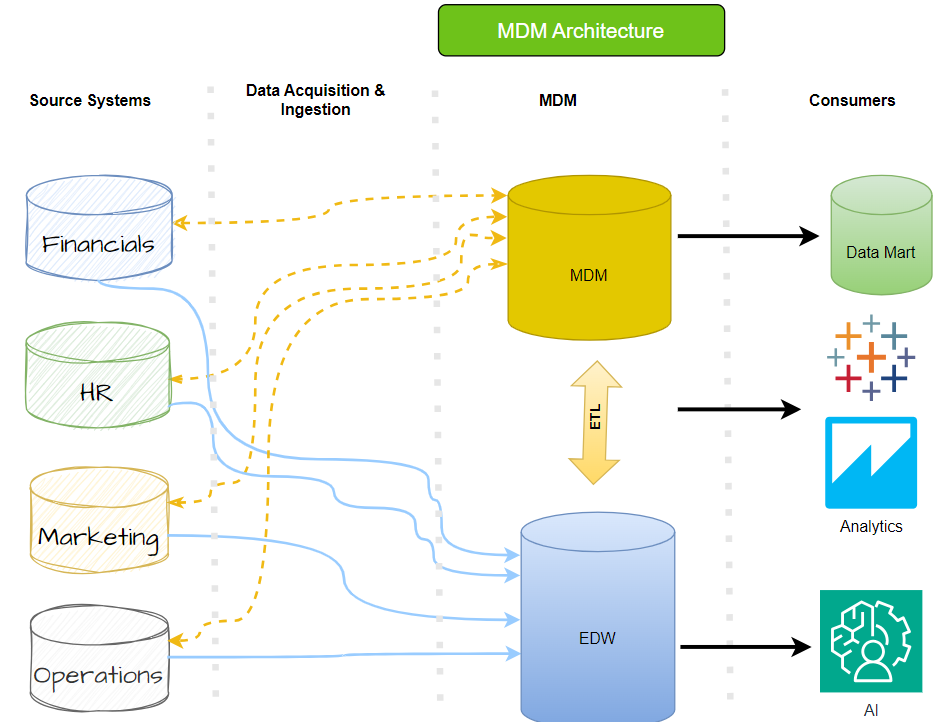
To achieve this, MDM uses technology to create a single master record for each entity, which is enriched, reconciled and de-duplicated to form a reliable source of data. By implementing MDM, organizations can ensure that their data is accurate, consistent, and reliable, which is critical for informed decision-making and successful business operations.
MDM Implementation Style Types
There are multiple implementation types of MDM, and the appropriate model can be chosen based on several parameters such as cost, performance, reliability, and availability.
There are four most prominent MDM data architecture models being used in the industry. They are:
- Registry Style
- Consolidation Style
- Coexistence Style
- Centralized Style
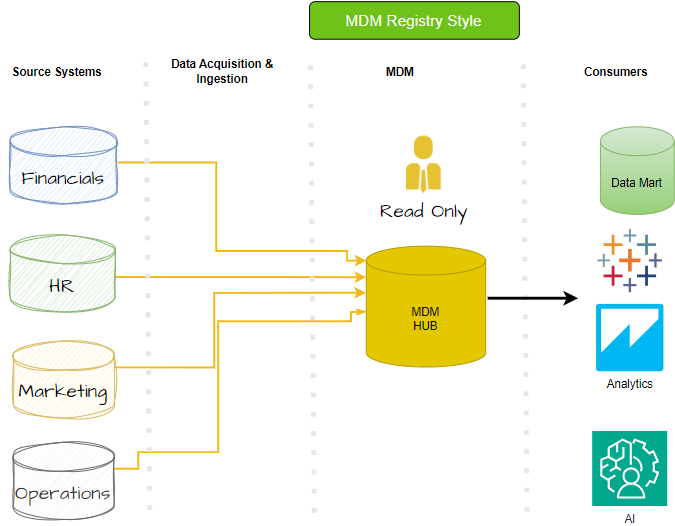
Registry MDM Implementation Style
The registry model is well-suited for rapidly ingesting data from multiple sources. If the business is in need of a low-cost and quick solution for developing a golden record, Registry systems can do this by applying algorithms to cleanse data before it is stored in the MDM platform. From the MDM the master data can be read (only), or sent to downstream data users and applications. Because data at the sources is not updated from the MDM registry, source data systems remain unchanged, providing a historical record of all unclean data.
Core MDM data attributes are indexed for a single read-only truth record. It does not master an extended set of data attributes authored in multiple federated MDM systems.
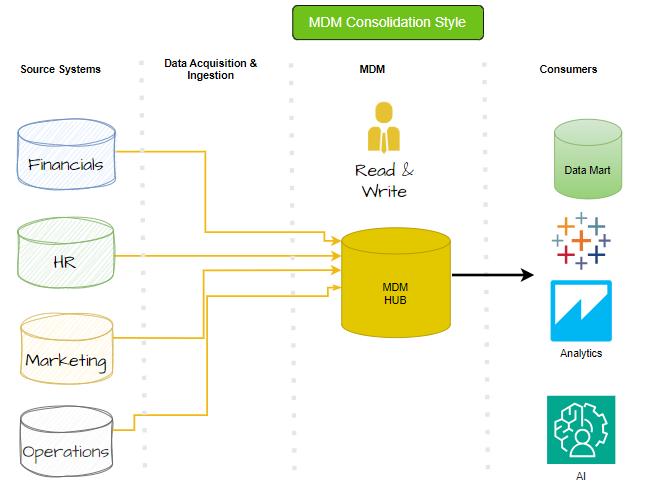
Consolidation MDM Implementation Style
The Consolidation MDM implementation style is an upgraded Registry style with an added layer of data stewardship. Consolidation models are suited for multiple sources and follow the same data pipeline procedures as the Registry model. Multiple data sources are consolidated into the MDM hub, where algorithms cleanse data, and questionable data is then inspected by human data stewards who can make appropriate corrections. In this way, data accuracy passes through a layer of human wisdom unavailable to computers, resulting in greater data accuracy. Greater data accuracy is helpful in supporting the high-quality analytics and reported features found in consolidated models.
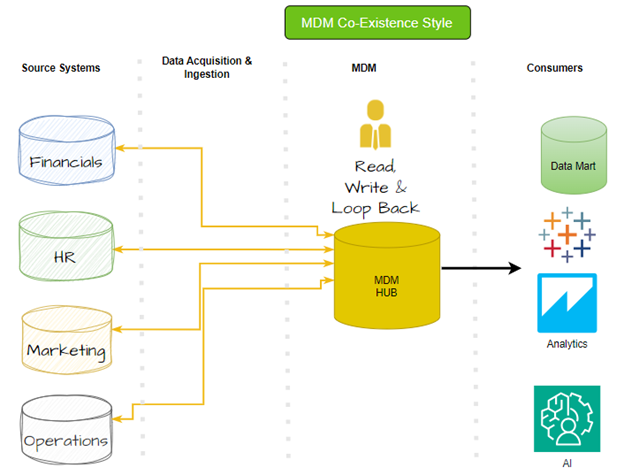
Coexistence MDM Implementation Style
Beginning with a Consolidated model, the Coexistence of MDM implementation styles builds loopback features into the MDM system that updates source systems with Master Data records. This results in a Master Data record in both the hub and the upstream data sources. This helps authors retain the most updated information from the sources. This configuration demands that sources have cleansing features to ensure data integrity.
![MDM coexistence style]() Centralized MDM Implementation Style
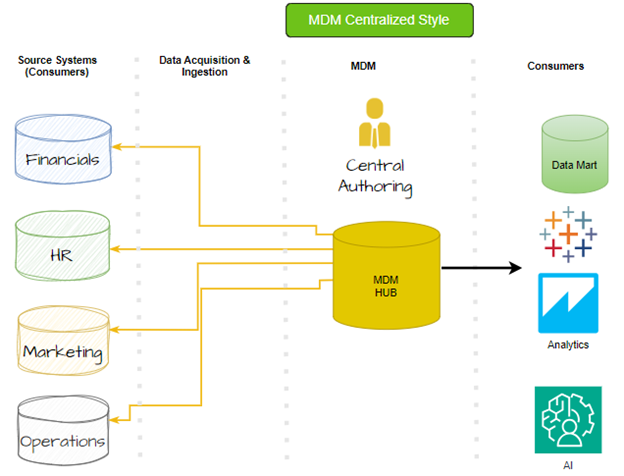
Centralized MDM Implementation Style
A Centralized MDM implementation style offers maximum control over security, visibility policies, and ownership of master data from the MDM hub, allowing no other system to adjust the master data record. Authors originate data at the hub; stewards review questionable records at the MDM hub. There are no sources, only data destinations that subscribe to the MDM for master data. Centralized systems are the most accurate at all times across all domains, with the price tag to prove it.
MDM Tools
Some of the MDM tools available in the market are:
- Ataccama
- Collibra
- Informatica
- Precise
- Oracle
Reference Data Management (RDM)
Reference data management (RDM) is a system that organizes, updates, and consolidates reference data and manages classifications and hierarchies across systems and business lines. RDM encompasses both internal and external data and focuses on standardizing values and definitions within and across systems.
This system is crucial for ensuring the honesty and reliability of business processes while also reducing errors and improving efficiency.
Conclusion
Here are the main points to take away from this article:
- When integrating data from different source systems, it's important to have a strong data governance framework in place.
- Master Data Management (MDM) is a vital discipline that helps organizations ensure their shared data assets are consistent, accurate, and accountable.
- MDM requires collaboration between business and IT teams to maintain semantic consistency, stewardship, and uniformity of the enterprise's official master data.
- There are four types of MDM styles, and we should choose the appropriate model based on different parameters.
- Reference data management is critical for ensuring the honesty and reliability of business processes while also reducing errors and improving efficiency.
References
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

 Centralized MDM Implementation Style
Centralized MDM Implementation Style
Comments