Counting Faster With Postgres
Explore how count and distinct queries work behind the scenes, how to make them run faster, and alternative approaches to the problem of speed.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free
Count queries are probably the most-used aggregate queries in a relational database. Counting is a fundamental operation required for many CRUD applications like sorting, pagination, and searching. But counting records can become terribly slow as your dataset grows. Fortunately, there are strategies for dealing with this problem. This article will show you a few approaches.
Data Setup
Since we are just exploring count queries, we do not need an extensive data setup. We can create a simple table with just one column. You can do that with the commands below:
CREATE TABLE sample_data (id int);
INSERT INTO sample_data SELECT generate_series(1, 200000);Simple Count Query
Let's understand the query plan of a simple count query.
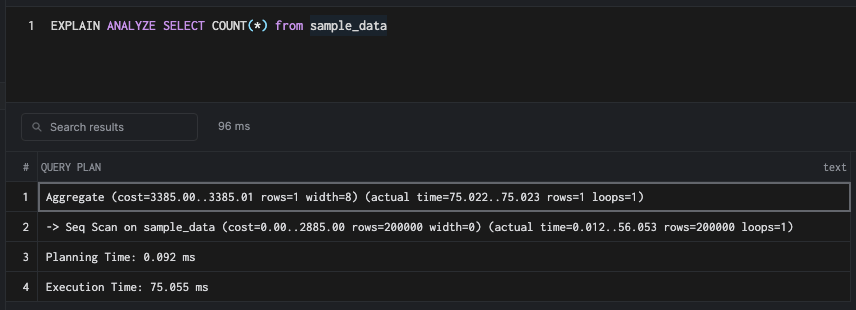
This runs a rudimentary Seq Scan on the table. If you are not familiar with reading query plans, then I would highly recommend reading the article linked here.
To understand about Scans in general, you might also find this article helpful.
Parallel Processing for Counts
PostgreSQL does not use parallel processing since the row count is too small, and using parallel workers might slow the counting process. So let's insert more data into our sample table and enable PostgreSQL to use more workers.
INSERT INTO sample_data SELECT generate_series(200000, 4000000);
SET max_parallel_workers_per_gather = 4;And then try to analyze the plan, as shown below:
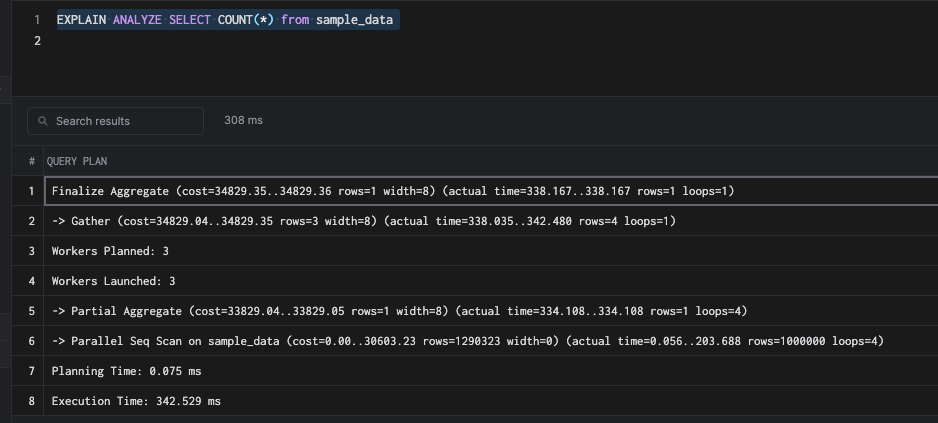
This uses three workers out of the four we have configured. Parallel queries are a no-brainer. They throw hardware at the problem to enable faster query execution. But in a transactional database, we cannot simply rely on parallel queries - as you can see in this example, it still takes 342 milliseconds.
Why Indexes Don't Help With Plain count
The first thing that any database user would do is add an index to speed up a query. Let's try that here.
CREATE INDEX id_btree ON sample_data USING BTREE(id)Unlike other queries, the index does not help here.
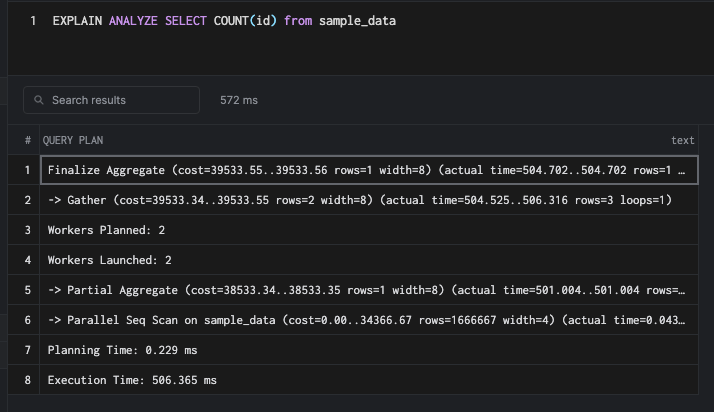
This is because the count has to touch all of the rows of the table. An index helps if there is a where clause, but scanning the index will be slow. We can understand that when we turn off Seq scan.
SET enable_seqscan = OFF; 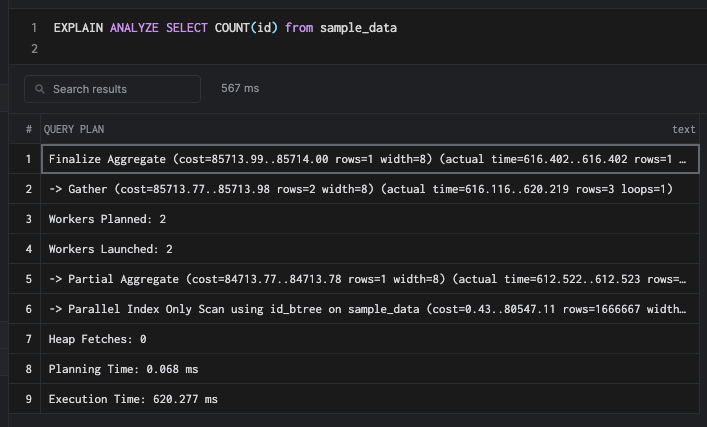
Counting nodes in a BTree data structure takes O(n), where n is the number of rows and also takes extra memory - O(h) where h is the height of the tree. There are also increased access costs by directly accessing the index, due to which a sequential scan over normal tuples/table data is preferable.
Counting With the Where Clause
Once there is a where clause involved, then it is very easy for the planner to use the index since it cuts down a lot of rows from the result. Let's consider a full index and a partial index.
Full Index
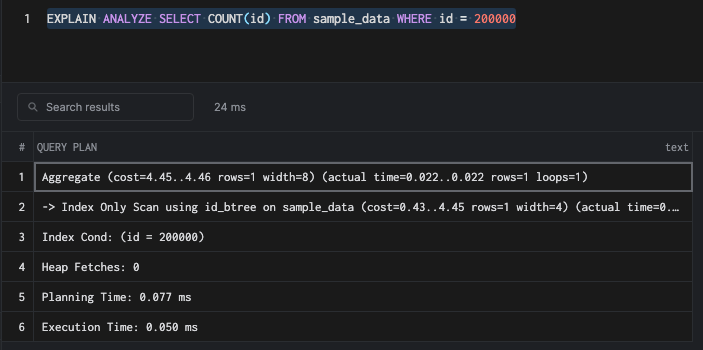
Since we already have a full index, a count query with a where clause on the id the column would be very fast.
SELECT COUNT(id) FROM sample_data WHERE id = 200000Partial Index
If we are going to count rows only with a specific where clause, then we can use a partial index.
CREATE INDEX id_btree ON sample_data USING BTREE(id) WHERE id = 200000;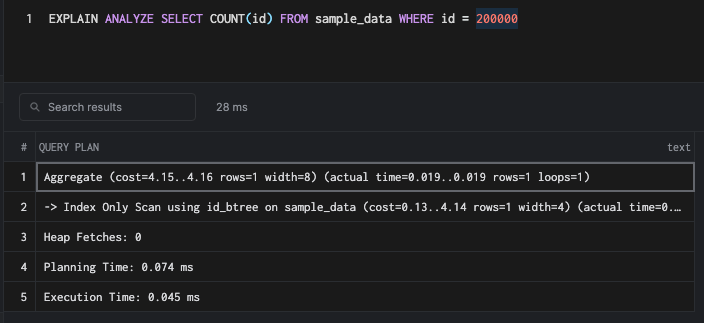
Partial indexes are faster, easier to cache because of their size, and easier to maintain.
Distinct vs. Duplicate Counts
By default, count query counts everything, including duplicates. Let's touch upon which is often used alongside count.
SELECT DISTINCT(id) FROM sample_data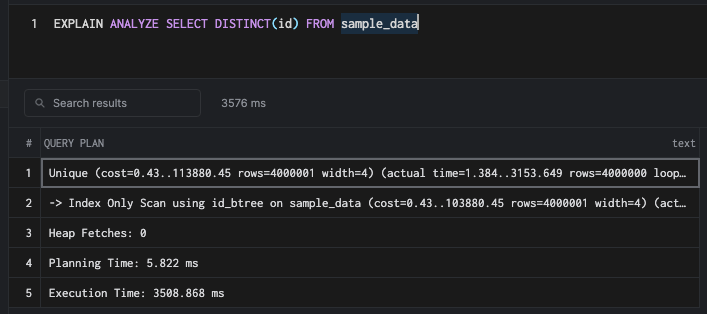
This command uses an index-only scan but still takes around 3.5 seconds. The speed depends on many factors, including cardinality, size of the table, and whether the index is cached. Now, let's try to count the number of unique rows in the table.
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT(id)) FROM sample_data 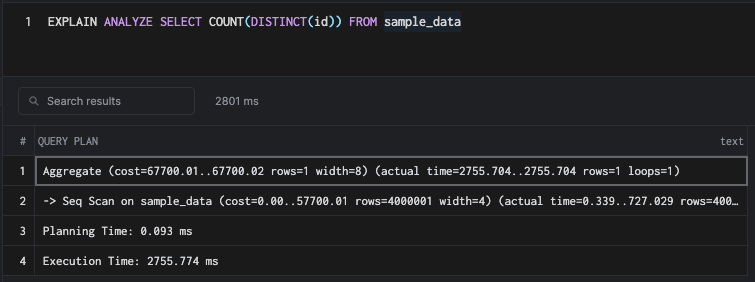
This command does not use the index and resorts to sequential scan. As a planner, you'd be correct in choosing a sequential scan since walking over an index completely is more costly, as we already saw above.
The rule of thumb in relational database systems is to never deal with distinct queries. Of course, we can never fully get away from, but with proper database modeling (moving duplicate rows to a different table and using a one-to-many relationship, storing unique counts separately, etc.), a query with a where clause will be faster.
Approximate Counting
In most real-world use cases, we would never want the exact row count of a table. We might want to count specific rows with a where clause (which can be solved with an index), but never a full row count. A typical OLTP workload does not add a million rows in a day. Maybe a few thousand rows split across different time windows. There are ways in PostgreSQL to get an approximate row count instead of an actual row count and still be ok with the business use case.
Getting Approx Counts With Statistics
The cost-based query planner in PostgreSQL uses the statistics information for planning queries. For example, we can utilize this information to give an approximate row count.
SELECT
reltuples::bigint AS estimate
FROM
pg_class
WHERE
oid = 'public.sample_data' ::regclass;This will return the row count as 4000001. We can also run a full count query to verify that this row count is accurate. This might not be accurate in production workloads depending on when the VACCUM ANALYZE runs. We see that in the next section.
Keeping the Statistics up to Date
Discussing the internals of the Vaccuum process is beyond the scope of this blog, but for most OLTP workloads, the default Auto Vacuum settings work just fine. If there is any huge data load on the table, we can do a manual Vacuum Analyze <table_name> if required. The Vacuum process does what it is named after. It cleans up and updates the statistics table with the latest and most accurate information.
Re-thinking the Problem and External Solutions
Keeping accurate table counts need not necessarily be a database problem alone. Various other ways can be used to keep a count. Let's go through a few simple ideas.
Using a Cache at the Application Level
If the application is a simple two-tier app with only UI and some form of the backend, then we can use a caching layer such as EH Cache or Cache tools to maintain the count of rows as and when we insert it. These caches can be backed by persistence so that the data is not lost. Caches are lightweight and pretty fast. Alternatively, one can store the count in the database itself. The key feature of this approach is that the trigger to update the count is the application's responsibility.
Use a Variable With the Help of Triggers/Hooks
If you are not familiar with hooks or triggers, these articles will give you a good starting point for understanding them:
Hooks: The secret feature powering the Postgres ecosystem
A Complete Guide to SQL Triggers in PostgreSQL - DB Tracking Example
Using a trigger or a hook, we can maintain a variable in either a Postgres table or outside the system. Choosing this strategy comes down to how your database is set up and is generally suited for applications with many downstream systems for consumption. The trigger or hook is, in general, more reliable and suited for more complex applications.
A Cache Like Redis
In a microservice architecture where many services talk to the database, storing all row count-related information for many tables will be a bottleneck since there can be hundreds of microservices and many databases. It can also result in synchronization-related issues as well.
Architecting Database Systems for the Microservices World
Redis is a system that suits such kind of N-Tier architecture. It is:
- Fast.
- Thread-safe
- Scalable (using sharding)
- Persistent (can be enabled)
All individual services can call Redis based on the Saga pattern or API Composition pattern to update the values.
It is widely used as a cache in the microservices world, but we must keep in mind that bringing one more external system into the picture leads to an increased learning curve, maintenance, and troubleshooting. If you do not have a complex N-Tier system, you are better off using more straightforward solutions.
Conclusion
We saw in detail how count & distinct queries operate underneath the surface and how they can be made faster. To summarize:
- If you need a reasonably accurate count, then go for approximate counting.
- A sequential scan is very slow and puts strain on the database.
- Parallel scans can be used to speed up Sequential Scans.
- Count for specific use cases can be made faster with full indexes or partial Indexes.
- External solutions can be used if the use cases for maintaining counts are very demanding.
Published at DZone with permission of Zach Naimon. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments