Cloud Governance: A Holistic View
Cloud Governance is a set of rules, processes, and policies involved in the planning, architecture, etc., that guide the management and use of cloud computing services.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIntroduction
For any organization, the success of Cloud transformation measured through the factors like,
- Productivity, savings, and efficiency,
- Delivering Business value through Velocity, speed from ideation to rollout, and,
- Experience, happiness index of the team.
“Cloud Governance consists of leadership, organizational structure, direction, processes that ensure Information Technology (IT) sustains, extends the enterprise's mission, strategies and objectives in a planned manner.”
It establishes the governance covering policies, guidance, processes, and decision-rights for a given area of responsibility.
In a nutshell, Cloud governance is about processes, people, and technologies, and tools related to infrastructure, security, and operations. It will ensure that the application workloads are optimized for cost, security, adhering to regulatory and compliance, technology standardization, acceleration in deployment, and resilience while delivering business value through agility. Cloud Governance is a set of rules, processes, and policies involved in the planning, architecture, acquisition, deployment, and operations that guide the management and use of cloud computing services.
Lack of Cloud governance would result in wastage of resources, leading to increased costs, security challenges such as threats, data breaches, and non-standardized technology/product, inconsistent architecture may lead to monolithic implementations ('built-in silos'). It also results in poor cloud integration, cloud vendor lock-in, poor cloud interoperability, and portability.
The Cloud Governance helps the organization in achieving significant cost savings and the following benefits:
- Brings clarity in roles and responsibilities through management oversight.
- Facilitates straightforward and quick decision-making on contentious issues by bringing in transparency and accountability.
- Preserves architectural coherence by weaving in a compliance culture.
- Keeps architecture relevant and valuable in a pragmatic manner.
- Elevates the role of and accentuates visibility accorded to architecture within the enterprise.
- Expedites adoption of architecture thinking.
- Ensures that architecture efforts are expended in suitable activities.
- Sets focus on performance improvement leading to the attainment of best practices.
Cloud Governance Context
Conceptually, Cloud governance is an approach covering People, Process, and Technology. The following diagram represents the critical components involved in the Cloud Governance Framework. It covers decision-making processes, policies involved in the planning, reference architecture for enterprise teams to follow, deployment, and management of a Cloud adoption capability.
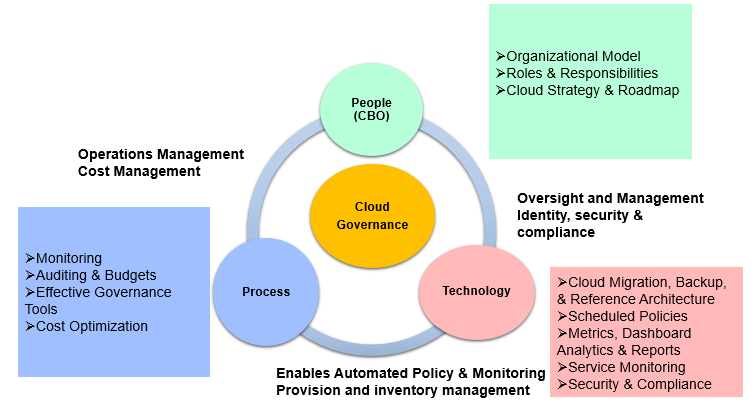
Fig 1: Cloud Governance Context.
Cloud Business Office for Effective Cloud Governance
The purpose of Cloud Business Office is to ensure:
- Increased operational effectiveness, the fast pace, and constant disruptions in the market push businesses to improve operational efficiency.
- CBO will take on a more management and directive role as the central bridge between the business and Service Provider (SP) delivery and make appropriate Cloud decisions.
- Appropriate coverage for critical decisions, investments, and risks while achieving the benefits of Clouds.
- Simplification of Organization structure for cost efficiency and better business adoption.
- Integrate with existing Enterprise IT Governance processes, policies, architecture boards, and tools.
The guiding principles for establishing a successful Cloud Business Office are:
- Discipline: All involved parties will commit to adhere to procedures, processes, and authority structures established. Ensure stakeholder engagement and commitment to navigate potential challenges and effectively drive the change.
- Transparency: All actions implemented, and their decision support will be available for inspection by the authorized organization and provider parties.
- Independence: Establish all processes, decision-making, and mechanisms to minimize or avoid potential conflicts of interest.
- Capability: Rapidly build capability enabling individuals to be effective in new roles, applying innovative learning techniques to minimize the impact on the organization's business model.
- Accountability: Identifiable groups within the organization — e.g., governance boards who take actions or make decisions are authorized and accountable for their actions. Also, target sustainable high performance, hold individuals to account, provide instant feedback and apply corrective action.
- Responsibility: Each contracted party is required to act responsibly to the organization and its stakeholders. Proactively engage middle-level management to generate ownership and advocacy, creating a 'pull' for the new ways of working.
- Fairness: All decisions taken, processes used, and their implementation is not allowed to create an unfair advantage to any one particular party.
Cloud Governance Framework
A sound governance framework to support implementation and management of the enterprise architecture is necessary to ensure that organization achieves its EA objectives.
The Cloud Governance Framework comprises of the following components required in maintaining enterprise architecture:
- Cloud Business Office
- Policies
- Governance Processes
- Standards and Guidelines
- Cloud Metrics
- Cloud Tools
The following diagram shows the constituents of these foundational elements.
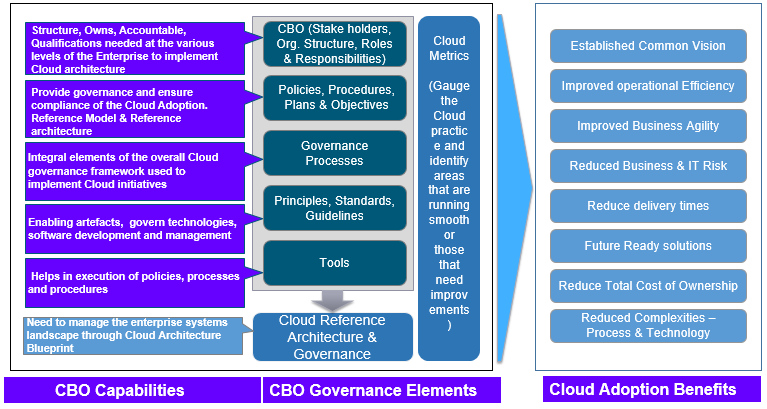
Fig 2: Cloud Governance Framework.
While establishing Cloud governance, it is crucial to ensure that all these elements are addressed adequately.
Cloud Business Office
Cloud Business Office (CBO) helps in establishing consistency, robustness, and oversight across the enterprise while maintaining agility for innovation and scalability. CBO will also critical to governing and overseeing cloud operations. Key responsibilities of the CBO are:
- Define and publish a set of reusable assets, standards, and metrics.
- Promote the adoption of cloud services.
- Enable self-reliance of lines of businesses in applying the suggested cloud best practices.
- Promote collaboration across multiple areas of the business including cloud governance, compliance, data privacy, and architecture.
- Provide a set of guiding principles that enable the environment to meet regulatory and compliance requirements.
- Clarity of ownership and 'rules of engagement' of old and new ways of working.
The significant stakeholders who form part of the Cloud Business Office are the Cloud Steering committee, the IT Executive Team, Cloud Operations Team, and the Cloud Transformation Working group.
The Cloud steering committee is one of the most efficient ways to formalize Cloud Governance across the enterprise. The committee consists of enterprise business and IT leadership. It approves cloud policies and provides an overall direction for cloud adoption. Roles and responsibilities of the Steering committee covers a broad range of activities, including, but not limited to:
- Providing leadership streamlines communication enables the leadership to speak to a single voice.
- Envisioning, leading, and guiding the development of overall cloud adoption in compliance with IT transformation.
- Understanding of business areas, technologies mapped to the capability models.
- Establishing and maintaining the link between the implementation of the Cloud architecture, the architectural strategy and objectives embodied in the enterprise architecture, and the strategic objectives of the business.
- Providing a mechanism for the formal acceptance and approval of architecture through consensus and authorized publication.
- Providing a fundamental control mechanism for ensuring effective cloud adoption.
Business/IT Executive Team is the Cross-functional IT construct to ensure IT governance and oversight end-to-end. This team gathers inputs for cloud requirements and defines cloud services, establishes pricing, accounting, and chargeback models. It assists cloud services-related projects in identifying and implementing cloud management best practices. Develops and implements cloud service improvement plans, including developing and tracking milestones.
Cloud Operations Team manages day-to-day operations, management, resource management, and provisioning.
Establish a Cloud Transformation Working Group to address addressing specific objectives or improvements. This group is responsible for assessing conformance to established governance and management of processes and procedures. They also establish the new technologies, perform the POC activities, and establish the enterprise's cloud adoption process.
Cloud Governance Policies
Cloud Governance policies are reviewed periodically by the steering committee, managers, and IT experts. The Cloud Governance policies include:
- Standards for the design of infrastructure.
- Monitoring of infrastructure and application.
- Security Policy.
- Programming standards.
The most important Cloud Governance Policies are:
- Strategic guidance (formal strategy and roadmap).
- Enterprise Architecture and Technology policies.
- Acquisition, Contracts and Legal, Vendor Management.
- Security and Privacy, Compliance.
- Cloud Operational Policies: Access, Consumption, Bursting, Management, Monitoring.
Cloud Governance Processes
The process is a sequence of operations or events, possibly taking up time, space, expertise, or other resources, which produces a specific outcome. Cloud Governance processes are integral elements of the overall EA governance framework used to implement technology solutions.
Governance processes deal with the stakeholder governance objectives like value delivery, risk optimization, and resource optimization. It includes practices and activities in evaluating strategic options, providing direction to cloud service initiatives, and monitoring the outcomes. The various governance processes are:
- Cloud Strategy development process.
- Cloud Architecture Review, vetting processes.
- Cloud adoption funding and budgeting processes.
- Deployment and Onboarding processes.
- Access, Resource Management, Provisioning, Operational processes.
- SLA monitoring, Cloud Management, Operations and Support, Escalation processes.
- Cloud operations processes, capacity management, bursting processes, oversight, and escalation processes.
Standards and Guidelines
Develop a set of principles, standards, and guidelines by which the organization can align its functions and processes for optimized effectiveness.
Cloud Metrics
Metrics estimate Cloud adoption's progress during the early stages of Cloud migration/implementation across the enterprise. It also helps recognize the efficiency and effectiveness of Cloud Governance to ensure the required business value delivered.
Measuring Cloud metrics is necessary to:
- Determine how effectively and efficiently the process or service satisfies the Customer while achieving operational efficiency and cost optimizations.
- Level of adoption.
- Alignment to business vision and priorities.
- Identify improvement opportunities.
- Make decisions based on facts and data to mitigate risks.
Measurement should:
- Translate Organization expectations into goals.
- Evaluate the quality of processes.
- Track improvements.
- Support enterprise strategies.
For Cloud Governance to be successful, it needs to be monitor and measure periodically to a set of defined Metrics. Metrics' status across the organization can be captured, presented, and communicated effectively using Cloud adoption scorecards or dashboards.
Cloud Governance Tools
Cloud Governance tools help in standardizing the execution of policies, processes, and procedures. In addition, the tool enforces the desired policies and procedures.
It helps the stakeholders analyze and optimize business strategies, organizational structures, business processes/tasks and activities, information flows, applications, and technology infrastructure.
The various Cloud Governance tools are:
- Cloud Portal and Self-Service Access.
- Cloud Service Catalog.
- Cloud Billing and Accounting modules.
- Cloud Lifecycle Management Tooling.
- Cloud Services Portfolio and Contracts Management Tools.
- Cloud Management and Monitoring Tools.
- Application Design and Development for Cloud.
- QA and Testing for Clouds and Cloud-centric Applications.
Benefits of Cloud Governance
An overall framework for Cloud governance and cost optimization help enterprises to reap the following benefits:
- Reduce total cost of ownership.
- AI/ML models help to fine-tune cost recommendations to suit individual cloud services and reduce TCO.
- Improve overall operations efficiency.
- Ensures security and scalability during the application of cloud governance policies to suit the needs of enterprises.
- Provides future-ready holistic solutions in reduced delivery time.
- Helps publish enterprise-approved cloud services using an in-built service catalog that offers a self-service feature that allows companies to use public resources with the pay-as-you-go pricing model.
Summary
In summary, Cloud Business Office would help in cost optimizations, managing security and risk, adherence to regulatory compliance, and accelerate decision-making and delivery. Cloud Governance ensures that cloud adoption adequately managed and produces artifacts and plans that are genuinely representative of organizational goals and needs. It ensures the Investment decisions are in alignment with the EA from initiation to implementation.
Cloud governance's best practices vary for each business as per their objectives and level of the cloud journey. In addition, today there are many Cloud Governance solutions providers available in the online marketplace. One needs to analyze the business assets and performance and then build accordingly.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank Kiran M.R, Raju Alluri of Digital Architecture Practice of Wipro Technologies for giving the required time and support in many ways in bringing up the article as part of architecture Practice efforts.
Authors
Dr. Gopala Krishna Behara is a Lead Enterprise Architect in the Wipro Digital Architecture Practice division of Wipro. He has a total of 24 years of IT experience.
Raju Myadam is a Chief Enterprise Architect in Wipro Digital, a division of Wipro. He has a total of 24 years of IT experience.
Disclaimer
The views expressed in this article/presentation are that of the authors and Wipro does not subscribe to the substance, veracity, or truthfulness of the said opinion.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments