BankNext Case Study: ServiceMesh With Docker-K8-Istio-Sidecar
My scratch notes and experience on using a Docker, K8, and Istio combination.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeGetting started with Docker and Kubernetes can be daunting. At times, seemingly straightforward steps in the instruction list don't seem to work as expected.
Reasons could be elusive. It could be your machine, your specific OS, your minikube version, the color of your T-shirt (kidding...).
Now imagine adding the mysterious ServiceMesh/Istio to the mix.
After going through this trepidation, I jotted down the detailed steps which could potentially save someone this pain.
This end-to-end ServiceMesh platform can be found on my GitHub.
Goal
- Add Istio ServiceMesh support to a set of microservices.
- Detail the steps required to make Istio work with Docker-minikube.
- Access this application over the external browser.
- Experience the immense flexibility this ServiceMesh adds to our architecture.
Business Scenario
- BankNext's rapid digital transformation is supported by a huge volume of microservices that interact with each other.
- Know-Your-Customer is one such critical mSvc that interacts with Credit-Check-Basic-Svc to evaluate the eligibility of new applicants.
- A newer and more sophisticated Credit-Check-Advanced-Svc is developed in line with the business demand for a more rigorous eligibility evaluation.
- Now the existing Know-Your-Customer mSvc needs to integrate with this new credit check svc to accomplish the highest level of accuracy.
Problem With Current Architecture
- As always, business wants this integration to happen fast because of the anticipated demand uptick in the upcoming fiscal quarter.
- Since the newer credit check svc is unexplored yet in production, a canary deployment is desired so that the migration can happen in a controlled manner.
- The engineering team analyzes and realizes — Houston, we have a problem!
- This adaptation requires intrusive changes not only in application but also may involve gateway level routing changes.
- This implies that time-consuming QA, regression, and production deployment cycles will be needed.
- This implies that there is a strong possibility of application downtime, which will hurt the Tier 1 accreditation of this service.
- Inevitably, this type of exercise demands deliberate multi-team coordination and much more time.
- Moreover, BankNext has many such integrations planned in the roadmap, and all these will face the same predicament as KYC.
- Business — Not happy!
Solution With New ServiceMesh Architecture Approach

KYC ServiceMesh Architecture /w Istio
- kyc-aggregator-mgt today invokes the legacy kyc-credit-check-basic directly.
- kyc-aggregator-mgt needs flexibility via an external configuration approach to switch invocations between the advanced and basic versions of credit checks.
- In the future, if a subsequent newer version of the credit check becomes available, then this approach should work for that too.
- The engineering team decides to incorporate the Istio ServiceMesh to meet all of the above design challenges.
- Istio has the capability to deploy itself as a sidecar with our mSvcs.
- Istio has the capability to intercept and redirect any traffic coming to our mSvc.
- Istio accomplishes this via the configurations specified in the Gateway, VirtualService, and DestinationRules ymls.
- Istio also has the capability to distribute the traffic load between services based off the weight specifications in the configuration.
Downloads and Installations
- Docker
(Kinematic does not work anymore)
Docker version 20.10.7, build f0df350 - Minikube
minikube version: v1.21.0
commit: 76d74191d82c47883dc7e1319ef7cebd3e00ee11 - Istio
client version: 1.8.0
control plane version: 1.8.0
data plane version: 1.8.0 (5 proxies) - Oracle VirtualBox
(20GB download- takes a long time)
VirtualBox-6.1.22–144080-Win - My Machine Specs
- Device name DESKTOP-D091LLJ
- Processor Intel(R) Core(TM) i7–3632QM CPU @ 2.20GHz 2.20 GHz
- Installed RAM 8.00 GB (7.88 GB usable)
- Device ID F80CBB2E-4E2F-464A-B594-A428352C8B8E
- Product ID 00330–80000–00000-AA124
- System type 64-bit operating system, x64-based processor
- Pen and touch: No pen or touch input is available for this display
- Edition Windows 10 Pro
- Version 20H2
- Installed on 5/25/2021
- OS build 19042.1348
- Experience Windows Feature Experience Pack 120.2212.3920.0
- Set your System PATH (for your reference — my PATH settings)
JAVA_HOME = C:\Vijay\Java\jdk-11.0.6
M2 = %M2_HOME%\bin
M2_HOME =C:\Vijay\Java\apache-maven-3.6.3
C:\Vijay\Java\apache-maven-3.6.3\bin
%JAVA_HOME%\bin
C:\Program Files\Docker\Docker\resources\bin
C:\ProgramData\DockerDesktop\version-bin
C:\Vijay\Java\Kubernetes\Minikube_2021
C:\Vijay\Java\Istio\istio-1.10.2\bin
C:\Vijay\Java\Istio\istio-1.10.2\bin\isoctl.exe
C:\Vijay\Java\Kubernetes\Minikube\kubectl.exe
C:\Vijay\Java\Kubernetes\Minikube\minikube.exeVirtualization Enable (very imp setting)
To enable Virtualization in Windows 10
- Navigate to
"Apps and Features" Programs and Features > Turn Windows Features on or off > Control Panel\Programs\Programs and Features > Turn Windows Features on or off. - Uncheck "Hyper-V or Windows Hypervisor platform" > OK.
- Restart Windows.
- When booting enter BIOS (usually "F2" press continuously)> Advanced > Virtualization > Enabled [update or verify that this is enabled. This may show up as other names like Vtx AMD.]
- Navigate to the saved location and launch the \Oracle\VirtualBox\VirtualBox.exe.
Docker Launch
Launch Docker Desktop and ensure that it has fully started:
C:\Program Files\Docker\Docker\Docker Desktop.exe
Console for Running Commands
Either DOS or GIT Bash in Administrator mode.
I prefer using GIT Bash on Windows because it helps run the Linux-type commands hassle-free.
Detailed Implementation Steps
1. Clear out any previous inconsistent references (cautionary step to ensure removal of any previous run remnants):$ minikube delete ! "minikube" profile does not exist, trying anyways. * Removed all traces of the "minikube" cluster.$ minikube stop E1112 13:02:54.085434 10628 daemonize_windows.go:38] error terminating scheduled stop for profile minikube: Error loading existing host. Please try running [minikube delete], then run [minikube start] again.: filestore "minikube": Docker machine "minikube" does not exist. Use "docker-machine ls" to list machines. Use "docker-machine create" to add a new one. * Profile "minikube" not found. Run "minikube profile list" to view all profiles. To start a cluster, run: "minikube start"
$ minikube start --driver=docker * minikube v1.21.0 on Microsoft Windows 10 Pro 10.0.19042 Build 19042 ! Both driver=docker and vm-driver=virtualbox have been set. Since vm-driver is deprecated, minikube will default to driver=docker. If vm-driver is set in the global config, please run "minikube config unset vm-driver" to resolve this warning. * minikube 1.24.0 is available! Download it: https://github.com/kubernetes/minikube/releases/tag/v1.24.0 * To disable this notice, run: 'minikube config set WantUpdateNotification false' * Using the docker driver based on user configuration * Starting control plane node minikube in cluster minikube * Pulling base image ... * Creating docker container (CPUs=2, Memory=2200MB) ... ! Executing "docker container inspect minikube --format={{.State.Status}}" took an unusually long time: 2.3729385s * Restarting the docker service may improve performance. ! This container is having trouble accessing https://k8s.gcr.io * To pull new external images, you may need to configure a proxy: https://minikube.sigs.k8s.io/docs/reference/networking/proxy/ * Preparing Kubernetes v1.20.7 on Docker 20.10.7 ... - Generating certificates and keys ... - Booting up control plane ... - Configuring RBAC rules ... * Verifying Kubernetes components... - Using image gcr.io/k8s-minikube/storage-provisioner:v5 * Enabled addons: default-storageclass, storage-provisioner * Done! kubectl is now configured to use "minikube" cluster and "default" namespace by default
$ docker login Authenticating with existing credentials... time="2021-11-12T13:09:16-08:00" level=error msg="(3a53acc8) a5b58191-CredentialHelperPKG C<-S No response POST /registry/credstore-updated (1.5370461s): Post \"http://ipc/registry/credstore-updated\": context deadline exceeded (Client.Timeout exceeded while awaiting headers)[[STACK]]" time="2021-11-12T13:09:18-08:00" level=error msg="(6dc7cfbd) a5b58191-CredentialHelperPKG C<-S No response GET /ping (1.1539758s): Get \"http://ipc/ping\": context deadline exceeded (Client.Timeout exceeded while awaiting headers)[[STACK]]" time="2021-11-12T13:09:21-08:00" level=error msg="(40232350) a5b58191-CredentialHelperPKG C<-S No response POST /registry/credstore-updated (1.0127004s): Post \"http://ipc/registry/credstore-updated\": context deadline exceeded (Client.Timeout exceeded while awaiting headers)[[STACK]]"Login Succeeded
$ minikube docker-env export DOCKER_TLS_VERIFY="1" export DOCKER_HOST="tcp://127.0.0.1:49962" export DOCKER_CERT_PATH="C:\Users\user\.minikube\certs" export MINIKUBE_ACTIVE_DOCKERD="minikube"# To point your shell to minikube's docker-daemon, run: # eval $(minikube -p minikube docker-env)
$ istioctl install --set profile=demo -y ✔ Istio core installed ✔ Istiod installed ✔ Egress gateways installed ✔ Ingress gateways installed ✔ Installation complete *If any errors, re-run this cmd till you get the items checked as shown
$ kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabled namespace/default labeled
$ minikube ip! Executing "docker container inspect minikube --format={{.State.Status}}" took an unusually long time: 3.0719554s * Restarting the docker service may improve performance. 192.168.49.2 *This is your Istio Gateway IP
$ kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(@.name=="http2")].nodePort}' 32716 *This is your Istio Gateway Port.
http://192.168.49.2:32716
kyc-aggregator-mgt svc to invoke this Istio Gateway instead of directly calling individual mSvc.Update \kyc-aggregator-mgt\src\main\resources\application.properties:
istio-base-url=http://192.168.49.2:
istio-gateway-port=32716
kyc-aggregator-mgt -build and create docker image.
(RMI for cautionary cleanup step):
$ cd /c/Vijay/Java/projects/kyc-k8-docker-istio/kyc-aggregator-mgt $ docker rmi kyc-aggregator-mgt:latest $ docker rmi -f kyc-aggregator-mgt:latest $ docker rmi -f vijayredkar/kyc-aggregator-mgt:latest$ mvn clean install $ docker build -t kyc-aggregator-mgt -f Dockerfile . $ docker tag kyc-aggregator-mgt vijayredkar/kyc-aggregator-mgt:latest $ docker push vijayredkar/kyc-aggregator-mgt
kyc-credit-check-basic -build and create docker image.
(RMI for cautionary cleanup step):
$ cd /c/Vijay/Java/projects/kyc-k8-docker-istio/kyc-credit-check-basic $ docker rmi -f kyc-credit-check-basic:latest $ docker rmi -f vijayredkar/kyc-credit-check-basic:latest$ mvn clean install $ docker build -t kyc-credit-check-basic -f Dockerfile . $ docker tag kyc-credit-check-basic vijayredkar/kyc-credit-check-basic:latest $ docker push vijayredkar/kyc-credit-check-basic
kyc-credit-check-advanced -build and create docker image.
(RMI for cautionary cleanup step):
$ cd /c/Vijay/Java/projects/kyc-k8-docker-istio/kyc-credit-check-advanced $ docker rmi -f kyc-credit-check-advanced:latest $ docker rmi -f vijayredkar/kyc-credit-check-advanced:latest$ mvn clean install $ docker build -t kyc-credit-check-advanced -f Dockerfile . $ docker tag kyc-credit-check-advanced vijayredkar/kyc-credit-check-advanced:latest $ docker push vijayredkar/kyc-credit-check-advanced
(ensure docker images are created and pushed — o/p for reference):
$ docker image lsREPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID kyc-credit-check-advanced latest f5694be8631d vijayredkar/kyc-credit-check-advanced latest f5694be8631d vijayredkar/kyc-credit-check-basic latest 49568e4da791 kyc-credit-check-basic latest 49568e4da791 kyc-aggregator-mgt latest 6ae3c011d1e3 vijayredkar/kyc-aggregator-mgt latest 6ae3c011d1e3
(cautionary step to eliminate any unpredictable behavior):
$ kubectl delete service kyc-aggregator-mgt $ kubectl delete deployment kyc-aggregator-mgt $ kubectl delete service kyc-credit-check-basic $ kubectl delete deployment kyc-credit-check-basic $ kubectl delete service kyc-credit-check-advanced $ kubectl delete deployment kyc-credit-check-advanced $ kubectl delete gateway kyc $ kubectl delete virtualservice kyc $ kubectl delete destinationrule kyc-aggregator-mgt $ kubectl delete gateway kyc-credit-check $ kubectl delete virtualservice kyc-credit-check $ kubectl delete destinationrule kyc-credit-check-basic $ kubectl delete destinationrule kyc-credit-check-advanced
(routing rules, gateway, virtual services, destination rules):
$ cd /c/Vijay/Java/projects/kyc-k8-docker-istio/networking $ kubectl apply -f kyc-aggregator-mgt-k8-istio.yml $ kubectl apply -f kyc-aggregator-mgt-istio-routing.yaml $ kubectl apply -f kyc-aggregator-mgt-destination-rule.yaml $ kubectl apply -f kyc-credit-check-basic-k8-istio.yml $ kubectl apply -f kyc-credit-check-basic-destination-rule.yaml $ kubectl apply -f kyc-credit-check-advanced-k8-istio.yml $ kubectl apply -f kyc-credit-check-advanced-destination-rule.yaml $ kubectl apply -f kyc-credit-check-istio-routing.yaml
(ensure resources are created — o/p for your reference):
$ kubectl get podsNAME READY STATUS kyc-aggregator-mgt-7f6ddc8bbd-sfjvg 2/2 Running kyc-credit-check-advanced-799795b457-bh2p8 2/2 Running kyc-credit-check-basic-d87477769-szd96 2/2 Running *wait until the pods show "2/2 Running" $ kubectl get services NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP kyc-aggregator-mgt ClusterIP 10.105.20.233 <none> 8080/TCP kyc-credit-check-advanced ClusterIP 10.102.235.90 <none> 8080/TCP kyc-credit-check-basic ClusterIP 10.105.250.45 <none> 8080/TCP $ kubectl get deployments NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE kyc-aggregator-mgt 1/1 1 1 37m kyc-credit-check-advanced 1/1 1 1 37m kyc-credit-check-basic 1/1 1 1 37m *ensure that deployments show "1/1 Ready" $ kubectl get virtualservices NAME GATEWAYS HOSTS AGE kyc ["kyc"] ["*"] 26s kyc-credit-check ["kyc"] ["*"] 19s $ kubectl get gateways NAME AGE kyc 28s $ kubectl get destinationrules NAME HOST AGE kyc-aggregator-mgt kyc-aggregator-mgt 25s kyc-credit-check-advanced kyc-credit-check-advanced 9s kyc-credit-check-basic kyc-credit-check-basic 18s
Testing KYC ServiceMesh
Port forwarding for browser access to kyc-aggregator-mgt inside ServiceMesh.
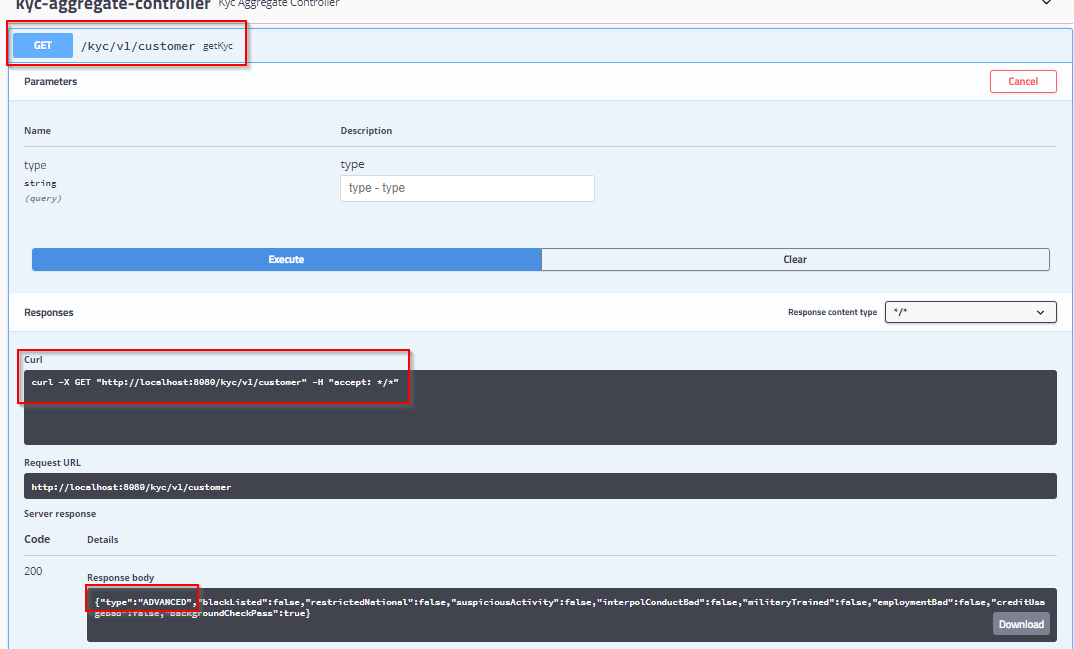
$ export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --no-headers -o custom-columns=":metadata.name" --selector app=kyc-aggregator-mgt) $ kubectl port-forward $POD_NAME 8080:8080 Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:8080 -> 8080 Forwarding from [::1]:8080 -> 8080 URLs for browser access - http://localhost:8080/kyc/v1/customer Alternately Swagger UI can be launched with - http://localhost:8080/
Output and Benefits of KYC ServiceMesh Invocation
- o/p shows 50–50% load distributed between credit-check-basic and credit-check-advanced.
- kyc-aggregator-mgt is completely oblivious to which version of credit check is serving the request.
- kyc-aggregator-mgt simply invokes the URL "/credit-check/report"
- The canary load distribution is managed entirely by our SeServiceMesh'sVirtualServiceonfiguration in \networking\kyc-credit-check-istio-routing.yaml
- In the future, when credit-check-advanced is vetted well enough in production, we can simply change this weight to 100 in the VirtualService configuration.
- All the credit-check traffic will then flow to the new version, without any code change.
- In the future, if another newer version of the credit check becomes available, the redirection to this version can be entirely managed in the VirtualService configuration, without any code change.
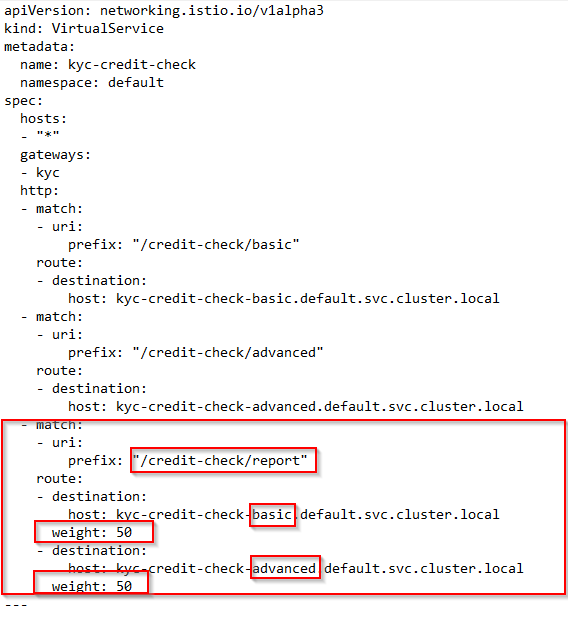
kyc-credit-check-istio-routing.yaml — VirtualService-50–50-LoadDistribution-Config
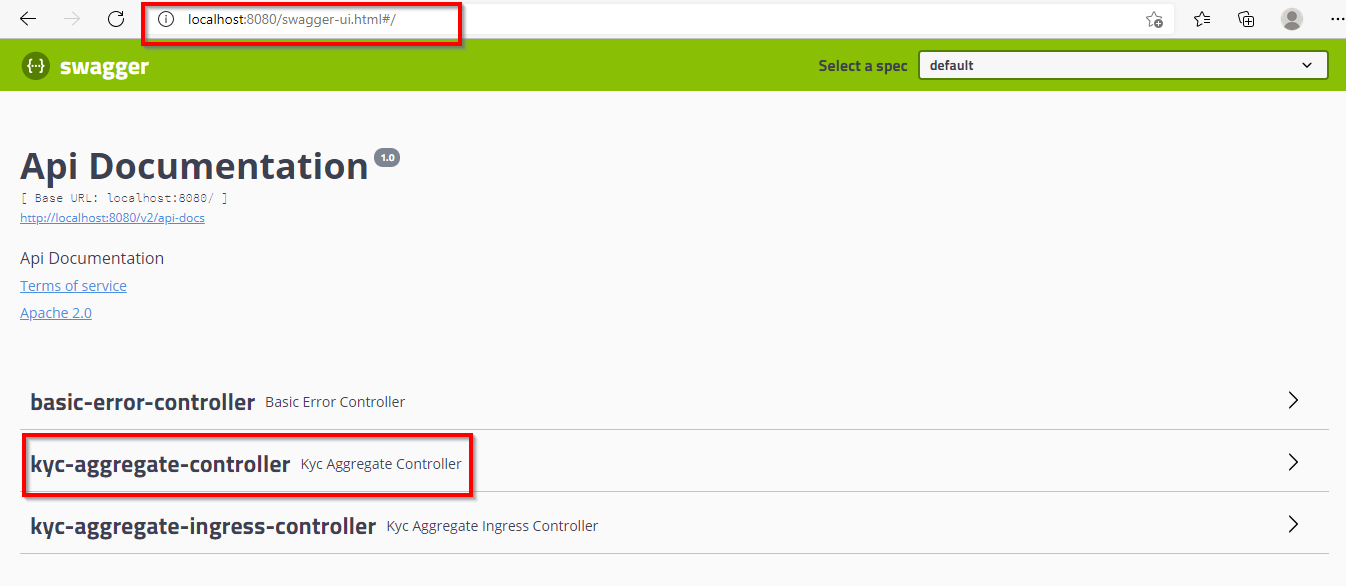
kyc-aggregator-mgt-Swagger UI

Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments