Build Your First App with JavaScript, Node.js, and DataStax Astra DB
Designed to help developers understand technologies like Node.js, GraphQL, React, Netlify, and JavaScript to kickstart their app development portfolio.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis is the first of a three-part app development workshop series designed to help developers understand technologies like Node.js, GraphQL, React, Netlify, and JavaScript to kickstart their app development portfolio. In this post, we’ll cover the fundamental concepts of website applications and introduce DataStax Astra DB as your free, fast, always-on database based on Apache Cassandra®.
In the U.S. we spend almost 88% of our mobile internet time buried in apps like Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, and games. With nearly a million new apps released each year and 218 billion app downloads in 2020, learning how to build them is an essential step in any front-end developer’s career.
So how can you start building apps? As a modern app developer, you’re spoiled for choice with multi-cloud platforms and open-source frameworks that do all the heavy lifting for you. Suppose you learn the basics and leverage the right tools. In that case, you can go from developing simple to-do lists to a full-stack Netflix clone — which is precisely what we’ll be covering in our application development workshop series.
This first workshop is about building a website application to put you on the right track. You’ll learn the fundamentals of web apps, become familiar with popular languages (like JavaScript), and then get a pre-coded to-do list app that you’ll learn how to modify and deploy. It’ll take you less than three hours to complete, and all you need is a web browser and an internet connection. Let’s get started.
The Basics of Web App Development
A website application (or web app) is software that runs on a remote server and can be accessed using a web browser on any device. Think of apps like Slack, Gmail, Google Docs, and Twitter, for example. Unlike native apps, which are installed directly on a device and designed for specific operating systems, web apps can reuse the same code and adapt their interface to any mobile device, laptop, or tablet.
While native apps perform much faster, they’re also expensive to develop because you need to learn different languages and frameworks for each platform or device. Web apps, on the other hand, can be “built once and reused forever,” and are vastly simpler to launch, manage and iterate.
When developing a web app, you’ll typically use the following architecture:
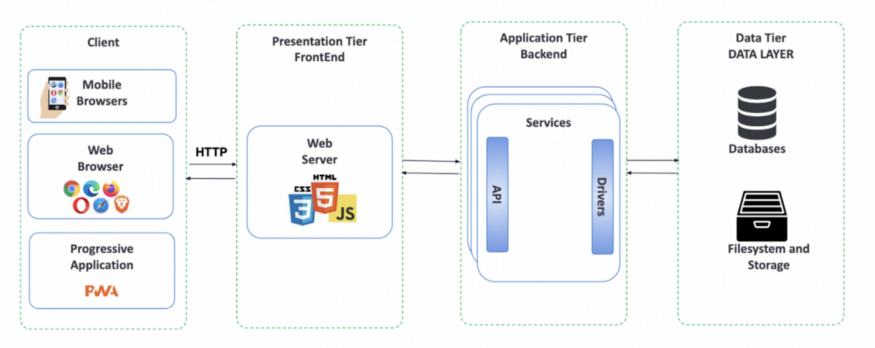
- The client is your device’s web browser, which you use to access the app.
- The front end is what the user interacts with, and is basically a web server that relies on three main technologies: HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- The backend is what interacts with the webserver and stores all the database drivers, APIs, and microservices that bridge the front end with the backend.
- The data layer is where you store the states of your app. This can be in a filesystem, external storage, document-oriented software, or a database.
A popular database you might already be familiar with is Apache Cassandra®, which powers high-performing applications for thousands of companies including Hulu, Netflix, Spotify, and Apple. While this free, open-source database is known for its high availability, scalability, and resilience; the downside is that it’s also notoriously complex to set up and manage.
This complexity is an ongoing theme when working with the data layer. As a developer, you need just four operations to interact with your database: create, read, update, and delete. But to execute them, you first have to learn the language for the database you’re using. For example, you’d need Cassandra Query Language (CQL) to interact with a Cassandra database. What’s more, you’d also need to learn how to design the data model (schema) so you can properly format and organize the data stored in your database.
It’s a steep learning curve for a new app developer, which is why DataStax built Astra DB, the serverless Cassandra-as-a-Service, as part of our mission to connect every developer to the power of Cassandra.
Simplify Cassandra App Development With Astra DB
Astra DB is the simplest way for developers to back their applications with cloud-native Cassandra, allowing them to:
- Deploy modern apps faster without the complexities of installing, managing, or scaling Cassandra.
- Interact with your database using multiple APIs to avoid data modelling.
- Bake in security from the ground up with encrypted data and JSON web token (JWT) based authentication for secure communication with your database.
- Choose whether to deploy your Astra DB on Azure, GCP, or AWS.
- Autoscale database resources are based on traffic and app requirements so you only pay for what you use.
As a developer, you can create an account on Astra DB for free. You get 3.5 million queries and 40 GB each month, and when you’re ready to scale, you can simply pay as you go.
Astra DB doesn’t just give you a database, it also gives you a collection of APIs that you can use to interact with your database out of the box. This API layer that sits between your app and your Astra DB is called Stargate.
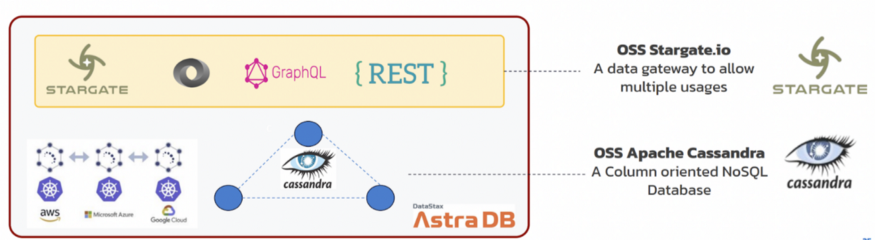
Stargate helps you streamline app development with Cassandra using popular APIs:
- REST provides a common gateway so you can access your data using a familiar interface through RESTful APIs for any Cassandra database.
- Document (JSON) is a documents API that lets you save and search schemaless JSON documents in Cassandra (with no data modelling needed).
- GraphQL is a query language for APIs that lets you insert, query, and change data within the database (without writing in CQL).
All of this means fewer languages and frameworks for you to learn and a shorter time to launch. Think of AstraDB as your own personal Samwise Gamgee, with all kinds of useful tools in its bag to make your app development journey easier.
Build Your First Web App With JS, Node.JS, and Astra DB
There’s no better exercise to get you started as an app developer than building a to-do list. The concepts and techniques you’ll learn in our first workshop are fundamental to building any web app and will put you on track to creating more advanced apps yourself. So, in this workshop you’ll learn how to:
- Set up a free Astra DB instance
- Run the web-based IDE Gitpod
- Interact with the database using APIs
- Build a to-do list app using React
You don’t have to install anything and the technologies involved are all open-source and free to use. Aside from Astra DB, here’s a quick intro to the other technologies we’ll cover in this first workshop:
- Gitpod is a cloud-based integrated development environment (IDE) powered by VS Code that lets you create ready-made dev environments and edit your code directly in your browser.
- Node.js is a runtime environment that executes JavaScript outside of a browser to let you generate dynamic page content and interact with the data in your database.
- React is a JavaScript library to create interactive user interfaces that easily adapt across most browsers and devices.
To give you the bigger picture, here’s the architecture we’ll be following to build the to-do list app:
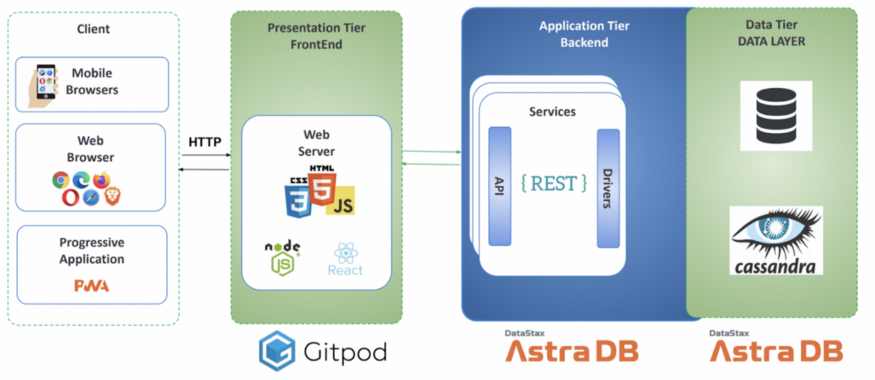
To get started, simply sign up for your free Astra DB account, then head over to the workshop video on YouTube.
For the source code, slides, exercises, and step-by-step guide go to our DataStax Developers repo on GitHub.
When you’ve completed your first app and are ready for the next step in your app development journey, dig into our second workshop on building a TikTok clone!
Published at DZone with permission of Cedrick Lunven. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments