Application Portfolio Rationalization: Risk Assessment for Digital Enterprise
This article focuses on the methodology to be adopted in defining the Risk assessment framework specific to Application Portfolio Rationalization.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIntroduction
Based on our experience of working on Application Portfolio Rationalization (APR) for various customers, over a period of time enterprises accumulated thousands of applications to their portfolios as a result of enterprise business drivers, change in their IT strategy, and adoption of next-generation technologies.
Challenges faced by various enterprises which lead to Application Portfolio Rationalization (APR) are:
- A large number of software applications with numerous redundancies
- Misalignment of application portfolio with future business needs
- Lack of consistency in the infrastructure used to run applications
- No idea on how to leverage cloud computing models to optimize costs
- Poor strategy to execute mergers and acquisitions
A few Industry “ Maturity in the Application Portfolio Analysis” areas are as follows:
“Business leaders demand that IT leaders “do more with less” to free resources for innovation and growth. Applications professionals are turning to application portfolio Rationalization (APR) to meet those challenges.” — Forester
"Application portfolio management is critical to understanding and managing the 40% to 80% of IT budgets devoted to maintaining and enhancing software" — Gartner
Most of the clients want to migrate as many as 80% of their applications within a period of four to five years. These applications typically span to thousands for large enterprises spread across the globe.
In order to have a balanced application portfolio, many organizations reduce IT spend by systematically identifying and decommissioning aging applications to drive operational efficiency, reduce the overall complexity, risks, and contain costs. The main goals of the Risk Management of IT Portfolio of an enterprise are:
- Improved user experience
- Decreased functional and technical complexity
- Increased application stability
- Address aging systems and inherent business and compliance risks
- Address maintenance and technology risk
- Regulatory compliance
This article focuses on the methodology to be adopted in defining the Risk assessment framework specific to Application Portfolio Rationalization that can help enterprises to be more successful.
Drivers for Application Portfolio Rationalization
Application rationalization helps in streamlining the processes, reducing maintenance costs, enhancing efficiency, lowering the total cost of ownership (TCO), adhering to compliance, and increasing the agility of an enterprise. It frees up time, cost, and resources.
Without active application portfolio management, organizations run the risk of application bloating. This application bloat leads to unmanageable growth of an IT portfolio.
The following are the drivers for the Application Portfolio Rationalization definition in the Digital Era,
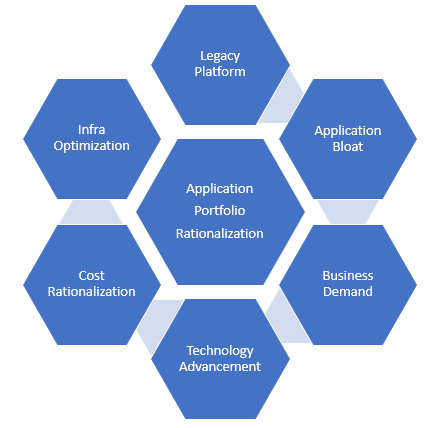
Fig: Drivers for Application Portfolio Rationalization in Digital Era
Legacy Platform: Many enterprises are still leveraging legacy systems to run the businesses. Most businesses don’t understand their entire inventory of applications, many of them being legacy systems with no clarity on the business value.
Application Bloat: Business operations and IT budgets of most large enterprises are still managed in silos. In addition to any new business functionalities, incremental enhancements the enterprises develop new systems. As a result, enterprises are developing/procuring and maintaining multiple systems with similar functionalities on diverse technology platforms. This leads to a tightly coupled, non-standardized, complex, and inflexible IT landscape. This IT Portfolio cannot fulfill the complete business capabilities of an enterprise
Business Demand: Change of business demands at a very fast rate to sustain in the industry. Re-align the applications to new business processes in support of business transformation
Technology Advancement: Enterprises face challenges as newer IT solution areas like cloud, big data, analytics, mobility, and social media are driving businesses to transform themselves in order to increase revenue and retain customers
Cost Rationalization: Rationalization of IT maintenance costs e.g. s/w licenses, support contracts, skill sets, etc
Infra Optimization: Rationalization of infrastructure like server consolidation enabled by application simplification
Types of Risks
The risks are classified as Business Risk, Strategic Risk, Technology Risk and other kind of risks.
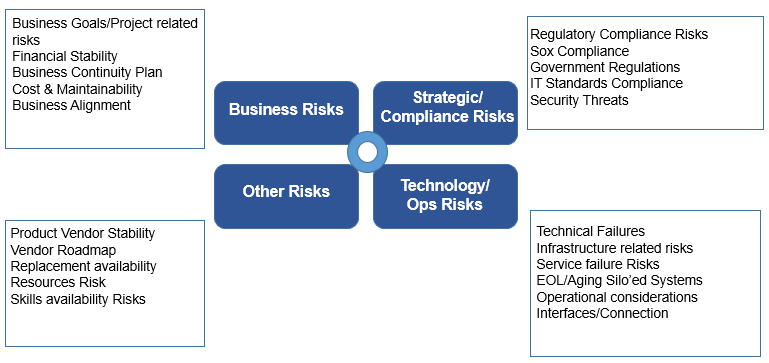
Fig: APR Risk Types
Business Risk addresses the business goals and business continuity plan. It looks at financial stability, cost, and maintainability.
Strategic Risk focuses on regulatory compliance and IT standards compliance. Application is appropriately secured from security threats. The application information has to be classified, sensitive information is encrypted, and a role-based access control mechanism is used. Government regulations like SOX compliance need to be followed by the enterprises are addressed as part of Strategic Risk.
Technology Risk addresses the technical failures, infrastructure-related risks, and service failures. It verifies whether the application offers an audit trail function i.e. are all/critical process steps logged or not? Checks in adequate skills and resources available to support the application. It also covers Operational considerations and aging of siloed systems.
The fourth category of the risks is classified as, Product stability, product replacement availability, resources risk, and skills availability risks. Checks the financial stability of the software and hardware vendor of the application. Verifies whether there is a clear/published roadmap for the technology/product by its supplier/vendor as part of this risk category.
APR Risk Assessment Framework
Application Portfolio Risk Analysis framework is a standardized repeatable process used for risk measurement assessment. The framework uses a combination of methods and artifacts to gather information on applications, carry out assessments and produce outputs determining recommended hosting requirements for applications.
Broadly, Risk assessment framework has 3 phases covering Discovery, Evaluation, and Prioritization. Input for the assessment are spotting opportunities.
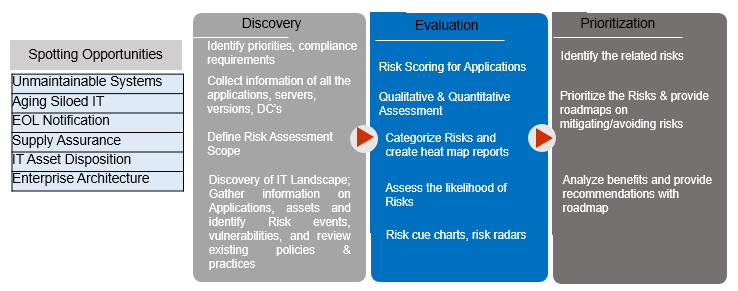
Fig: APR Risk Assessment Framework
- Spotting Opportunities: In this phase, the aggregation of all the systems that are unmaintainable and legacy in nature are done. The As-is assessment of the existing systems and their disposition is done during this phase. Applications that are marked for the end of life (EOL) are listed. All these activities and reports are taken as the input for the Discovery phase.
- Discovery: During this phase, gather the complete list of applications that are in use of an enterprise. Identify the key stakeholders, conduct the interviews, and determine the mandate for the definition of APR Risk assessment. Spend a significant amount of time with key stakeholders to understand the requirements of the Risk Assessment. As part of this phase, discuss stakeholder concerns, information needs, and desired uses of Application Portfolio Rationalization. Assess software versions, servers, and infrastructure in use. Identification of the priorities, compliance requirements is done during this phase. Risk assessment scope shall be defined during this phase. Gathering of the required information on Applications and underlying assets and identify Risk events, vulnerabilities, reviews of existing policies and practices are done during this phase.
- Evaluation: Risk Value assessment of Portfolio estate helps in addressing the maintenance and technology risk thereby resulting in decreased functional and technical complexity. The various risk value attributes that are considered during the Risk value evaluation are,
- Application Security, SOX compliance, Audit Trail Support, External Interfaces, Redundancy to handle availability, Business Continuity, Skills and Resources availability, Vendor financial stability, hardware financial stability, vendor roadmap.
- Risk scoring of applications is done during this phase. Qualitative and quantitative assessment of risk is evolved. Risk categorization is done during this phase and the heat map arrives. Used to ensure complete risk analysis and mitigation planning, risk management, and reporting
- Prioritization: Prioritize the Risks and provide roadmaps on mitigating/avoiding risks. Analyze benefits and provide recommendations with the roadmap. In this phase, develop the APR roadmap at the executive level as well as detail level. It also addresses the implementation plan of the APR strategy spanning in the short term, midterm, and long term with prioritization of initiatives, objective description, cost along with key business benefits and success factors.
Benefits of APR Risk Assessments
Application Portfolio Rationalization (APR) leads to reduced Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and maximization of business ROI. This is realized through application elimination, migration, consolidation, or modernization.
Various benefits of APR risk assessment are,
- Reducing cost: Adoption of next-generation technologies for the functional fit and for business criticality. This helps in reducing redundant applications and/or technologies
- Version Management: Helps in updating the software with the latest version and discard the old versions. Also, provides the clarity, to identify and understand which underlying technologies exist, their lifecycles, and any software dependencies
- Better Agility: Helps in establishing the standards and adherence by the stakeholders.
Last Words
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Kiran M R and Raju Alluri of Wipro Digital Architecture Practice of Wipro Ltd for giving the required time and support in many ways in bringing up this article.
Disclaimer
The views expressed in this article/presentation are that of the authors, and Wipro does not subscribe to the substance, veracity, or truthfulness of the said opinion.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments