Apache Ranger and AWS EMR Automated Installation and Integration Series (1): Solutions Overview
Automated installation and integration for Amazon EMR and Apache Ranger with this four-part series showing solutions against different technology stacks.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeSystem security usually includes two core topics: authentication and authorization. One solves the problem of “Who is s/he?” and the other solves the problem of “Does s/he have permission to perform an operation?” In the big data area, Apache Ranger is one of the most popular choices for authorization, it supports all mainstream big data components, including HDFS, Hive, HBase, and so on. As Amazon EMR rolls out native ranger (plugins) features, users can manage the authorization of EMRFS(S3), Spark, Hive, and Trino all together. For authentication, an organization usually has its own centralized authentication infrastructure, i.e., Windows AD or OpenLDAP; however, for most big data components, Kerberos is only supported authentication mechanism, so users usually need to integrate Windows AD/OpenLDAP and Kerberos together to unify authentication.
We will focus on how to implement automated installation and integration for Amazon EMR and Apache Ranger. This series is composed of four articles. Each article will introduce a completed solution against different technology stacks.
1. Solutions Overview
Installing Apache Ranger and integrating with Amazon EMR covers three main components:
- Install and integrate an authentication provider.
- Setup Ranger server and its plugins on EMR cluster.
- Configure all related components if Kerberos is enabled.
For authentication providers, Windows AD and OpenLDAP are most widely used. Their installation and integration are very different, so they should count as two separate jobs.
For Ranger installation, there are two options. The first is “open-source ranger server + EMR-native ranger plugins.” In the article, we will refer to it as an “EMR-native” ranger solution. The second is “open-source ranger server + open-source ranger plugins.” In the article, we will refer to it as an “open-source” ranger solution. Installing the two solutions will be two separate jobs.
For Kerberos, if enabled, it will bring a lot of changes to the above jobs, so enabling or disabling Kerberos is also two separate jobs.
In summary, based on the three factors above, there are eight possible scenarios (technology stacks) as follows:
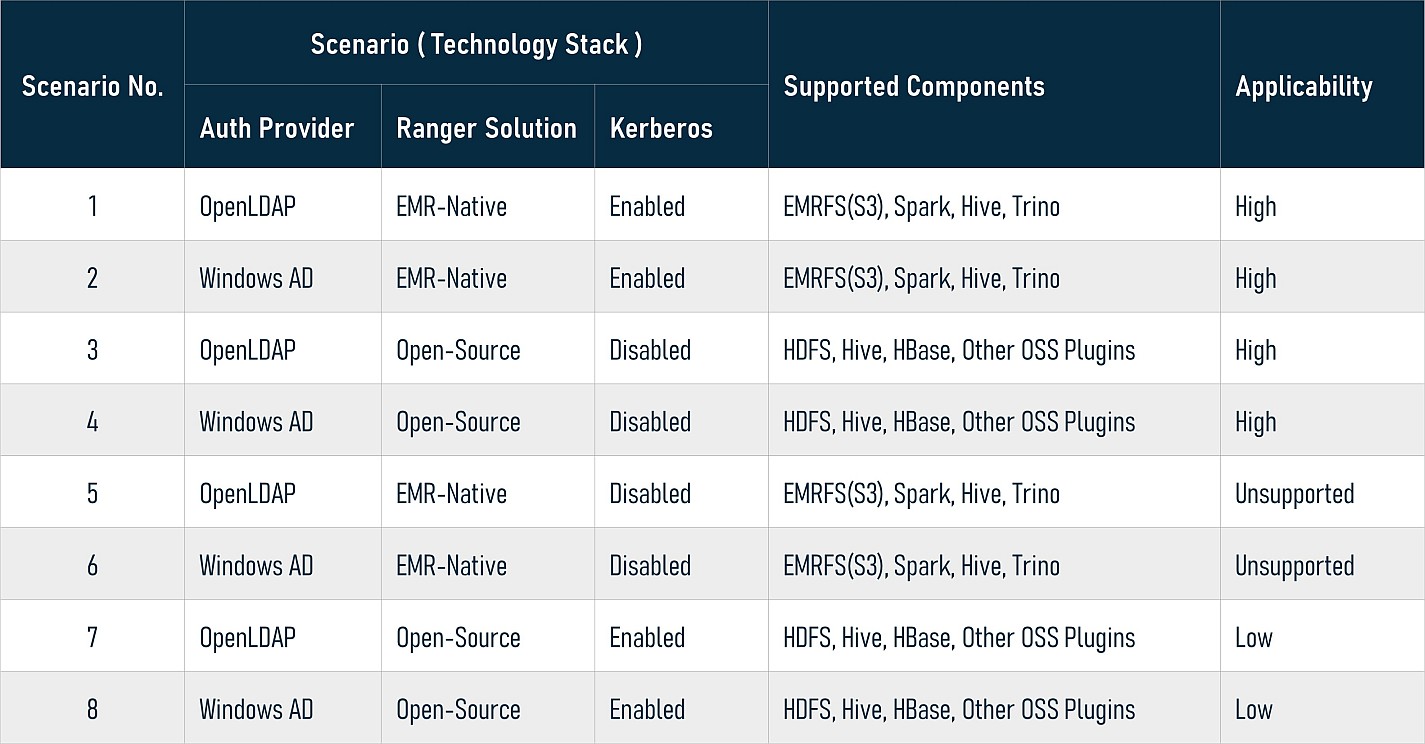
This series is composed of four articles, which are against the first four scenarios. The following is a scenarios and solution map:
|
Scenario
|
Solution
|
|---|---|
|
1
|
|
|
2
|
|
|
3
|
|
|
4
|
For scenarios 5 and 6, as of this writing, EMR is not yet supported. Since disabling Kerberos on EMR cluster is not a recommended practice, the AWS service team is working on a solution to meet the needs. For scenarios 7 and 8, considering few users pick them, we won't discuss them.
Note: At the time of writing, Trino plugin is NOT available yet, so this solution does NOT support Trino plugin at present.
2. Why Is Installing Ranger So Difficult?
Whether you’ve successfully made it before or not, installing and integrating Windows AD/OpenLDAP + Ranger + EMR is a very hard job, it is complicated, error-prone, and time-consuming for the following reasons:
- It requires operators have enough knowledge about Windows AD, OpenLDAP, Kerberos, and SSL/TLS, which are not core skills of big data engineers. Learning them will take a lot of time.
- The architecture of Ranger is complex, it includes two server-side components: Ranger Admin and Ranger UserSync. Two storage components: MySQL and Solr, and a variety of plugins. For plugins, they also need to be installed on cluster nodes, so a complete manual installation is a heavy job.
- It is not a self-contained job, usually it needs to integrate with an existing Windows AD/OpenLDAP server or an EMR cluster. Many external uncertain factors may result in installation failure, i.e., network issues, incorrect environment-specific configurations, and so on.
- The EMR-native ranger solution strongly depends on Kerberos and SSL/TLS. This significantly increases the complexity of integration.
- There is no out-of-the-box distribution package for Ranger. Installation has to start from compiling source codes, which is a challenge for non-java engineers.
The overlapping of the above factors makes this job very difficult.
3. Introduction to Automated Installer
As the voice of simplifying the Ranger usage experience is getting louder, since 2020, I took on the initiatives and reinvented an automated installer to improve the user experience for Ranger on EMR. Here is the automated installer repository address:
|
Project Name
|
Repository Address
|
|---|---|
|
Ranger EMR CLI Installer
|
It supports four scenarios (No. 1, 2, 3, 4) at the same time. In other words, it supports Windows AD and OpenLDAP and works in all AWS regions (including Chinese regions). For Scenarios 3/4, this installer can install on an existing cluster and supports multi-master clusters and single-master clusters. For each step, this installer always checks connectivity first then decides whether to go for the next steps. This is very helpful to identify network issues or service failure, i.e., when Ranger or OpenLDAP is not up. Finally, the actual installation job is a trial-and-error process. Users always need to try different parameter values to find the one that works in users' environment. The installer allows users to rerun an all-in-one installation anytime without side effects and users can also do a step-by-step run for debugging. The following is a key features summary:
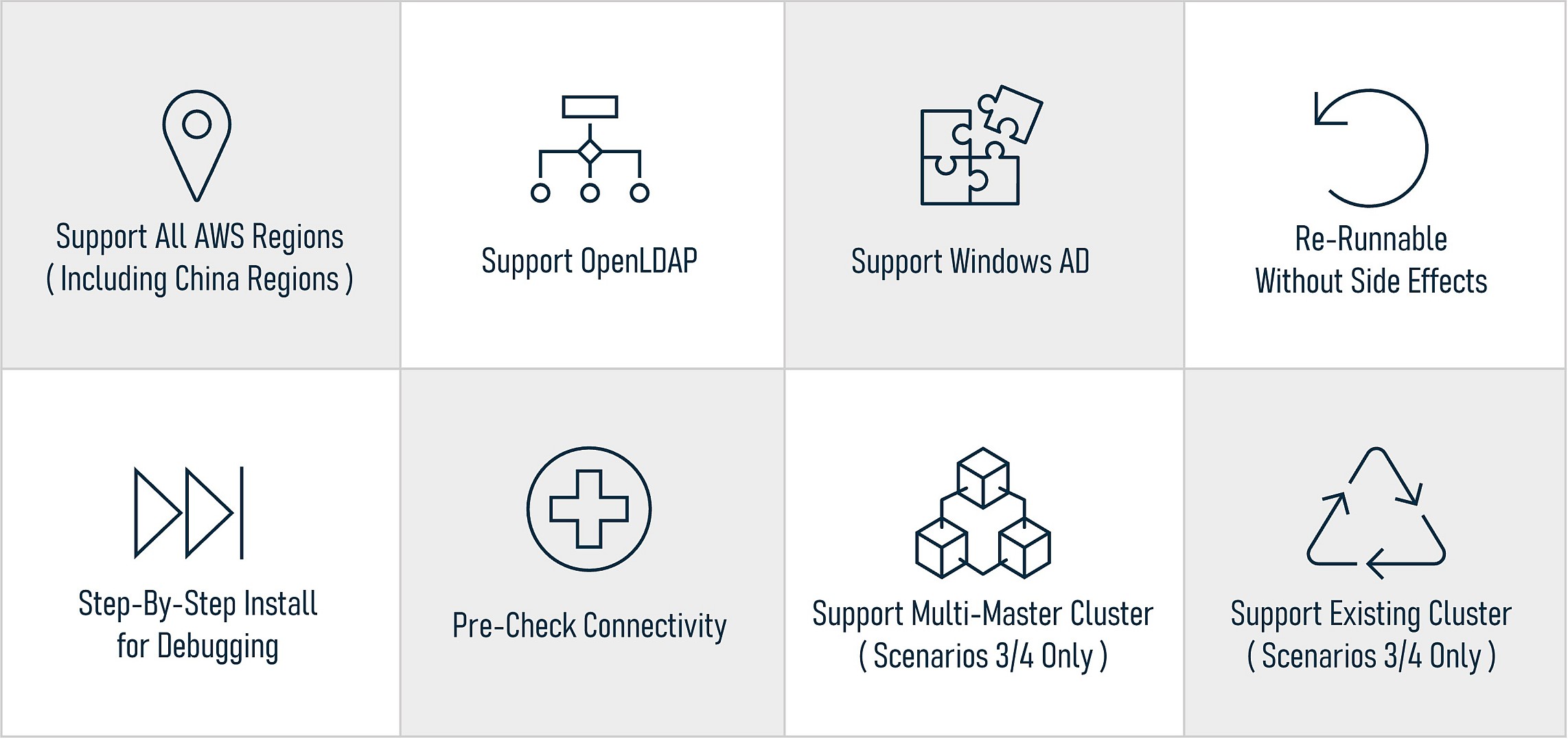
We know there is an existing solution on this AWS blog: “Implementing Authorization and Auditing using Apache Ranger on Amazon EMR.” However, this installer is very different from the solution to design to features. This solution only supports two scenarios, (No. 2, 4), and works in the us-east-1 region only. For Scenarios 3/4, this solution can not support existing or multi-master clusters, and so on. This series of articles are totally based on this tool to guide users through the installation for the first four scenarios.
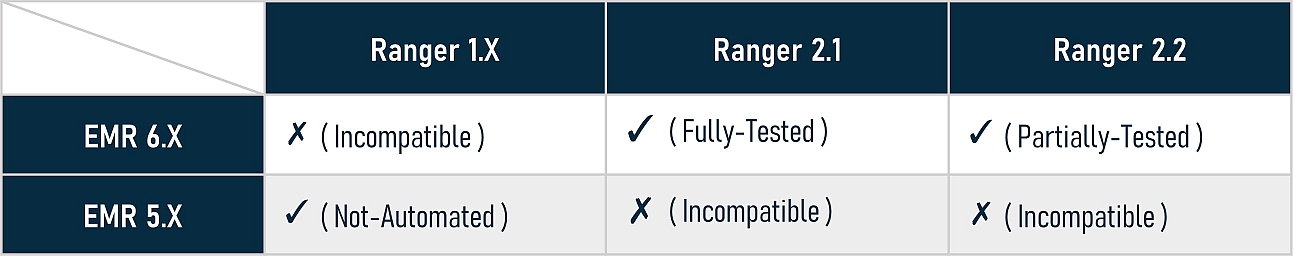
Because EMR and Ranger have multiple versions, the compatibility between different versions should be brought to our attention. Generally, Ranger 1 works with Hadoop 2 and Ranger 2 works with Hadoop 3. This installer is developed against Ranger 2.1.0 and 2.2.0, so it only supports EMR 6.X. We fully tested four solutions against Ranger 2.1.0, all passed, and we partially tested for Ranger 2.2.0, which also works, but there may be potential bugs which are not found yet. The following is Ranger and EMR version compatibility matrix:
In the next article, we start to introduce each solution one by one.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments