Apache Kafka vs. Memphis.dev
This article compares the differences between Apache Kafka and Memphis.dev; it includes ecosystems, user experience, availability and messaging, etc.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeWhat Is Apache Kafka?
Apache Kafka is an open-source distributed event streaming platform. Based on the abstraction of a distributed commit log, Kafka can handle a great number of events with functionality comprising pub/sub.
What Is Memphis.dev?
Memphis is a next-generation message broker.
A simple, robust, and durable cloud-native message broker wrapped with an entire ecosystem that enables fast and reliable development of next-generation event-driven use cases.
Memphis.dev enables building next-generation applications that require large volumes of streamed and enriched data, modern protocols, zero ops, rapid development, extreme cost reduction, and a significantly lower amount of dev time for data-oriented developers and data engineers.
License
Components
Message Consumption Model
Both Kafka and Memphis use a pull-based architecture where consumers pull messages from the server, and long-polling is used to ensure new messages are made available instantaneously.
Storage Architecture
|
Parameter
|
Memphis.dev
|
Apache Kafka
|
|---|---|---|
|
Deployment
|
Straight forward
|
Requires deep understanding and design
|
|
Enterprise support
|
Yes
|
3rd parties like Confluent, AWS MSK
|
|
Managed cloud offerings
|
Yes
|
3rd parties like Confluent, AWS MSK
|
|
Self-Healing
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Notifications
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Message tracing (aka Stream lineage)
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Storage balancing
|
Automatic based on policy
|
Manual
|
Enterprise Support and Managed Cloud Offering
Enterprise-grade support and managed cloud offerings for Kafka are available from several prominent vendors, including Confluent, AWS (MSK), Cloudera, and more.
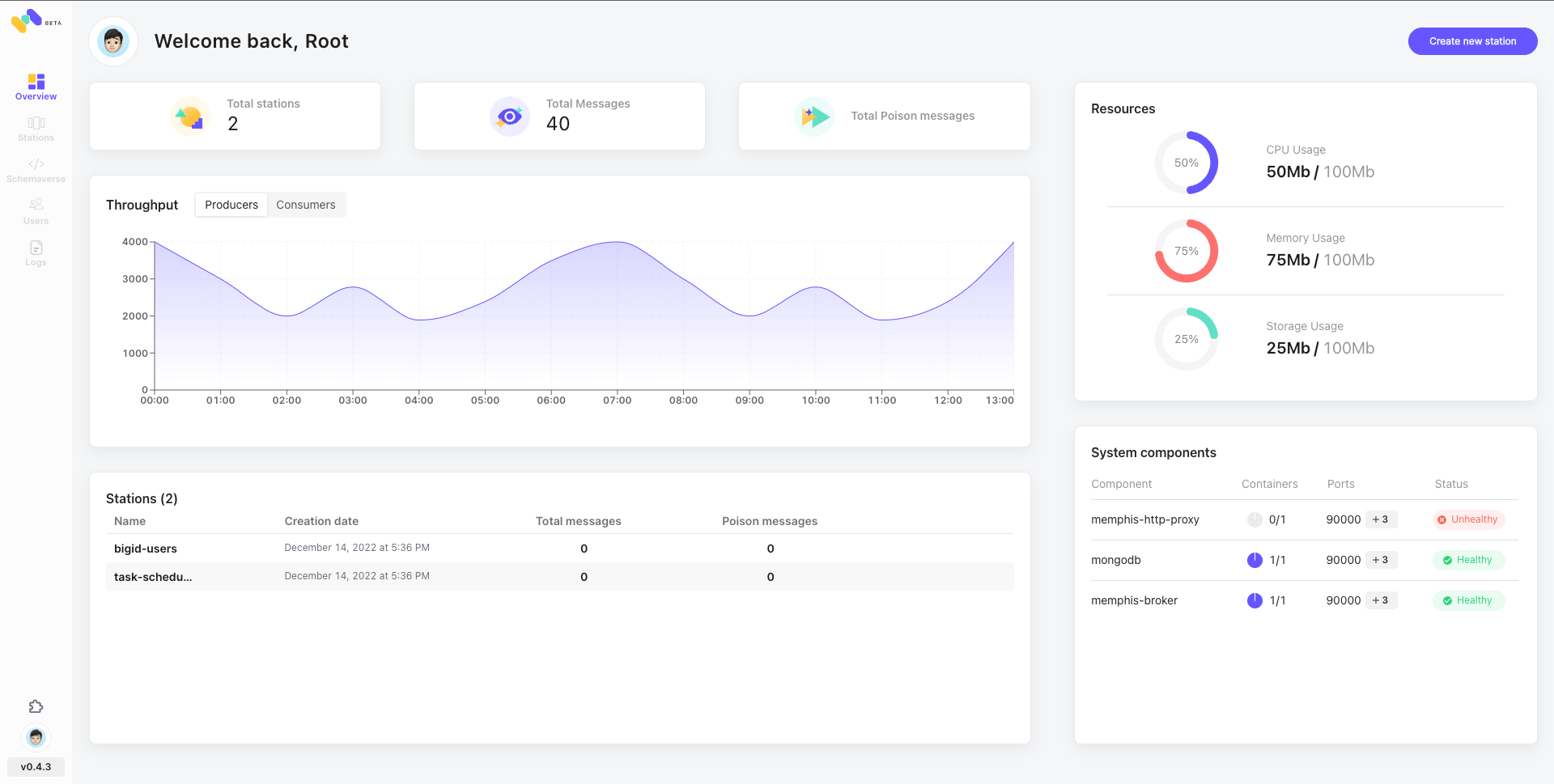
Self-Healing
Notifications
Memphis has a built-in notification center that can push real-time alerts based on defined triggers like client disconnections, resource depletion, schema violation, etc.
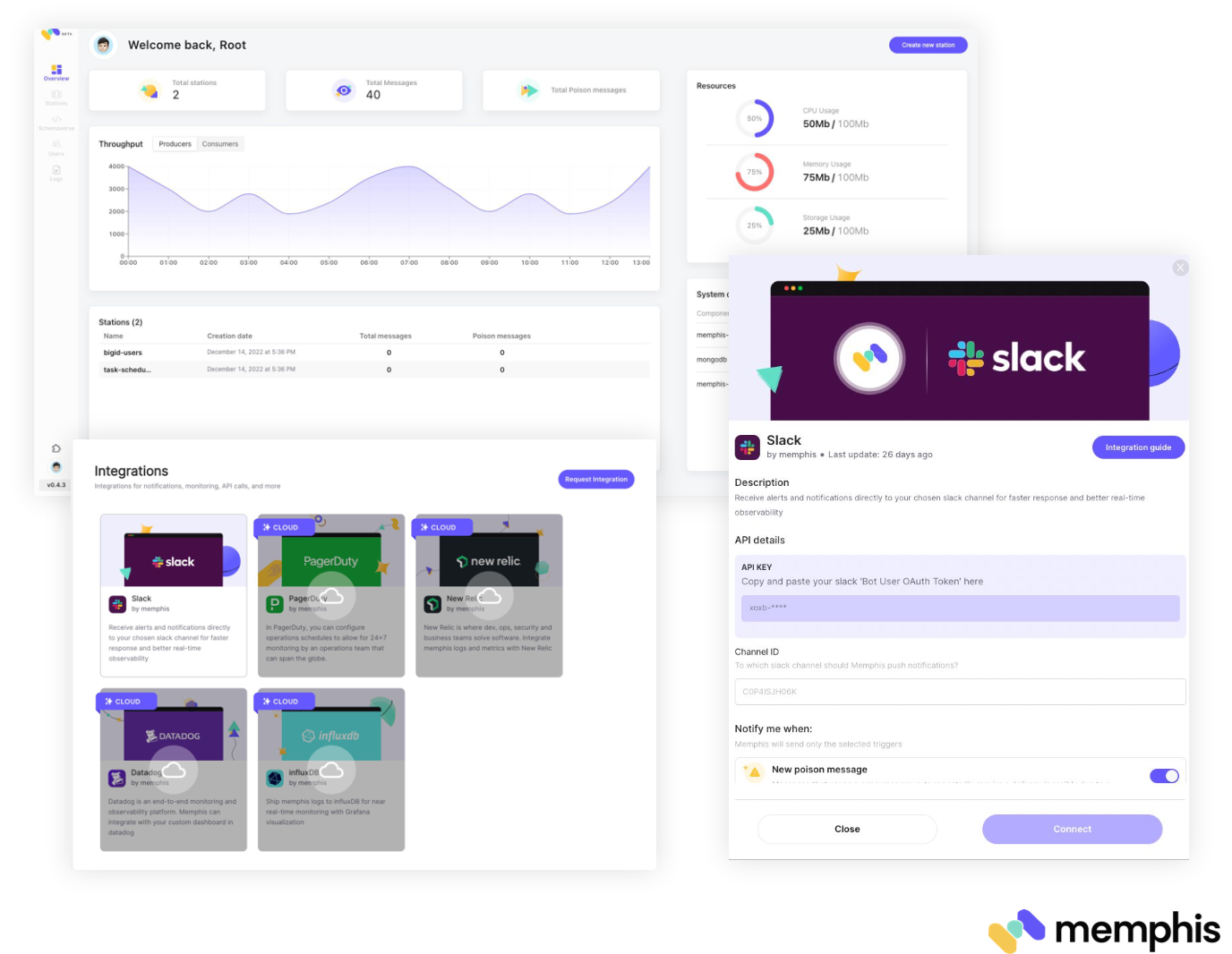
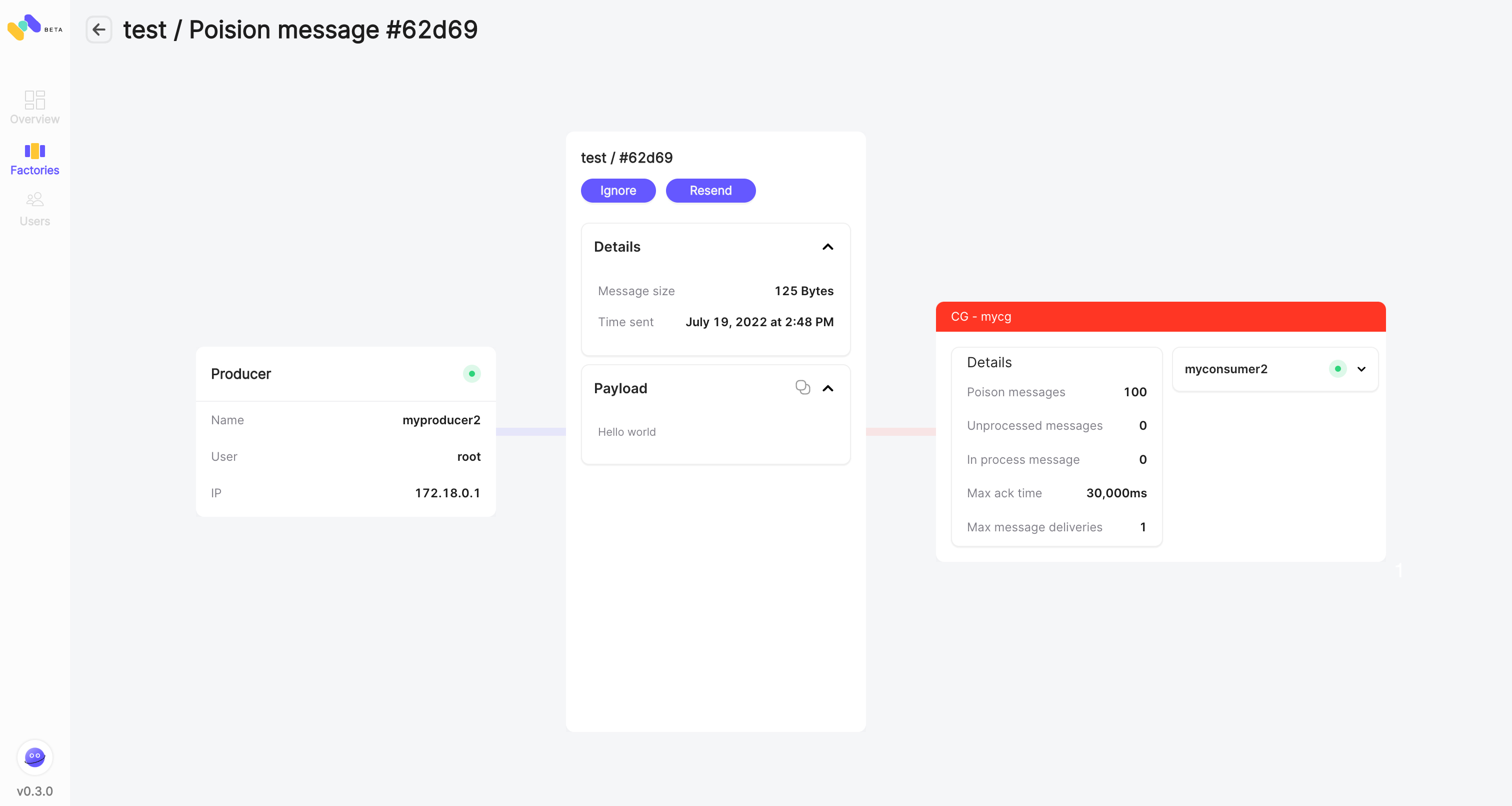
Message Tracing (aka Stream lineage)
Tracking stream lineage is the ability to understand the full path of a message from the very first producer through the final consumer, including the trail and evolvement of a message between topics. This ability is extremely handy in a troubleshooting process.
Apache Kafka does not provide a native ability for stream lineage. Still, it can be achieved using OpenTelemetry or OpenLineage frameworks, as well as integrating third-party applications such as Datadog, Epsagon or using Confluent's cloud offering.
Memphis provides stream lineage per message with out-of-the-box visualization for each stamped message using a generated header by the Memphis SDK.
|
Parameter
|
Memphis.dev
|
Apache Kafka
|
|---|---|---|
|
Mirroring (Replication)
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Multi-tenancy
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Ordering guarantees
|
Consumer group level
|
Partition level
|
|
Storage tiering
|
Yes
|
No. In progress (KIP-405)
|
|
Permanent storage
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Delivery guarantees
|
At least once, Exactly once
|
At least once, Exactly once
|
|
Idempotency
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Geo-Replication (Multi-region)
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Mirroring (Replication)
Multi-Tenancy
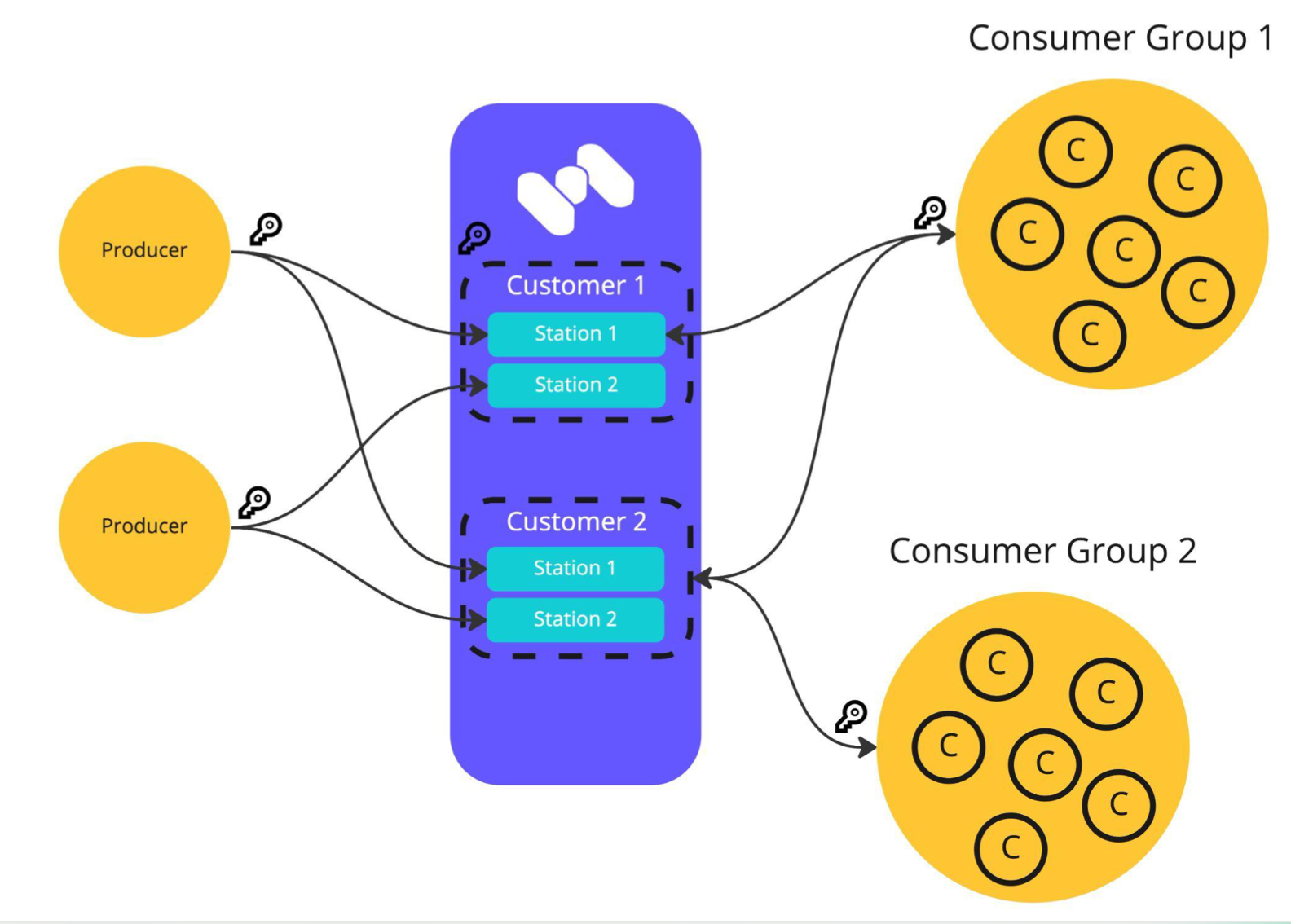
Storage Tiering
Permanent Storage
Idempotency
maxMsgDeliveries.
Geo-Replication (Multi-Region)
Common scenarios for a geo-replication include:
-
Geo-replication
-
Disaster recovery
-
Feeding edge clusters into a central, aggregate cluster
-
Physical isolation of clusters (such as production vs. testing)
-
Cloud migration or hybrid cloud deployments
-
Legal and compliance requirements
|
Parameter
|
Memphis.dev
|
Apache Kafka
|
|---|---|---|
|
GUI
|
Native
|
3rd Party
|
|
Dead-letter Queue
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Schema Management
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Message routing
|
Yes
|
Yes. Using Kafka connect and KStreams
|
|
Log compaction
|
Not yet
|
Yes
|
|
Message replay, time travel
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Stream Enrichment
|
SQL and Serverless functions
|
SQL-based using KStreams
|
|
Pull retry mechanism
|
Yes
|
Client Responsibility
|
GUI
Dead-Letter Queue
Schema Management
The very basic building block to control and ensure the quality of data that flows through your organization between the different owners is by defining well-written schemas and data models.
Confluent offers a "Schema Registry," which is a standalone component and provides a centralized repository for schemas and metadata, allowing services to flexibly interact and exchange data with each other without the challenge of managing and sharing schemas between them. However, it requires dedicated management, maintenance, scale, and monitoring.
As part of its open-source version, Memphis presents Schemaverse, which is also embedded within the broker. Schemaverse provides a robust schema store and schema management layer on top of Memphis broker without a standalone compute or dedicated resources. With a unique and modern UI and programmatic approach, technical and non-technical users can create and define different schemas, attach the schema to multiple stations and choose if the schema should be enforced or not. Furthermore, in counter to Schema Registry, the client does not need to implement serialization functions, and every schema update takes place during the producers' runtime.
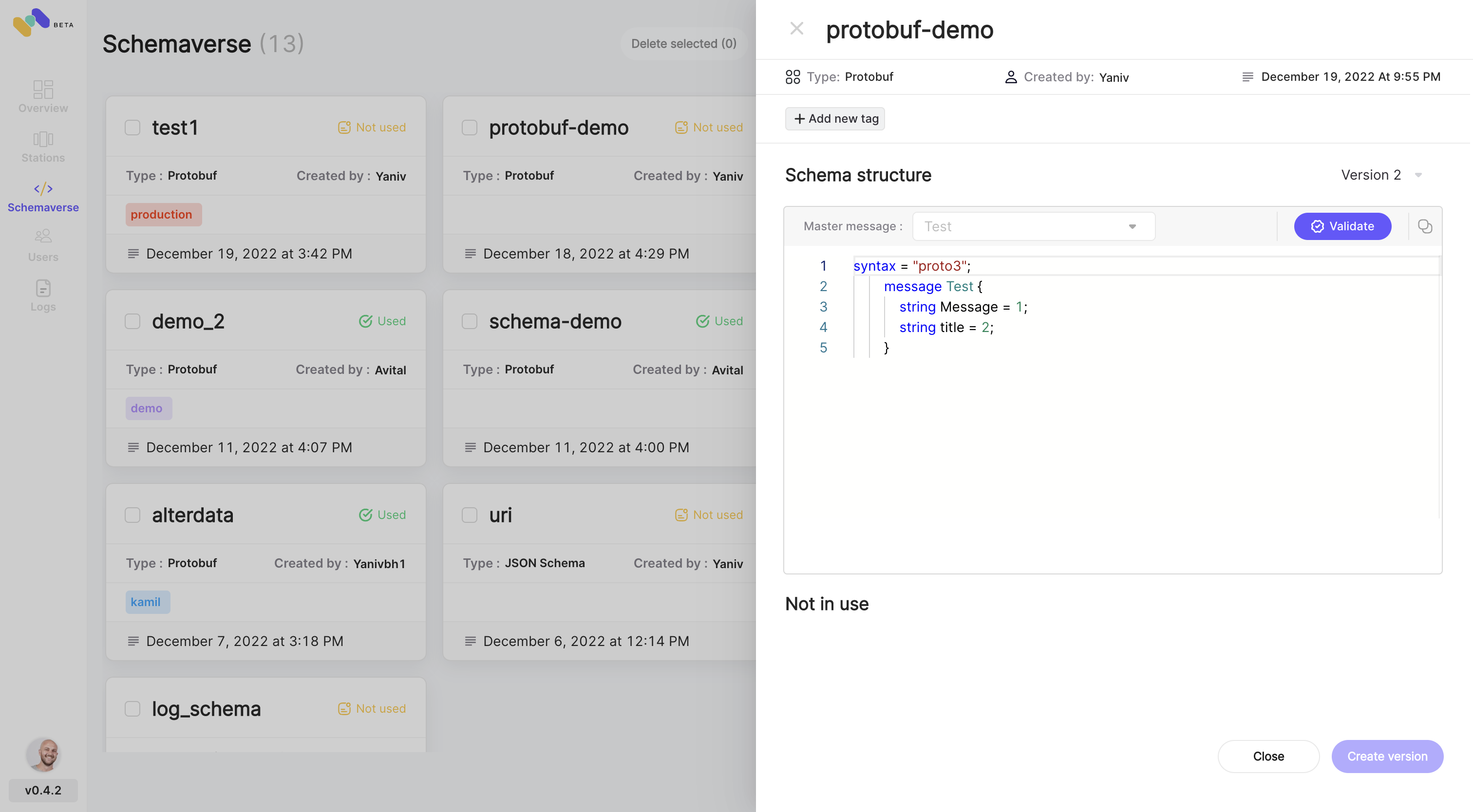
Message Routing
Kafka provides routing capabilities through Kafka Connect and Kafka Streams, including content-based routing, message transformation, and message enrichment.
Memphis message routing is similar to the implementation of RabbitMQ using routing keys, wildcards, content-based routing, and more. Similar to RabbitMQ, it is also embedded within the broker and does not require external libraries or tools.
Log Compaction
Compaction has been created to support a long-term, potentially infinite record store based on specific keys.
Kafka supports native topic compaction, which runs on all brokers. This runs automatically for compacted topics, condensing the log down to the latest version of messages sharing the same key.
At the moment, Memphis does not support compaction, but it will in the future.
Message Replay
The ability to re-consume committed messages.
Kafka does support replay by seeking specific offsets as the consumers have control over resetting the offset.
Memphis does not support replay yet but will in the near future (2023).
Stream Enrichment
Kafka, with its Kafka Streams library, allows developers to implement elastic and scalable client applications that can leverage essential stream processing features such as tables, joins, and aggregations of several topics and export to multiple sources via Kafka connect.
Memphis provides a similar behavior and more. Embedded inside the broker, Memphis users can create serverless-type functions or complete containerized applications that aggregate several stations and streams, decorate and enrich messages from different sources, write complex functions that cannot be achieved via SQL, and manipulate the schema. In addition, Memphis embedded connectors frameworks will help to push the results directly to a defined sink.
Pull Retry Mechanism
In case of a failure or lack of ability to acknowledge consumed messages, there should be a retry mechanism that will retry to pull the same offset or batch of messages.
In Kafka, it is the client's responsibility to implement one. Some key factors must be considered to implement such a mechanism, like blocking vs. non-blocking, offset tracking, idempotency, and more.
In Memphis, the retry mechanism is built-in and turned on by default within the SDK and broker. During consumer creation, the parameter maxMsgDeliveries will determine the number of retries the station will deliver a message if an acknowledgment does not arrive till maxAckTimeMs . The broker itself records the offsets given and will expose only the unacknowledged ones to the retry request.
Conclusion
Published at DZone with permission of Yaniv Ben Hemo. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments